+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | CryoEM structure of Ku heterodimer bound to DNA, PAXX and XLF | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  NHEJ / NHEJ /  Ku70 / Ku70 /  Ku80 / Ku80 /  DNA damage / DNA damage /  DNA BINDING PROTEIN / XLF DNA BINDING PROTEIN / XLF | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of ligase activity /  DNA ligase IV complex / DNA ligation involved in DNA repair / Ku70:Ku80 complex / negative regulation of t-circle formation / DNA ligase IV complex / DNA ligation involved in DNA repair / Ku70:Ku80 complex / negative regulation of t-circle formation /  DNA end binding / small-subunit processome assembly / positive regulation of lymphocyte differentiation / DNA-dependent protein kinase complex / DNA-dependent protein kinase-DNA ligase 4 complex ...positive regulation of ligase activity / DNA end binding / small-subunit processome assembly / positive regulation of lymphocyte differentiation / DNA-dependent protein kinase complex / DNA-dependent protein kinase-DNA ligase 4 complex ...positive regulation of ligase activity /  DNA ligase IV complex / DNA ligation involved in DNA repair / Ku70:Ku80 complex / negative regulation of t-circle formation / DNA ligase IV complex / DNA ligation involved in DNA repair / Ku70:Ku80 complex / negative regulation of t-circle formation /  DNA end binding / small-subunit processome assembly / positive regulation of lymphocyte differentiation / DNA-dependent protein kinase complex / DNA-dependent protein kinase-DNA ligase 4 complex / cellular response to X-ray / immunoglobulin V(D)J recombination / DNA end binding / small-subunit processome assembly / positive regulation of lymphocyte differentiation / DNA-dependent protein kinase complex / DNA-dependent protein kinase-DNA ligase 4 complex / cellular response to X-ray / immunoglobulin V(D)J recombination /  nonhomologous end joining complex / nonhomologous end joining complex /  DNA ligation / nuclear telomere cap complex / regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation / Cytosolic sensors of pathogen-associated DNA / double-strand break repair via classical nonhomologous end joining / IRF3-mediated induction of type I IFN / DNA ligation / nuclear telomere cap complex / regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation / Cytosolic sensors of pathogen-associated DNA / double-strand break repair via classical nonhomologous end joining / IRF3-mediated induction of type I IFN /  recombinational repair / recombinational repair /  regulation of telomere maintenance / U3 snoRNA binding / positive regulation of neurogenesis / protein localization to chromosome, telomeric region / cellular response to fatty acid / hematopoietic stem cell proliferation / cellular hyperosmotic salinity response / response to ionizing radiation / telomeric DNA binding / positive regulation of catalytic activity / 2-LTR circle formation / site of DNA damage / regulation of telomere maintenance / U3 snoRNA binding / positive regulation of neurogenesis / protein localization to chromosome, telomeric region / cellular response to fatty acid / hematopoietic stem cell proliferation / cellular hyperosmotic salinity response / response to ionizing radiation / telomeric DNA binding / positive regulation of catalytic activity / 2-LTR circle formation / site of DNA damage /  Lyases; Carbon-oxygen lyases; Other carbon-oxygen lyases / Lyases; Carbon-oxygen lyases; Other carbon-oxygen lyases /  enzyme activator activity / T cell differentiation / 5'-deoxyribose-5-phosphate lyase activity / hematopoietic stem cell differentiation / positive regulation of protein kinase activity / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / enzyme activator activity / T cell differentiation / 5'-deoxyribose-5-phosphate lyase activity / hematopoietic stem cell differentiation / positive regulation of protein kinase activity / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA /  DNA polymerase binding / positive regulation of telomerase activity / positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase / DNA polymerase binding / positive regulation of telomerase activity / positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase /  DNA helicase activity / activation of innate immune response / DNA helicase activity / activation of innate immune response /  telomere maintenance / cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor / telomere maintenance / cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor /  neurogenesis / neurogenesis /  cyclin binding / small-subunit processome / B cell differentiation / cyclin binding / small-subunit processome / B cell differentiation /  central nervous system development / central nervous system development /  protein-DNA complex / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / protein-DNA complex / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) /  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / cellular response to gamma radiation / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / cellular response to gamma radiation /  fibrillar center / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / double-strand break repair / site of double-strand break / fibrillar center / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / double-strand break repair / site of double-strand break /  double-stranded DNA binding / double-stranded DNA binding /  scaffold protein binding / secretory granule lumen / DNA recombination / ficolin-1-rich granule lumen / scaffold protein binding / secretory granule lumen / DNA recombination / ficolin-1-rich granule lumen /  transcription regulator complex / transcription regulator complex /  chromosome, telomeric region / damaged DNA binding / molecular adaptor activity / transcription cis-regulatory region binding / response to xenobiotic stimulus / chromosome, telomeric region / damaged DNA binding / molecular adaptor activity / transcription cis-regulatory region binding / response to xenobiotic stimulus /  ribonucleoprotein complex / ribonucleoprotein complex /  innate immune response / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / DNA damage response / innate immune response / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / DNA damage response /  ubiquitin protein ligase binding / Neutrophil degranulation / protein-containing complex binding / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / Neutrophil degranulation / protein-containing complex binding /  nucleolus / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / nucleolus / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription /  ATP hydrolysis activity / protein homodimerization activity / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein-containing complex / ATP hydrolysis activity / protein homodimerization activity / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein-containing complex /  DNA binding / DNA binding /  RNA binding / extracellular region / RNA binding / extracellular region /  nucleoplasm / nucleoplasm /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  membrane / identical protein binding / membrane / identical protein binding /  nucleus / nucleus /  plasma membrane / plasma membrane /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.68 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.68 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hardwick SW / Kefala-Stavridi A / Chirgadze DY / Blundell TL / Chaplin AK | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1 items United Kingdom, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023Title: PAXX binding to the NHEJ machinery explains functional redundancy with XLF. Authors: Murielle Seif-El-Dahan / Antonia Kefala-Stavridi / Philippe Frit / Steven W Hardwick / Dima Y Chirgadze / Taiana Maia De Oliviera / Jessica Andreani / Sébastien Britton / Nadia Barboule / ...Authors: Murielle Seif-El-Dahan / Antonia Kefala-Stavridi / Philippe Frit / Steven W Hardwick / Dima Y Chirgadze / Taiana Maia De Oliviera / Jessica Andreani / Sébastien Britton / Nadia Barboule / Madeleine Bossaert / Arun Prasad Pandurangan / Katheryn Meek / Tom L Blundell / Virginie Ropars / Patrick Calsou / Jean-Baptiste Charbonnier / Amanda K Chaplin /    Abstract: Nonhomologous end joining is a critical mechanism that repairs DNA double-strand breaks in human cells. In this work, we address the structural and functional role of the accessory protein PAXX ...Nonhomologous end joining is a critical mechanism that repairs DNA double-strand breaks in human cells. In this work, we address the structural and functional role of the accessory protein PAXX [paralog of x-ray repair cross-complementing protein 4 (XRCC4) and XRCC4-like factor (XLF)] in this mechanism. Here, we report high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and x-ray crystallography structures of the PAXX C-terminal Ku-binding motif bound to Ku70/80 and cryo-EM structures of PAXX bound to two alternate DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) end-bridging dimers, mediated by either Ku80 or XLF. We identify residues critical for the Ku70/PAXX interaction in vitro and in cells. We demonstrate that PAXX and XLF can bind simultaneously to the Ku heterodimer and act as structural bridges in alternate forms of DNA-PK dimers. Last, we show that engagement of both proteins provides a complementary advantage for DNA end synapsis and end joining in cells. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_15022.map.gz emd_15022.map.gz | 226.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-15022-v30.xml emd-15022-v30.xml emd-15022.xml emd-15022.xml | 22.2 KB 22.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_15022_fsc.xml emd_15022_fsc.xml | 13.2 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_15022.png emd_15022.png | 60.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_15022_half_map_1.map.gz emd_15022_half_map_1.map.gz emd_15022_half_map_2.map.gz emd_15022_half_map_2.map.gz | 226.5 MB 226.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15022 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15022 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15022 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15022 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 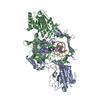 7zygMC  7zwaC  8ascC  8bh3C  8bhvC  8bhyC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_15022.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_15022.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.65 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_15022_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
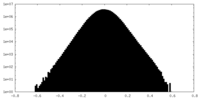
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_15022_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Ku70/80 hetero dimer bound to DNA, PAXX and XLF
| Entire | Name: Ku70/80 hetero dimer bound to DNA, PAXX and XLF |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Ku70/80 hetero dimer bound to DNA, PAXX and XLF
| Supramolecule | Name: Ku70/80 hetero dimer bound to DNA, PAXX and XLF / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#4, #6 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 160 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 6
| Macromolecule | Name: X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 6 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number:  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 69.945039 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) |
| Sequence | String: MSGWESYYKT EGDEEAEEEQ EENLEASGDY KYSGRDSLIF LVDASKAMFE SQSEDELTPF DMSIQCIQSV YISKIISSDR DLLAVVFYG TEKDKNSVNF KNIYVLQELD NPGAKRILEL DQFKGQQGQK RFQDMMGHGS DYSLSEVLWV CANLFSDVQF K MSHKRIML ...String: MSGWESYYKT EGDEEAEEEQ EENLEASGDY KYSGRDSLIF LVDASKAMFE SQSEDELTPF DMSIQCIQSV YISKIISSDR DLLAVVFYG TEKDKNSVNF KNIYVLQELD NPGAKRILEL DQFKGQQGQK RFQDMMGHGS DYSLSEVLWV CANLFSDVQF K MSHKRIML FTNEDNPHGN DSAKASRART KAGDLRDTGI FLDLMHLKKP GGFDISLFYR DIISIAEDED LRVHFEESSK LE DLLRKVR AKETRKRALS RLKLKLNKDI VISVGIYNLV QKALKPPPIK LYRETNEPVK TKTRTFNTST GGLLLPSDTK RSQ IYGSRQ IILEKEETEE LKRFDDPGLM LMGFKPLVLL KKHHYLRPSL FVYPEESLVI GSSTLFSALL IKCLEKEVAA LCRY TPRRN IPPYFVALVP QEEELDDQKI QVTPPGFQLV FLPFADDKRK MPFTEKIMAT PEQVGKMKAI VEKLRFTYRS DSFEN PVLQ QHFRNLEALA LDLMEPEQAV DLTLPKVEAM NKRLGSLVDE FKELVYPPDY NPEGKVTKRK HDNEGSGSKR PKVEYS EEE LKTHISKGTL GKFTVPMLKE ACRAYGLKSG LKKQELLEAL TKHFQD |
-Macromolecule #2: X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 5
| Macromolecule | Name: X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 5 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number:  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 82.812438 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) |
| Sequence | String: MVRSGNKAAV VLCMDVGFTM SNSIPGIESP FEQAKKVITM FVQRQVFAEN KDEIALVLFG TDGTDNPLSG GDQYQNITVH RHLMLPDFD LLEDIESKIQ PGSQQADFLD ALIVSMDVIQ HETIGKKFEK RHIEIFTDLS SRFSKSQLDI IIHSLKKCDI S LQFFLPFS ...String: MVRSGNKAAV VLCMDVGFTM SNSIPGIESP FEQAKKVITM FVQRQVFAEN KDEIALVLFG TDGTDNPLSG GDQYQNITVH RHLMLPDFD LLEDIESKIQ PGSQQADFLD ALIVSMDVIQ HETIGKKFEK RHIEIFTDLS SRFSKSQLDI IIHSLKKCDI S LQFFLPFS LGKEDGSGDR GDGPFRLGGH GPSFPLKGIT EQQKEGLEIV KMVMISLEGE DGLDEIYSFS ESLRKLCVFK KI ERHSIHW PCRLTIGSNL SIRIAAYKSI LQERVKKTWT VVDAKTLKKE DIQKETVYCL NDDDETEVLK EDIIQGFRYG SDI VPFSKV DEEQMKYKSE GKCFSVLGFC KSSQVQRRFF MGNQVLKVFA ARDDEAAAVA LSSLIHALDD LDMVAIVRYA YDKR ANPQV GVAFPHIKHN YECLVYVQLP FMEDLRQYMF SSLKNSKKYA PTEAQLNAVD ALIDSMSLAK KDEKTDTLED LFPTT KIPN PRFQRLFQCL LHRALHPREP LPPIQQHIWN MLNPPAEVTT KSQIPLSKIK TLFPLIEAKK KDQVTAQEIF QDNHED GPT AKKLKTEQGG AHFSVSSLAE GSVTSVGSVN PAENFRVLVK QKKASFEEAS NQLINHIEQF LDTNETPYFM KSIDCIR AF REEAIKFSEE QRFNNFLKAL QEKVEIKQLN HFWEIVVQDG ITLITKEEAS GSSVTAEEAK KFLAPKDKPS GDTAAVFE E GGDVDDLLDM I |
-Macromolecule #3: Protein PAXX
| Macromolecule | Name: Protein PAXX / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 21.663498 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) |
| Sequence | String: MDPLSPPLCT LPPGPEPPRF VCYCEGEESG EGDRGGFNLY VTDAAELWST CFTPDSLAAL KARFGLSAAE DITPRFRAAC EQQAVALTL QEDRASLTLS GGPSALAFDL SKVPGPEAAP RLRALTLGLA KRVWSLERRL AAAEETAVSP RKSPRPAGPQ L FLPDPDPQ ...String: MDPLSPPLCT LPPGPEPPRF VCYCEGEESG EGDRGGFNLY VTDAAELWST CFTPDSLAAL KARFGLSAAE DITPRFRAAC EQQAVALTL QEDRASLTLS GGPSALAFDL SKVPGPEAAP RLRALTLGLA KRVWSLERRL AAAEETAVSP RKSPRPAGPQ L FLPDPDPQ RGGPGPGVRR RCPGESLINP GFKSKKPAGG VDFDET |
-Macromolecule #4: Non-homologous end-joining factor 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Non-homologous end-joining factor 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 33.372234 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) |
| Sequence | String: MEELEQGLLM QPWAWLQLAE NSLLAKVFIT KQGYALLVSD LQQVWHEQVD TSVVSQRAKE LNKRLTAPPA AFLCHLDNLL RPLLKDAAH PSEATFSCDC VADALILRVR SELSGLPFYW NFHCMLASPS LVSQHLIRPL MGMSLALQCQ VRELATLLHM K DLEIQDYQ ...String: MEELEQGLLM QPWAWLQLAE NSLLAKVFIT KQGYALLVSD LQQVWHEQVD TSVVSQRAKE LNKRLTAPPA AFLCHLDNLL RPLLKDAAH PSEATFSCDC VADALILRVR SELSGLPFYW NFHCMLASPS LVSQHLIRPL MGMSLALQCQ VRELATLLHM K DLEIQDYQ ESGATLIRDR LKTEPFEENS FLEQFMIEKL PEACSIGDGK PFVMNLQDLY MAVTTQEVQV GQKHQGAGDP HT SNSASLQ GIDSQCVNQP EQLVSSAPTL SAPEKESTGT SGPLQRPQLS KVKRKKPRGL FS |
-Macromolecule #5: DNA
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA / type: dna / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 4.503948 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG) (DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC) |
-Macromolecule #6: DNA
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA / type: dna / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 4.673059 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DG)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DA) (DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT) |
-Macromolecule #7: PHOSPHATE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHATE ION / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: PO4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 94.971 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PO4: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm / Nominal magnification: 130000 Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm / Nominal magnification: 130000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 13024 / Average exposure time: 1.37 sec. / Average electron dose: 52.1 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller















 Z
Z Y
Y X
X