+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7qv7 | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Hydrogen-dependent CO2 reductase. | ||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | (Hydrogen dependent carbon dioxide reductase subunit ...) x 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  ELECTRON TRANSPORT / Hydrogen-dependent CO2 reduction / ELECTRON TRANSPORT / Hydrogen-dependent CO2 reduction /  Carbon fixation / Protein nanowire filament / Carbon fixation / Protein nanowire filament /  enzyme catalysis enzyme catalysis | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information formate dehydrogenase / formate metabolic process / formate dehydrogenase / formate metabolic process /  ferredoxin hydrogenase / formate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity / ferredoxin hydrogenase / formate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity /  ferredoxin hydrogenase activity / ferredoxin hydrogenase activity /  Oxidoreductases / molybdopterin cofactor binding / Oxidoreductases / molybdopterin cofactor binding /  iron-sulfur cluster binding / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / iron-sulfur cluster binding / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding /  oxidoreductase activity ... oxidoreductase activity ... formate dehydrogenase / formate metabolic process / formate dehydrogenase / formate metabolic process /  ferredoxin hydrogenase / formate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity / ferredoxin hydrogenase / formate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity /  ferredoxin hydrogenase activity / ferredoxin hydrogenase activity /  Oxidoreductases / molybdopterin cofactor binding / Oxidoreductases / molybdopterin cofactor binding /  iron-sulfur cluster binding / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / iron-sulfur cluster binding / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding /  oxidoreductase activity / iron ion binding / oxidoreductase activity / iron ion binding /  metal ion binding metal ion bindingSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |    Thermoanaerobacter kivui (bacteria) Thermoanaerobacter kivui (bacteria) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Dietrich, H.M. / Righetto, R.D. / Kumar, A. / Wietrzynski, W. / Schuller, S.K. / Trischler, R. / Wagner, J. / Schwarz, F.M. / Engel, B.D. / Mueller, V. / Schuller, J.M. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, European Union, 5items Germany, European Union, 5items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2022 Journal: Nature / Year: 2022Title: Membrane-anchored HDCR nanowires drive hydrogen-powered CO fixation. Authors: Helge M Dietrich / Ricardo D Righetto / Anuj Kumar / Wojciech Wietrzynski / Raphael Trischler / Sandra K Schuller / Jonathan Wagner / Fabian M Schwarz / Benjamin D Engel / Volker Müller / Jan M Schuller /   Abstract: Filamentous enzymes have been found in all domains of life, but the advantage of filamentation is often elusive. Some anaerobic, autotrophic bacteria have an unusual filamentous enzyme for CO ...Filamentous enzymes have been found in all domains of life, but the advantage of filamentation is often elusive. Some anaerobic, autotrophic bacteria have an unusual filamentous enzyme for CO fixation-hydrogen-dependent CO reductase (HDCR)-which directly converts H and CO into formic acid. HDCR reduces CO with a higher activity than any other known biological or chemical catalyst, and it has therefore gained considerable interest in two areas of global relevance: hydrogen storage and combating climate change by capturing atmospheric CO. However, the mechanistic basis of the high catalytic turnover rate of HDCR has remained unknown. Here we use cryo-electron microscopy to reveal the structure of a short HDCR filament from the acetogenic bacterium Thermoanaerobacter kivui. The minimum repeating unit is a hexamer that consists of a formate dehydrogenase (FdhF) and two hydrogenases (HydA2) bound around a central core of hydrogenase Fe-S subunits, one HycB3 and two HycB4. These small bacterial polyferredoxin-like proteins oligomerize through their C-terminal helices to form the backbone of the filament. By combining structure-directed mutagenesis with enzymatic analysis, we show that filamentation and rapid electron transfer through the filament enhance the activity of HDCR. To investigate the structure of HDCR in situ, we imaged T. kivui cells with cryo-electron tomography and found that HDCR filaments bundle into large ring-shaped superstructures attached to the plasma membrane. This supramolecular organization may further enhance the stability and connectivity of HDCR to form a specialized metabolic subcompartment within the cell. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7qv7.cif.gz 7qv7.cif.gz | 914.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7qv7.ent.gz pdb7qv7.ent.gz | 760.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7qv7.json.gz 7qv7.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qv/7qv7 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qv/7qv7 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qv/7qv7 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qv/7qv7 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  14169MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Hydrogen dependent carbon dioxide reductase subunit ... , 4 types, 16 molecules AGBCJNPXDKQRVZSY
| #1: Protein | Mass: 20520.934 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermoanaerobacter kivui (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A097ATJ9, Thermoanaerobacter kivui (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A097ATJ9,  Oxidoreductases Oxidoreductases#2: Protein | Mass: 23052.180 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermoanaerobacter kivui (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A097ATK6, Thermoanaerobacter kivui (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A097ATK6,  Oxidoreductases Oxidoreductases#3: Protein | Mass: 51430.270 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermoanaerobacter kivui (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A097ATH7, Thermoanaerobacter kivui (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A097ATH7,  ferredoxin hydrogenase ferredoxin hydrogenase#4: Protein | Mass: 82505.711 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermoanaerobacter kivui (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A097ATK5, Thermoanaerobacter kivui (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A097ATK5,  formate dehydrogenase formate dehydrogenase |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 58 molecules 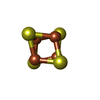
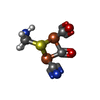

| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-SF4 /  Iron–sulfur cluster Iron–sulfur cluster#6: Chemical | ChemComp-402 / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Hydrogen-dependent CO2 reductase (HDCR) complex with iron-sulphur clusters and the H-cluster. Type: COMPLEX Details: A single functional unit of HDCR complex consists of 4 subunits - FdhF, HydA2, HycB3, and HycB4(1) Entity ID: #1-#4 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:    Thermoanaerobacter kivui LKT-1 (bacteria) Thermoanaerobacter kivui LKT-1 (bacteria) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 5500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 5500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 52 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: cryoSPARC / Category: 3D reconstruction |
|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 719937 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj