[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-16382: Transmembrane domain of resting state homomeric GluA2 F231A mutan... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Transmembrane domain of resting state homomeric GluA2 F231A mutant AMPA receptor in complex with TARP gamma 2 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  AMPAR / AMPAR /  ion channels / ion channels /  neurotransmission / neurotransmission /  MEMBRANE PROTEIN MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationPresynaptic depolarization and calcium channel opening / eye blink reflex / positive regulation of protein localization to basolateral plasma membrane / cerebellar mossy fiber / neurotransmitter receptor transport, postsynaptic endosome to lysosome / LGI-ADAM interactions / Trafficking of AMPA receptors /  regulation of AMPA receptor activity / neurotransmitter receptor internalization / channel regulator activity ...Presynaptic depolarization and calcium channel opening / eye blink reflex / positive regulation of protein localization to basolateral plasma membrane / cerebellar mossy fiber / neurotransmitter receptor transport, postsynaptic endosome to lysosome / LGI-ADAM interactions / Trafficking of AMPA receptors / regulation of AMPA receptor activity / neurotransmitter receptor internalization / channel regulator activity ...Presynaptic depolarization and calcium channel opening / eye blink reflex / positive regulation of protein localization to basolateral plasma membrane / cerebellar mossy fiber / neurotransmitter receptor transport, postsynaptic endosome to lysosome / LGI-ADAM interactions / Trafficking of AMPA receptors /  regulation of AMPA receptor activity / neurotransmitter receptor internalization / channel regulator activity / membrane hyperpolarization / regulation of AMPA receptor activity / neurotransmitter receptor internalization / channel regulator activity / membrane hyperpolarization /  nervous system process / postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor diffusion trapping / protein targeting to membrane / neurotransmitter receptor localization to postsynaptic specialization membrane / nervous system process / postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor diffusion trapping / protein targeting to membrane / neurotransmitter receptor localization to postsynaptic specialization membrane /  voltage-gated calcium channel complex / neuromuscular junction development / spine synapse / dendritic spine neck / dendritic spine head / Activation of AMPA receptors / perisynaptic space / transmission of nerve impulse / AMPA glutamate receptor activity / regulation of postsynaptic membrane neurotransmitter receptor levels / Trafficking of GluR2-containing AMPA receptors / response to lithium ion / voltage-gated calcium channel complex / neuromuscular junction development / spine synapse / dendritic spine neck / dendritic spine head / Activation of AMPA receptors / perisynaptic space / transmission of nerve impulse / AMPA glutamate receptor activity / regulation of postsynaptic membrane neurotransmitter receptor levels / Trafficking of GluR2-containing AMPA receptors / response to lithium ion /  membrane depolarization / membrane depolarization /  immunoglobulin binding / AMPA glutamate receptor complex / kainate selective glutamate receptor activity / immunoglobulin binding / AMPA glutamate receptor complex / kainate selective glutamate receptor activity /  ionotropic glutamate receptor complex / extracellularly glutamate-gated ion channel activity / cellular response to glycine / calcium channel regulator activity / asymmetric synapse / regulation of receptor recycling / ionotropic glutamate receptor complex / extracellularly glutamate-gated ion channel activity / cellular response to glycine / calcium channel regulator activity / asymmetric synapse / regulation of receptor recycling /  voltage-gated calcium channel activity / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation /  glutamate receptor binding / positive regulation of synaptic transmission / presynaptic active zone membrane / glutamate-gated receptor activity / response to fungicide / glutamate receptor binding / positive regulation of synaptic transmission / presynaptic active zone membrane / glutamate-gated receptor activity / response to fungicide /  regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / somatodendritic compartment / cellular response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulus / dendrite membrane / ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / somatodendritic compartment / cellular response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulus / dendrite membrane / ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential /  ionotropic glutamate receptor binding / ionotropic glutamate receptor binding /  cytoskeletal protein binding / ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway / dendrite cytoplasm / hippocampal mossy fiber to CA3 synapse / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / cytoskeletal protein binding / ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway / dendrite cytoplasm / hippocampal mossy fiber to CA3 synapse / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic /  SNARE binding / dendritic shaft / SNARE binding / dendritic shaft /  synaptic membrane / synaptic membrane /  synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / transmitter-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / transmitter-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential /  regulation of membrane potential / regulation of membrane potential /  PDZ domain binding / protein tetramerization / postsynaptic density membrane / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / establishment of protein localization / PDZ domain binding / protein tetramerization / postsynaptic density membrane / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / establishment of protein localization /  receptor internalization / receptor internalization /  terminal bouton / cerebral cortex development / synaptic vesicle membrane / response to calcium ion / terminal bouton / cerebral cortex development / synaptic vesicle membrane / response to calcium ion /  synaptic vesicle / presynapse / synaptic vesicle / presynapse /  presynaptic membrane / presynaptic membrane /  signaling receptor activity / signaling receptor activity /  amyloid-beta binding / amyloid-beta binding /  growth cone / growth cone /  scaffold protein binding / chemical synaptic transmission / scaffold protein binding / chemical synaptic transmission /  perikaryon / perikaryon /  postsynaptic membrane / postsynaptic membrane /  dendritic spine / dendritic spine /  postsynaptic density / neuron projection / postsynaptic density / neuron projection /  axon / neuronal cell body / glutamatergic synapse / axon / neuronal cell body / glutamatergic synapse /  synapse / synapse /  dendrite / protein-containing complex binding / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / dendrite / protein-containing complex binding / endoplasmic reticulum membrane /  protein kinase binding / protein kinase binding /  cell surface / cell surface /  endoplasmic reticulum / protein-containing complex / endoplasmic reticulum / protein-containing complex /  membrane / identical protein binding / membrane / identical protein binding /  plasma membrane plasma membraneSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Rattus (rat) / Rattus (rat) /   Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.0 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang D / Ivica J / Krieger JM / Ho H / Yamashita K / Cais O / Greger I | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2 items United Kingdom, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2023 Journal: Nature / Year: 2023Title: Structural mobility tunes signalling of the GluA1 AMPA glutamate receptor. Authors: Danyang Zhang / Josip Ivica / James M Krieger / Hinze Ho / Keitaro Yamashita / Imogen Stockwell / Rozbeh Baradaran / Ondrej Cais / Ingo H Greger /   Abstract: AMPA glutamate receptors (AMPARs), the primary mediators of excitatory neurotransmission in the brain, are either GluA2 subunit-containing and thus Ca-impermeable, or GluA2-lacking and Ca-permeable. ...AMPA glutamate receptors (AMPARs), the primary mediators of excitatory neurotransmission in the brain, are either GluA2 subunit-containing and thus Ca-impermeable, or GluA2-lacking and Ca-permeable. Despite their prominent expression throughout interneurons and glia, their role in long-term potentiation and their involvement in a range of neuropathologies, structural information for GluA2-lacking receptors is currently absent. Here we determine and characterize cryo-electron microscopy structures of the GluA1 homotetramer, fully occupied with TARPγ3 auxiliary subunits (GluA1/γ3). The gating core of both resting and open-state GluA1/γ3 closely resembles GluA2-containing receptors. However, the sequence-diverse N-terminal domains (NTDs) give rise to a highly mobile assembly, enabling domain swapping and subunit re-alignments in the ligand-binding domain tier that are pronounced in desensitized states. These transitions underlie the unique kinetic properties of GluA1. A GluA2 mutant (F231A) increasing NTD dynamics phenocopies this behaviour, and exhibits reduced synaptic responses, reflecting the anchoring function of the AMPAR NTD at the synapse. Together, this work underscores how the subunit-diverse NTDs determine subunit arrangement, gating properties and ultimately synaptic signalling efficiency among AMPAR subtypes. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_16382.map.gz emd_16382.map.gz | 12.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-16382-v30.xml emd-16382-v30.xml emd-16382.xml emd-16382.xml | 17.7 KB 17.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_16382_fsc.xml emd_16382_fsc.xml | 15.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_16382.png emd_16382.png | 49.2 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_16382_msk_1.map emd_16382_msk_1.map | 107.2 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-16382.cif.gz emd-16382.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_16382_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16382_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16382_half_map_2.map.gz emd_16382_half_map_2.map.gz | 99 MB 99 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16382 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16382 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16382 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16382 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8c1sMC  8c1pC  8c1qC  8c1rC  8c2hC  8c2iC  8p3qC  8p3sC  8p3tC  8p3uC  8p3vC  8p3wC  8p3xC  8p3yC  8p3zC  8pivC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_16382.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 107.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_16382.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 107.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.826 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_16382_msk_1.map emd_16382_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_16382_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_16382_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : homomeric GluA2 F231A mutant AMPA receptor in complex with TARP g...
| Entire | Name: homomeric GluA2 F231A mutant AMPA receptor in complex with TARP gamma 2 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: homomeric GluA2 F231A mutant AMPA receptor in complex with TARP g...
| Supramolecule | Name: homomeric GluA2 F231A mutant AMPA receptor in complex with TARP gamma 2 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Rattus (rat) Rattus (rat) |
-Macromolecule #1: Glutamate receptor 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Glutamate receptor 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 99.981031 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MQKIMHISVL LSPVLWGLIF GDYKDDDDKV SSNSIQIGGL FPRGADQEYS AFRVGMVQFS TSEFRLTPHI DNLEVANSFA VTNAFCSQF SRGVYAIFGF YDKKSVNTIT SFCGTLHVSF ITPSFPTDGT HPFVIQMRPD LKGALLSLIE YYQWDKFAYL Y DSDRGLST ...String: MQKIMHISVL LSPVLWGLIF GDYKDDDDKV SSNSIQIGGL FPRGADQEYS AFRVGMVQFS TSEFRLTPHI DNLEVANSFA VTNAFCSQF SRGVYAIFGF YDKKSVNTIT SFCGTLHVSF ITPSFPTDGT HPFVIQMRPD LKGALLSLIE YYQWDKFAYL Y DSDRGLST LQAVLDSAAE KKWQVTAINV GNINNDKKDE TYRSLFQDLE LKKERRVILD CERDKVNDIV DQVITIGKHV KG YHYIIAN LGFTDGDLLK IQFGGANVSG FQIVDYDDSL VSKFIERWST LEEKEYPGAH TATIKYTSAL TYDAVQVMTE AFR NLRKQR IEISRRGNAG DCLANPAVPW GQGVEIERAL KQVQVEGLSG NIKFDQNGKR INYTINIMEL KTNGPRKIGY WSEV DKMVV TLTELPSGND TSGLENKTVV VTTILESPYV MMKKNHEMLE GNERYEGYCV DLAAEIAKHC GFKYKLTIVG DGKYG ARDA DTKIWNGMVG ELVYGKADIA IAPLTITLVR EEVIDFSKPF MSLGISIMIK KPQKSKPGVF SFLDPLAYEI WMCIVF AYI GVSVVLFLVS RFSPYEWHTE EFEDGRETQS SESTNEFGIF NSLWFSLGAF MRQGCDISPR SLSGRIVGGV WWFFTLI II SSYTANLAAF LTVERMVSPI ESAEDLSKQT EIAYGTLDSG STKEFFRRSK IAVFDKMWTY MRSAEPSVFV RTTAEGVA R VRKSKGKYAY LLESTMNEYI EQRKPCDTMK VGGNLDSKGY GIATPKGSSL RTPVNLAVLK LSEQGVLDKL KNKWWYDKG ECGAKDSGSK EKTSALSLSN VAGVFYILVG GLGLAMLVAL IEFCYKSRAE AKRMKVAKNP QNINPSSSQN SQNFATYKEG YNVYGIESV KI UniProtKB:  Glutamate receptor 2 Glutamate receptor 2 |
-Macromolecule #2: Voltage-dependent calcium channel gamma-2 subunit
| Macromolecule | Name: Voltage-dependent calcium channel gamma-2 subunit / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 35.807555 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: GLFDRGVQML LTTVGAFAAF SLMTIAVGTD YWLYSRGVCK TKSVSENETS KKNEEVMTHS GLWRTCCLEG NFKGLCKQID HFPEDADYE ADTAEYFLRA VRASSIFPIL SVILLFMGGL CIAASEFYKT RHNIILSAGI FFVSAGLSNI IGIIVYISAN A GDPSKSDS ...String: GLFDRGVQML LTTVGAFAAF SLMTIAVGTD YWLYSRGVCK TKSVSENETS KKNEEVMTHS GLWRTCCLEG NFKGLCKQID HFPEDADYE ADTAEYFLRA VRASSIFPIL SVILLFMGGL CIAASEFYKT RHNIILSAGI FFVSAGLSNI IGIIVYISAN A GDPSKSDS KKNSYSYGWS FYFGALSFII AEMVGVLAVH MFIDRHKQLR ATARATDYLQ ASAITRIPSY RYRYQRRSRS SS RSTEPSH SRDASPVGVK GFNTLPSTEI SMYTLSRDPL KAATTPTATY NSDRDNSFLQ VHNCIQKDSK DSLHANTANR RTT PV UniProtKB: Voltage-dependent calcium channel gamma-2 subunit |
-Macromolecule #3: PALMITIC ACID
| Macromolecule | Name: PALMITIC ACID / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: PLM |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 256.424 Da |
| Chemical component information | 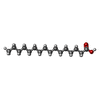 ChemComp-PLM: |
-Macromolecule #4: (2R)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl (9Z)-octadec-9-enoate
| Macromolecule | Name: (2R)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl (9Z)-octadec-9-enoate / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: OLC |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 356.54 Da |
| Chemical component information | 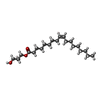 ChemComp-OLC: |
-Macromolecule #5: (2S)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]propyl 2-(tri...
| Macromolecule | Name: (2S)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]propyl 2-(trimethylammonio)ethyl phosphate type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: POV |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 760.076 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-POV: |
-Macromolecule #6: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.4 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.4000000000000001 µm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.4 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.4000000000000001 µm |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Details | Servalcat |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: RECIPROCAL |
| Output model |  PDB-8c1s: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)













































