+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7l30 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
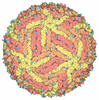
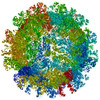
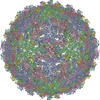
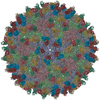
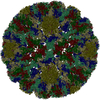
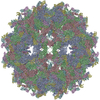
| Title | Binjari virus (BinJV) | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  VIRUS / VIRUS /  Flavivirus / Flavivirus /  glycoprotein / glycoprotein /  fusion fusion | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information flavivirin / symbiont-mediated suppression of host JAK-STAT cascade via inhibition of STAT2 activity / flavivirin / symbiont-mediated suppression of host JAK-STAT cascade via inhibition of STAT2 activity /  viral capsid / nucleoside-triphosphate phosphatase / viral capsid / nucleoside-triphosphate phosphatase /  double-stranded RNA binding / double-stranded RNA binding /  mRNA (nucleoside-2'-O-)-methyltransferase activity / mRNA 5'-cap (guanine-N7-)-methyltransferase activity / mRNA (nucleoside-2'-O-)-methyltransferase activity / mRNA 5'-cap (guanine-N7-)-methyltransferase activity /  RNA helicase activity / membrane => GO:0016020 / host cell endoplasmic reticulum membrane ... RNA helicase activity / membrane => GO:0016020 / host cell endoplasmic reticulum membrane ... flavivirin / symbiont-mediated suppression of host JAK-STAT cascade via inhibition of STAT2 activity / flavivirin / symbiont-mediated suppression of host JAK-STAT cascade via inhibition of STAT2 activity /  viral capsid / nucleoside-triphosphate phosphatase / viral capsid / nucleoside-triphosphate phosphatase /  double-stranded RNA binding / double-stranded RNA binding /  mRNA (nucleoside-2'-O-)-methyltransferase activity / mRNA 5'-cap (guanine-N7-)-methyltransferase activity / mRNA (nucleoside-2'-O-)-methyltransferase activity / mRNA 5'-cap (guanine-N7-)-methyltransferase activity /  RNA helicase activity / membrane => GO:0016020 / host cell endoplasmic reticulum membrane / RNA helicase activity / membrane => GO:0016020 / host cell endoplasmic reticulum membrane /  protein dimerization activity / protein dimerization activity /  RNA helicase / induction by virus of host autophagy / viral RNA genome replication / RNA helicase / induction by virus of host autophagy / viral RNA genome replication /  RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity / serine-type endopeptidase activity / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / symbiont-mediated suppression of host type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway / host cell nucleus / virion attachment to host cell / virion membrane / structural molecule activity / extracellular region / RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity / serine-type endopeptidase activity / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / symbiont-mediated suppression of host type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway / host cell nucleus / virion attachment to host cell / virion membrane / structural molecule activity / extracellular region /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  metal ion binding metal ion bindingSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Binjari virus Binjari virus | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 4.4 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 4.4 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Hardy, J.M. / Venugopal, H.V. / Newton, N.D. / Watterson, D. / Coulibaly, F.J. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, 1items Australia, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2021 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2021Title: The structure of an infectious immature flavivirus redefines viral architecture and maturation. Authors: Natalee D Newton / Joshua M Hardy / Naphak Modhiran / Leon E Hugo / Alberto A Amarilla / Summa Bibby / Hariprasad Venugopal / Jessica J Harrison / Renee J Traves / Roy A Hall / Jody Hobson- ...Authors: Natalee D Newton / Joshua M Hardy / Naphak Modhiran / Leon E Hugo / Alberto A Amarilla / Summa Bibby / Hariprasad Venugopal / Jessica J Harrison / Renee J Traves / Roy A Hall / Jody Hobson-Peters / Fasséli Coulibaly / Daniel Watterson /  Abstract: Flaviviruses are the cause of severe human diseases transmitted by mosquitoes and ticks. These viruses use a potent fusion machinery to enter target cells that needs to be restrained during viral ...Flaviviruses are the cause of severe human diseases transmitted by mosquitoes and ticks. These viruses use a potent fusion machinery to enter target cells that needs to be restrained during viral assembly and egress. A molecular chaperone, premembrane (prM) maintains the virus particles in an immature, fusion-incompetent state until they exit the cell. Taking advantage of an insect virus that produces particles that are both immature and infectious, we determined the structure of the first immature flavivirus with a complete spike by cryo-electron microscopy. Unexpectedly, the prM chaperone forms a supporting pillar that maintains the immature spike in an asymmetric and upright state, primed for large rearrangements upon acidification. The collapse of the spike along a path defined by the prM chaperone is required, and its inhibition by a multivalent immunoglobulin M blocks infection. The revised architecture and collapse model are likely to be conserved across flaviviruses. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7l30.cif.gz 7l30.cif.gz | 310.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7l30.ent.gz pdb7l30.ent.gz | 253.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7l30.json.gz 7l30.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l3/7l30 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l3/7l30 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l3/7l30 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l3/7l30 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 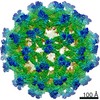 23147MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | x 60
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 | x 5
|
| 4 | x 6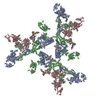
|
| 5 | 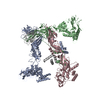
|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: (Schoenflies symbol : I (icosahedral : I (icosahedral )) )) |
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein |  Mass: 53495.086 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Fragment: UNP residues 294-790 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Binjari virus / Cell line (production host): C6/36 / Production host: Binjari virus / Cell line (production host): C6/36 / Production host:   Aedes albopictus (Asian tiger mosquito) / References: UniProt: A0A5K6VMX2 Aedes albopictus (Asian tiger mosquito) / References: UniProt: A0A5K6VMX2#2: Protein | Mass: 18946.809 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Fragment: UNP residues 125-293 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Binjari virus / Cell line (production host): C6/36 / Production host: Binjari virus / Cell line (production host): C6/36 / Production host:   Aedes albopictus (Asian tiger mosquito) / References: UniProt: A0A5K6VMX2 Aedes albopictus (Asian tiger mosquito) / References: UniProt: A0A5K6VMX2 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Binjari virus / Type: VIRUS Details: M and E from Binjari virus form a complex that assembles into anti-parallel dimers, (M-E)2, in the T=3 icosahedral particle. Entity ID: all / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 22 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Binjari virus / Strain: BFTA20 Binjari virus / Strain: BFTA20 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Aedes albopictus (Asian tiger mosquito) / Cell: C6/36 Aedes albopictus (Asian tiger mosquito) / Cell: C6/36 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details of virus | Empty: NO / Enveloped: YES / Isolate: SPECIES / Type: VIRION | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural host | Organism: Ochlerotatus normanensis | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Virus shell | Diameter: 470 nm / Triangulation number (T number): 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 4 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K Details: 0 second wait time 2.5 second blot time -4 blot force 1 second drain time |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Calibrated magnification: 105000 X / Calibrated defocus min: 100 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 4300 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Calibrated magnification: 105000 X / Calibrated defocus min: 100 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 4300 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm : 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 12.8 sec. / Electron dose: 43.2768 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 6226 |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 32 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 55992 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : I (icosahedral : I (icosahedral ) ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 26038 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 82.99 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj