+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-11063 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
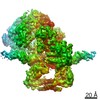
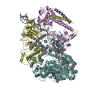
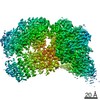
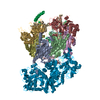
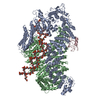
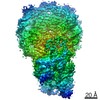
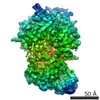
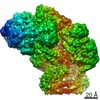
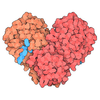
| Title | Structure of SMG1-8-9 kinase complex bound to UPF1-LSQ | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | SMG1-8-9 with bound UPF1-LSQ | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationdouble-stranded DNA helicase activity / supraspliceosomal complex / positive regulation of mRNA cis splicing, via spliceosome / exon-exon junction complex / telomere maintenance via semi-conservative replication / positive regulation of mRNA catabolic process / cell cycle phase transition / diacylglycerol-dependent serine/threonine kinase activity / regulation of translational termination /  chromatoid body ...double-stranded DNA helicase activity / supraspliceosomal complex / positive regulation of mRNA cis splicing, via spliceosome / exon-exon junction complex / telomere maintenance via semi-conservative replication / positive regulation of mRNA catabolic process / cell cycle phase transition / diacylglycerol-dependent serine/threonine kinase activity / regulation of translational termination / chromatoid body ...double-stranded DNA helicase activity / supraspliceosomal complex / positive regulation of mRNA cis splicing, via spliceosome / exon-exon junction complex / telomere maintenance via semi-conservative replication / positive regulation of mRNA catabolic process / cell cycle phase transition / diacylglycerol-dependent serine/threonine kinase activity / regulation of translational termination /  chromatoid body / histone mRNA catabolic process / chromatoid body / histone mRNA catabolic process /  eye development / 3'-UTR-mediated mRNA destabilization / nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process / eye development / 3'-UTR-mediated mRNA destabilization / nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process /  regulation of telomere maintenance / regulation of telomere maintenance /  regulation of protein kinase activity / nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, nonsense-mediated decay / DNA duplex unwinding / telomeric DNA binding / phosphatidylinositol phosphate biosynthetic process / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / cellular response to interleukin-1 / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / mRNA export from nucleus / regulation of protein kinase activity / nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, nonsense-mediated decay / DNA duplex unwinding / telomeric DNA binding / phosphatidylinositol phosphate biosynthetic process / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / cellular response to interleukin-1 / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / mRNA export from nucleus /  helicase activity / helicase activity /  P-body / P-body /  brain development / brain development /  heart development / peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / heart development / peptidyl-serine phosphorylation /  DNA helicase / cellular response to lipopolysaccharide / in utero embryonic development / DNA helicase / cellular response to lipopolysaccharide / in utero embryonic development /  RNA helicase activity / RNA helicase activity /  DNA replication / DNA replication /  chromosome, telomeric region / protein autophosphorylation / chromosome, telomeric region / protein autophosphorylation /  RNA helicase / RNA helicase /  non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase / non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase /  protein kinase activity / protein kinase activity /  DNA repair / protein serine kinase activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activity / DNA damage response / DNA repair / protein serine kinase activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activity / DNA damage response /  chromatin binding / chromatin binding /  chromatin / protein-containing complex binding / negative regulation of apoptotic process / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / chromatin / protein-containing complex binding / negative regulation of apoptotic process / perinuclear region of cytoplasm /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  RNA binding / zinc ion binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding /  nucleoplasm / nucleoplasm /  ATP binding / identical protein binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  nucleus / nucleus /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.97 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.97 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Langer LM / Gat Y / Conti E | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2020 Journal: Elife / Year: 2020Title: Structure of substrate-bound SMG1-8-9 kinase complex reveals molecular basis for phosphorylation specificity. Authors: Lukas M Langer / Yair Gat / Fabien Bonneau / Elena Conti /  Abstract: PI3K-related kinases (PIKKs) are large Serine/Threonine (Ser/Thr)-protein kinases central to the regulation of many fundamental cellular processes. PIKK family member SMG1 orchestrates progression of ...PI3K-related kinases (PIKKs) are large Serine/Threonine (Ser/Thr)-protein kinases central to the regulation of many fundamental cellular processes. PIKK family member SMG1 orchestrates progression of an RNA quality control pathway, termed nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD), by phosphorylating the NMD factor UPF1. Phosphorylation of UPF1 occurs in its unstructured N- and C-terminal regions at Serine/Threonine-Glutamine (SQ) motifs. How SMG1 and other PIKKs specifically recognize SQ motifs has remained unclear. Here, we present a cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) reconstruction of a human SMG1-8-9 kinase complex bound to a UPF1 phosphorylation site at an overall resolution of 2.9 Å. This structure provides the first snapshot of a human PIKK with a substrate-bound active site. Together with biochemical assays, it rationalizes how SMG1 and perhaps other PIKKs specifically phosphorylate Ser/Thr-containing motifs with a glutamine residue at position +1 and a hydrophobic residue at position -1, thus elucidating the molecular basis for phosphorylation site recognition. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_11063.map.gz emd_11063.map.gz | 9.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-11063-v30.xml emd-11063-v30.xml emd-11063.xml emd-11063.xml | 21.4 KB 21.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_11063_fsc.xml emd_11063_fsc.xml | 11.3 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_11063.png emd_11063.png | 86.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11063 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11063 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11063 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11063 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6z3rMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_11063.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_11063.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | SMG1-8-9 with bound UPF1-LSQ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.096 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : SMG1-8-9 bound to AMPPNP and UPF1-LSQ
+Supramolecule #1: SMG1-8-9 bound to AMPPNP and UPF1-LSQ
+Supramolecule #2: SMG1-8-9
+Supramolecule #3: UPF1-LSQ
+Macromolecule #1: Serine/threonine-protein kinase SMG1,Serine/threonine-protein kin...
+Macromolecule #2: Protein SMG8
+Macromolecule #3: Protein SMG9
+Macromolecule #4: Regulator of nonsense transcripts 1
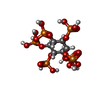
+Macromolecule #5: PHOSPHOAMINOPHOSPHONIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER
+Macromolecule #6: INOSITOL HEXAKISPHOSPHATE
+Macromolecule #7: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
+Macromolecule #8: MAGNESIUM ION
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: OTHER |
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Quantum LS / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 6293 / Average exposure time: 5.5 sec. / Average electron dose: 68.75 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller