[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7zki: Cryo-EM structure of aIF1A:aIF5B:Met-tRNAiMet complex from a Pyro... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7zki | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of aIF1A:aIF5B:Met-tRNAiMet complex from a Pyrococcus abyssi 30S initiation complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  TRANSLATION / TRANSLATION /  Initiation complex / Initiation complex /  translation initiation / small ribosomal subunit / aIF5b translation initiation / small ribosomal subunit / aIF5b | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnucleoside diphosphate phosphatase activity / intron homing / intein-mediated protein splicing /  translation initiation factor activity / translation initiation factor activity /  endonuclease activity / endonuclease activity /  GTPase activity / GTPase activity /  calcium ion binding / GTP binding / calcium ion binding / GTP binding /  RNA binding RNA bindingSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli)   Pyrococcus abyssi GE5 (archaea) Pyrococcus abyssi GE5 (archaea) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Coureux, P.D. / Bourgeois, G. / Mechulam, Y. / Schmitt, E. / Kazan, R. | ||||||
| Funding support |  France, 1items France, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2022 Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2022Title: Role of aIF5B in archaeal translation initiation. Authors: Ramy Kazan / Gabrielle Bourgeois / Christine Lazennec-Schurdevin / Eric Larquet / Yves Mechulam / Pierre-Damien Coureux / Emmanuelle Schmitt /  Abstract: In eukaryotes and in archaea late steps of translation initiation involve the two initiation factors e/aIF5B and e/aIF1A. In eukaryotes, the role of eIF5B in ribosomal subunit joining is established ...In eukaryotes and in archaea late steps of translation initiation involve the two initiation factors e/aIF5B and e/aIF1A. In eukaryotes, the role of eIF5B in ribosomal subunit joining is established and structural data showing eIF5B bound to the full ribosome were obtained. To achieve its function, eIF5B collaborates with eIF1A. However, structural data illustrating how these two factors interact on the small ribosomal subunit have long been awaited. The role of the archaeal counterparts, aIF5B and aIF1A, remains to be extensively addressed. Here, we study the late steps of Pyrococcus abyssi translation initiation. Using in vitro reconstituted initiation complexes and light scattering, we show that aIF5B bound to GTP accelerates subunit joining without the need for GTP hydrolysis. We report the crystallographic structures of aIF5B bound to GDP and GTP and analyze domain movements associated to these two nucleotide states. Finally, we present the cryo-EM structure of an initiation complex containing 30S bound to mRNA, Met-tRNAiMet, aIF5B and aIF1A at 2.7 Å resolution. Structural data shows how archaeal 5B and 1A factors cooperate to induce a conformation of the initiator tRNA favorable to subunit joining. Archaeal and eukaryotic features of late steps of translation initiation are discussed. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7zki.cif.gz 7zki.cif.gz | 170.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7zki.ent.gz pdb7zki.ent.gz | 132.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7zki.json.gz 7zki.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zk/7zki https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zk/7zki ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zk/7zki ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zk/7zki | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  14763MC  7yypC  7yznC 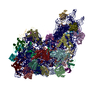 7zagC  7zahC  7zaiC  7zhgC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-RNA chain , 1 types, 1 molecules 4
| #1: RNA chain | Mass: 24833.904 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: C1A, A72U Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Production host: Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: GenBank: 1334604293 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: GenBank: 1334604293 |
|---|
-Translation initiation factor ... , 2 types, 2 molecules 67
| #2: Protein | Mass: 15336.709 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)    Pyrococcus abyssi GE5 (archaea) / Gene: eIF1A, aif1A, PYRAB05910, PAB2441 / Strain: GE5 / Orsay / Production host: Pyrococcus abyssi GE5 (archaea) / Gene: eIF1A, aif1A, PYRAB05910, PAB2441 / Strain: GE5 / Orsay / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: Q9V138 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: Q9V138 |
|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 69122.945 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)    Pyrococcus abyssi GE5 (archaea) / Gene: WBA_LOCUS12468, infB, PYRAB11390, PAB0755 / Strain: GE5 / Orsay / Production host: Pyrococcus abyssi GE5 (archaea) / Gene: WBA_LOCUS12468, infB, PYRAB11390, PAB0755 / Strain: GE5 / Orsay / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: A0A3P7EHT1, UniProt: Q9UZK7 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: A0A3P7EHT1, UniProt: Q9UZK7 |
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 3 molecules 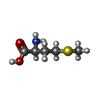



| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-MET /  Methionine Methionine |
|---|---|
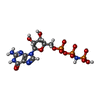
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-GNP /  5'-Guanylyl imidodiphosphate 5'-Guanylyl imidodiphosphate |
| #6: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 6.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 39 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19_4092: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 2000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 37000 Details: Resolution calculated by the post-processing procedure in Relion. Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj



































