[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-1492: hDmc1-ssDNA filament in the compressed state, determined by elect... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-1492 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
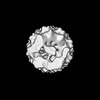
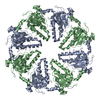
| Title | hDmc1-ssDNA filament in the compressed state, determined by electron microscopy and single particle analysis | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | This is a 3d map of hDmc1 in the compressed state,a recombinase that plays a crucial role in faithful chromosome segregation during meiosis | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Dmc1-ssDNA filament /  recombinase / recombinase /  electron microscopy / electron microscopy /  single particle analysis single particle analysis | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction /  negative staining / Resolution: 17.0 Å negative staining / Resolution: 17.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Okorokov AL / Bugreev DV / Hodgkinson J / Mazin AV / Orlova EV | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: PLoS One / Year: 2010 Journal: PLoS One / Year: 2010Title: Structure of the hDmc1-ssDNA filament reveals the principles of its architecture. Authors: Andrei L Okorokov / Yuriy L Chaban / Dmitry V Bugreev / Julie Hodgkinson / Alexander V Mazin / Elena V Orlova /  Abstract: In eukaryotes, meiotic recombination is a major source of genetic diversity, but its defects in humans lead to abnormalities such as Down's, Klinefelter's and other syndromes. Human Dmc1 (hDmc1), a ...In eukaryotes, meiotic recombination is a major source of genetic diversity, but its defects in humans lead to abnormalities such as Down's, Klinefelter's and other syndromes. Human Dmc1 (hDmc1), a RecA/Rad51 homologue, is a recombinase that plays a crucial role in faithful chromosome segregation during meiosis. The initial step of homologous recombination occurs when hDmc1 forms a filament on single-stranded (ss) DNA. However the structure of this presynaptic complex filament for hDmc1 remains unknown. To compare hDmc1-ssDNA complexes to those known for the RecA/Rad51 family we have obtained electron microscopy (EM) structures of hDmc1-ssDNA nucleoprotein filaments using single particle approach. The EM maps were analysed by docking crystal structures of Dmc1, Rad51, RadA, RecA and DNA. To fully characterise hDmc1-DNA complexes we have analysed their organisation in the presence of Ca2+, Mg2+, ATP, AMP-PNP, ssDNA and dsDNA. The 3D EM structures of the hDmc1-ssDNA filaments allowed us to elucidate the principles of their internal architecture. Similar to the RecA/Rad51 family, hDmc1 forms helical filaments on ssDNA in two states: extended (active) and compressed (inactive). However, in contrast to the RecA/Rad51 family, and the recently reported structure of hDmc1-double stranded (ds) DNA nucleoprotein filaments, the extended (active) state of the hDmc1 filament formed on ssDNA has nine protomers per helical turn, instead of the conventional six, resulting in one protomer covering two nucleotides instead of three. The control reconstruction of the hDmc1-dsDNA filament revealed 6.4 protein subunits per helical turn indicating that the filament organisation varies depending on the DNA templates. Our structural analysis has also revealed that the N-terminal domain of hDmc1 accomplishes its important role in complex formation through domain swapping between adjacent protomers, thus providing a mechanistic basis for coordinated action of hDmc1 protomers during meiotic recombination. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_1492.map.gz emd_1492.map.gz | 2.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-1492-v30.xml emd-1492-v30.xml emd-1492.xml emd-1492.xml | 10.7 KB 10.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_1492.jpg emd_1492.jpg | 48 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1492 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1492 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1492 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1492 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_1492.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 15.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_1492.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 15.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | This is a 3d map of hDmc1 in the compressed state,a recombinase that plays a crucial role in faithful chromosome segregation during meiosis | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.68 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human Dmc1 protein complexed with ssDNA
| Entire | Name: Human Dmc1 protein complexed with ssDNA |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Human Dmc1 protein complexed with ssDNA
| Supramolecule | Name: Human Dmc1 protein complexed with ssDNA / type: sample / ID: 1000 / Oligomeric state: helica filaments / Number unique components: 2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 38 KDa |
-Supramolecule #1: Dmc1-ssDNA filament
| Supramolecule | Name: Dmc1-ssDNA filament / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: recombinase / Details: helical hDmc1-ssDNA nucleoprotein filament / Oligomeric state: filaments / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Ref INTERPRO | divclassse qspanoncli ckpopupspa nclassgree n(this)spandata popltspanc lassquotlo adingbarqu otgtltimgs rcquotimgl oadinggifq uotdecodin gquotasync quotgtltsp angtdataur lajaxphp?m odetaxoamp ... divclassse qspanoncli ckpopupspa nclassgree n(this)spandata popltspanc lassquotlo adingbarqu otgtltimgs rcquotimgl oadinggifq uotdecodin gquotasync quotgtltsp angtdataur lajaxphp?m odetaxoamp kIPR011940 ampajax1cl asspoptrgi IPR011940i spandiv |
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: human / Location in cell: nucleus Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: human / Location in cell: nucleus |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Escherichia coli EG1271 / Recombinant plasmid: pEG 8A_4 Escherichia coli EG1271 / Recombinant plasmid: pEG 8A_4 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  negative staining negative staining |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7 Details: 25 mM Tris-acetate (pH 7.0), 2 mM ATP, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT, and 2 mM CaCl2 |
|---|---|
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE Details: 2% w/v methylamine tungstate, pH 6.8 (Nano-W, Nanoprobes Inc.) |
| Grid | Details: carbon-coated copper grids (400 mesh, freshly glow-discharged in air) |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: NONE / Instrument: OTHER |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI 12 |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 100 kV / Electron source: TUNGSTEN HAIRPIN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 41400 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: OTHER / Cs: 2.4 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 44000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: Eucentric / Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Category: FILM / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM / Digitization - Scanner: ZEISS SCAI / Digitization - Sampling interval: 1.68 µm / Number real images: 15 / Average electron dose: 25 e/Å2 / Details: densitometer, Zeiss-SCAI, a step size of 7 micron / Od range: 1.7 / Bits/pixel: 8 |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Details: Each segment |
|---|---|
| Final angle assignment | Details: Euler angles were determined by angular reconstitution and refined by projection matching |
| Final reconstruction | Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 17.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: SPIDER, IMAGIC Details: 250 classes were used for the compressed conformation, containing approximatly 15 images per class |
| Details | Segments of hDmc1 filaments were selected manually |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Software | Name: UROX and Chimera |
| Details | Protocol: Rigid body. The domains were separately fitted |
| Refinement | Space: RECIPROCAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Target criteria: Correlation coefficient |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)