+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structure of the insulin receptor-insulin complex by single-particle cryo-EM analysis. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 556, Issue 7699, Page 122-125, Year 2018 |
| Publish date | Apr 5, 2018 |
 Authors Authors | Giovanna Scapin / Venkata P Dandey / Zhening Zhang / Winifred Prosise / Alan Hruza / Theresa Kelly / Todd Mayhood / Corey Strickland / Clinton S Potter / Bridget Carragher /  |
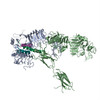
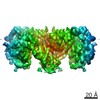
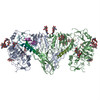
| PubMed Abstract | The insulin receptor is a dimeric protein that has a crucial role in controlling glucose homeostasis, regulating lipid, protein and carbohydrate metabolism, and modulating brain neurotransmitter ...The insulin receptor is a dimeric protein that has a crucial role in controlling glucose homeostasis, regulating lipid, protein and carbohydrate metabolism, and modulating brain neurotransmitter levels. Insulin receptor dysfunction has been associated with many diseases, including diabetes, cancer and Alzheimer's disease. The primary sequence of the receptor has been known since the 1980s, and is composed of an extracellular portion (the ectodomain, ECD), a single transmembrane helix and an intracellular tyrosine kinase domain. Binding of insulin to the dimeric ECD triggers auto-phosphorylation of the tyrosine kinase domain and subsequent activation of downstream signalling molecules. Biochemical and mutagenesis data have identified two putative insulin-binding sites, S1 and S2. The structures of insulin bound to an ECD fragment containing S1 and of the apo ectodomain have previously been reported, but details of insulin binding to the full receptor and the signal propagation mechanism are still not understood. Here we report single-particle cryo-electron microscopy reconstructions of the 1:2 (4.3 Å) and 1:1 (7.4 Å) complexes of the insulin receptor ECD dimer with insulin. The symmetrical 4.3 Å structure shows two insulin molecules per dimer, each bound between the leucine-rich subdomain L1 of one monomer and the first fibronectin-like domain (FnIII-1) of the other monomer, and making extensive interactions with the α-subunit C-terminal helix (α-CT helix). The 7.4 Å structure has only one similarly bound insulin per receptor dimer. The structures confirm the binding interactions at S1 and define the full S2 binding site. These insulin receptor states suggest that recruitment of the α-CT helix upon binding of the first insulin changes the relative subdomain orientations and triggers downstream signal propagation. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:29512653 / PubMed:29512653 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 4.3 - 7.4 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-7461, PDB-6ce7: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-NAG: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords |  SIGNALING PROTEIN / SIGNALING PROTEIN /  signaling signaling |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers