[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-21353: Mammalian V-ATPase from rat brain collar and peripheral stalks ro... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-21353 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
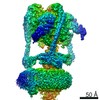
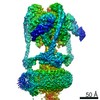
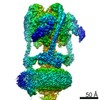
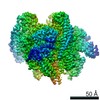
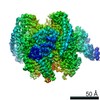
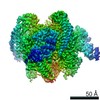
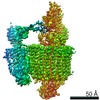
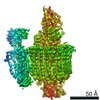
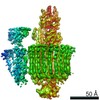
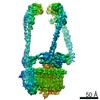
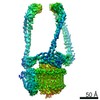
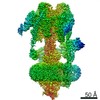
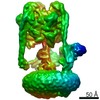
| Title | Mammalian V-ATPase from rat brain collar and peripheral stalks rotational state 3 (from focused refinement) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Mammalian rat brain V-ATPase with SidK bound, focused refinement of the collar and membrane proximal regions conformational state 3 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  membrane protein complex / rotary atpase / membrane protein complex / rotary atpase /  PROTON TRANSPORT PROTON TRANSPORT | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationTransferrin endocytosis and recycling / Ion channel transport / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / Insulin receptor recycling / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / synaptic vesicle lumen acidification / P-type proton-exporting transporter activity /  extrinsic component of synaptic vesicle membrane / intracellular organelle / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain ...Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / Ion channel transport / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / Insulin receptor recycling / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / synaptic vesicle lumen acidification / P-type proton-exporting transporter activity / extrinsic component of synaptic vesicle membrane / intracellular organelle / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain ...Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / Ion channel transport / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / Insulin receptor recycling / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / synaptic vesicle lumen acidification / P-type proton-exporting transporter activity /  extrinsic component of synaptic vesicle membrane / intracellular organelle / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / clathrin-coated vesicle membrane / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / vacuolar acidification / transmembrane transporter complex / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / Neutrophil degranulation / extrinsic component of synaptic vesicle membrane / intracellular organelle / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / clathrin-coated vesicle membrane / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / vacuolar acidification / transmembrane transporter complex / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / Neutrophil degranulation /  ATPase complex / ATPase complex /  microvillus / microvillus /  regulation of macroautophagy / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / proton transmembrane transport / regulation of macroautophagy / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / proton transmembrane transport /  terminal bouton / synaptic vesicle membrane / terminal bouton / synaptic vesicle membrane /  melanosome / melanosome /  synaptic vesicle / apical part of cell / synaptic vesicle / apical part of cell /  ATPase binding / ATPase binding /  endosome / apical plasma membrane / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / endosome / apical plasma membrane / perinuclear region of cytoplasm /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  membrane / membrane /  plasma membrane / plasma membrane /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 5.7 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 5.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Abbas YM / Rubinstein JL | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 1 items Canada, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2020 Journal: Science / Year: 2020Title: Structure of V-ATPase from the mammalian brain. Authors: Yazan M Abbas / Di Wu / Stephanie A Bueler / Carol V Robinson / John L Rubinstein /   Abstract: In neurons, the loading of neurotransmitters into synaptic vesicles uses energy from proton-pumping vesicular- or vacuolar-type adenosine triphosphatases (V-ATPases). These membrane protein complexes ...In neurons, the loading of neurotransmitters into synaptic vesicles uses energy from proton-pumping vesicular- or vacuolar-type adenosine triphosphatases (V-ATPases). These membrane protein complexes possess numerous subunit isoforms, which complicates their analysis. We isolated homogeneous rat brain V-ATPase through its interaction with SidK, a effector protein. Cryo-electron microscopy allowed the construction of an atomic model, defining the enzyme's ATP:proton ratio as 3:10 and revealing a homolog of yeast subunit f in the membrane region, which we tentatively identify as RNAseK. The c ring encloses the transmembrane anchors for cleaved ATP6AP1/Ac45 and ATP6AP2/PRR, the latter of which is the (pro)renin receptor that, in other contexts, is involved in both Wnt signaling and the renin-angiotensin system that regulates blood pressure. This structure shows how ATP6AP1/Ac45 and ATP6AP2/PRR enable assembly of the enzyme's catalytic and membrane regions. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_21353.map.gz emd_21353.map.gz | 140.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-21353-v30.xml emd-21353-v30.xml emd-21353.xml emd-21353.xml | 13.3 KB 13.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_21353.png emd_21353.png | 83.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-21353.cif.gz emd-21353.cif.gz | 5.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21353 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21353 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21353 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21353 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6vqkMC  6vq6C  6vq7C  6vq8C  6vq9C  6vqaC  6vqbC  6vqcC  6vqgC  6vqhC  6vqiC  6vqjC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_21353.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 149.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_21353.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 149.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Mammalian rat brain V-ATPase with SidK bound, focused refinement of the collar and membrane proximal regions conformational state 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Peripheral stalk and collar region of mammalian V-ATPase composed...
| Entire | Name: Peripheral stalk and collar region of mammalian V-ATPase composed of subunits E1, G2, N-terminal domain of a1, and C1. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Peripheral stalk and collar region of mammalian V-ATPase composed...
| Supramolecule | Name: Peripheral stalk and collar region of mammalian V-ATPase composed of subunits E1, G2, N-terminal domain of a1, and C1. type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) |
-Macromolecule #1: V-type proton ATPase subunit C 1
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type proton ATPase subunit C 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 43.958453 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MTEFWLISAP GEKTCQQTWE KLHAATTKNN NLAVSSKFNI PDLKVGTLDV LVGLSDELAK LDAFVEGVVK KVAQYMADVL EDSKDKVQE NLLASGVDLV TYITRFQWDM AKYPIKQSLK NISEIIAKGV TQIDNDLKSR ASAYNNLKGN LQNLERKNAG S LLTRSLAE ...String: MTEFWLISAP GEKTCQQTWE KLHAATTKNN NLAVSSKFNI PDLKVGTLDV LVGLSDELAK LDAFVEGVVK KVAQYMADVL EDSKDKVQE NLLASGVDLV TYITRFQWDM AKYPIKQSLK NISEIIAKGV TQIDNDLKSR ASAYNNLKGN LQNLERKNAG S LLTRSLAE IVKKDDFVLD SEYLVTLLVV VPKLNHNDWI KQYETLAEMV VPRSSNVLSE DQDSYLCNVT LFKKAVDDFR HK ARENKFI VRDFQYNEEE MRADKEEMNR LSTDKKKQFG PLVRWLKVNF SEAFIAWIHI KALRVFVESV LRYGLPVNFQ AML LQPNKK SVKKLREVLH ELYKHLDSSA AAIIDAPMDI PGLNLSQQEY YPYVYYKIDC NLLEFK UniProtKB: V-type proton ATPase subunit C 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: V-type proton ATPase subunit E 1
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type proton ATPase subunit E 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 26.167453 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MALSDADVQK QIKHMMAFIE QEANEKAEEI DAKAEEEFNI EKGRLVQTQR LKIMEYYEKK EKQIEQQKKI QMSNLMNQAR LKVLRARDD LITDLLNEAK QRLSKVVKDT TRYQVLLDGL VLQGLYQLLE PRMIVRCRKQ DFPLVKAAVQ KAIPMYKIAT K KDVDVQID ...String: MALSDADVQK QIKHMMAFIE QEANEKAEEI DAKAEEEFNI EKGRLVQTQR LKIMEYYEKK EKQIEQQKKI QMSNLMNQAR LKVLRARDD LITDLLNEAK QRLSKVVKDT TRYQVLLDGL VLQGLYQLLE PRMIVRCRKQ DFPLVKAAVQ KAIPMYKIAT K KDVDVQID LEAYLPEDIA GGVEIYNGDR KIKVSNTLES RLDLIAQQMM PEVRGALFGA NANRKFLD UniProtKB: V-type proton ATPase subunit E 1 |
-Macromolecule #3: V-type proton ATPase subunit G
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type proton ATPase subunit G / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.690476 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MASQSQGIQQ LLQAEKRAAE KVADARKRKA RRLKQAKEEA QMEVEQYRRE REQEFQSKQQ AAMGSQGNLS AEVEQATRRQ VQGMQSSQQ RNRERVLTQL LGMVCDVRPQ VHPNYRITV UniProtKB: V-type proton ATPase subunit G |
-Macromolecule #4: V-type proton ATPase 116 kDa subunit a isoform 1
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type proton ATPase 116 kDa subunit a isoform 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 96.429438 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MGELFRSEEM TLAQLFLQSE AAYCCVSELE ELGKVQFRDL NPDVNVFQRK FVNEVRRCEE MDRKLRFVEK EIRKANIPIM DTGENPEVP FPRDMIDLEA NFEKIENELK EINTNQEALK RNFLELTELK FILRKTQQFF DEMADPDLLE ESSSLLEPNE M GRGAPLRL ...String: MGELFRSEEM TLAQLFLQSE AAYCCVSELE ELGKVQFRDL NPDVNVFQRK FVNEVRRCEE MDRKLRFVEK EIRKANIPIM DTGENPEVP FPRDMIDLEA NFEKIENELK EINTNQEALK RNFLELTELK FILRKTQQFF DEMADPDLLE ESSSLLEPNE M GRGAPLRL GFVAGVINRE RIPTFERMLW RVCRGNVFLR QAEIENPLED PVTGDYVHKS VFIIFFQGDQ LKNRVKKICE GF RASLYPC PETPQERKEM ASGVNTRIDD LQMVLNQTED HRQRVLQAAA KNIRVWFIKV RKMKAIYHTL NLCNIDVTQK CLI AEVWCP VTDLDSIQFA LRRGTEHSGS TVPSILNRMQ TNQTPPTYNK TNKFTHGFQN IVDAYGIGTY REINPAPYTV ITFP FLFAV MFGDFGHGIL MTLFAVWMVL RESRILSQKN ENEMFSMVFS GRYIILLMGL FSIYTGLIYN DCFSKSLNIF GSSWS VRPM FTIGNWTEET LLGSSVLQLN PAIPGVFGGP YPFGIDPIWN IATNKLTFLN SFKMKMSVIL GIIHMLFGVS LSLFNH IYF KKPLNIYFGF IPEIIFMSSL FGYLVILIFY KWTAYDAHSS RNAPSLLIHF INMFLFSYPE SGNAMLYSGQ KGIQCFL IV VAMLCVPWML LFKPLILRHQ YLRKKHLGTL NFGGIRVGNG PTEEDAEIIQ HDQLSTHSED AEEPTEDEVF DFGDTMVH Q AIHTIEYCLG CISNTASYLR LWALSLAHAQ LSEVLWTMVI HIGLHVRSLA GGLGLFFIFA AFATLTVAIL LIMEGLSAF LHALRLHWVE FQNKFYTGTG FKFLPFSFEH IREGKFDE UniProtKB: V-type proton ATPase 116 kDa subunit a 1 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy Bright-field microscopy |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 43.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: RANDOM ASSIGNMENT |
| Final angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 5.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: cryoSPARC / Number images used: 79654 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller