+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7jsx | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
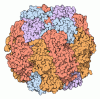
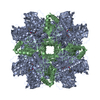
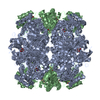
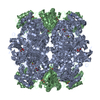
| Title | EPYC1(106-135) peptide-bound Rubisco | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  PLANT PROTEIN / PLANT PROTEIN /  Lyase / Lyase /  Rubisco / Rubisco /  Pyrenoid Pyrenoid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information photorespiration / photorespiration /  ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase /  ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity / reductive pentose-phosphate cycle / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity / reductive pentose-phosphate cycle /  chloroplast stroma / chloroplast stroma /  chloroplast / chloroplast /  monooxygenase activity / magnesium ion binding monooxygenase activity / magnesium ion bindingSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (plant) Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (plant) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.06 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Matthies, D. / He, S. / Jonikas, M.C. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, United States,  Singapore, Singapore,  United Kingdom, 9items United Kingdom, 9items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Plants / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Plants / Year: 2020Title: The structural basis of Rubisco phase separation in the pyrenoid. Authors: Shan He / Hui-Ting Chou / Doreen Matthies / Tobias Wunder / Moritz T Meyer / Nicky Atkinson / Antonio Martinez-Sanchez / Philip D Jeffrey / Sarah A Port / Weronika Patena / Guanhua He / ...Authors: Shan He / Hui-Ting Chou / Doreen Matthies / Tobias Wunder / Moritz T Meyer / Nicky Atkinson / Antonio Martinez-Sanchez / Philip D Jeffrey / Sarah A Port / Weronika Patena / Guanhua He / Vivian K Chen / Frederick M Hughson / Alistair J McCormick / Oliver Mueller-Cajar / Benjamin D Engel / Zhiheng Yu / Martin C Jonikas /     Abstract: Approximately one-third of global CO fixation occurs in a phase-separated algal organelle called the pyrenoid. The existing data suggest that the pyrenoid forms by the phase separation of the CO- ...Approximately one-third of global CO fixation occurs in a phase-separated algal organelle called the pyrenoid. The existing data suggest that the pyrenoid forms by the phase separation of the CO-fixing enzyme Rubisco with a linker protein; however, the molecular interactions underlying this phase separation remain unknown. Here we present the structural basis of the interactions between Rubisco and its intrinsically disordered linker protein Essential Pyrenoid Component 1 (EPYC1) in the model alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. We find that EPYC1 consists of five evenly spaced Rubisco-binding regions that share sequence similarity. Single-particle cryo-electron microscopy of these regions in complex with Rubisco indicates that each Rubisco holoenzyme has eight binding sites for EPYC1, one on each Rubisco small subunit. Interface mutations disrupt binding, phase separation and pyrenoid formation. Cryo-electron tomography supports a model in which EPYC1 and Rubisco form a codependent multivalent network of specific low-affinity bonds, giving the matrix liquid-like properties. Our results advance the structural and functional understanding of the phase separation underlying the pyrenoid, an organelle that plays a fundamental role in the global carbon cycle. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7jsx.cif.gz 7jsx.cif.gz | 809.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7jsx.ent.gz pdb7jsx.ent.gz | 671.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7jsx.json.gz 7jsx.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/js/7jsx https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/js/7jsx ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/js/7jsx ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/js/7jsx | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  22462MC 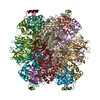 7jfoC  7jn4C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10501 (Title: CryoEM structure of EPYC1(106-135) peptide-bound Rubisco EMPIAR-10501 (Title: CryoEM structure of EPYC1(106-135) peptide-bound RubiscoData size: 5.8 TB Data #1: Unaligned multuframe micrographs of EPYC1(106-135) peptide-bound Rubisco [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 52607.812 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (plant) Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (plant)References: UniProt: A0A218N8A3, UniProt: P00877*PLUS,  ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase#2: Protein | Mass: 20667.959 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (plant) Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (plant)References: UniProt: P08475,  ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase#3: Protein/peptide | Mass: 3294.677 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (plant) / References: UniProt: A0A2K3DA85 Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (plant) / References: UniProt: A0A2K3DA85#4: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |  Water WaterHas ligand of interest | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: EPYC1(106-135) peptide-bound Rubisco / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (plant) Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (plant) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 6.8 Details: 200 mM sorbitol, 50 mM HEPES, 50 mM KOAc, 2 mM Mg(OAc)2.4H2O and 1 mM CaCl2 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
| Specimen support | Details: glow discharging for 60 seconds with a current of 15 mA in a Pelico EasiGlow system Grid material: COPPER / Grid type: Quantifoil |
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Cs : 0 mm : 0 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 3.56 sec. / Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 13727 |
| Image scans | Width: 11520 / Height: 8184 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 2257131 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : D4 (2x4 fold dihedral : D4 (2x4 fold dihedral ) ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.06 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 152839 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 1GK8 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj