+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | The U4 Antibody Epitope on Human Papillomavirus 16 Identified by Cryo-electron Microscopy. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | J Virol, Vol. 89, Issue 23, Page 12108-12117, Year 2015 |
| Publish date | Sep 23, 2015 |
 Authors Authors | Jian Guan / Stephanie M Bywaters / Sarah A Brendle / Hyunwook Lee / Robert E Ashley / Neil D Christensen / Susan Hafenstein /  |
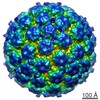
| PubMed Abstract | The human papillomavirus (HPV) major structural protein L1 composes capsomers that are linked together through interactions mediated by the L1 C terminus to constitute a T=7 icosahedral capsid. H16. ...The human papillomavirus (HPV) major structural protein L1 composes capsomers that are linked together through interactions mediated by the L1 C terminus to constitute a T=7 icosahedral capsid. H16.U4 is a type-specific monoclonal antibody recognizing a conformation-dependent neutralizing epitope of HPV thought to include the L1 protein C terminus. The structure of human papillomavirus 16 (HPV16) complexed with H16.U4 fragments of antibody (Fab) was solved by cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) image reconstruction. Atomic structures of virus and Fab were fitted into the corresponding cryo-EM densities to identify the antigenic epitope. The antibody footprint mapped predominately to the L1 C-terminal arm with an additional contact point on the side of the capsomer. This footprint describes an epitope that is presented capsid-wide. However, although the H16.U4 epitope suggests the presence of 360 potential binding sites exposed in the capsid valley between each capsomer, H16.U4 Fab bound only to epitopes located around the icosahedral five-fold vertex of the capsid. Thus, the binding characteristics of H16.U4 defined in this study showed a distinctive selectivity for local conformation-dependent interactions with specific L1 invading arms between five-fold related capsomers. IMPORTANCE: Human papillomavirus 16 (HPV16) is the most prevalent oncogenic genotype in HPV-associated anogenital and oral cancers. Here we use cryo-EM reconstruction techniques to solve the structures of the HPV16 capsid complexes using H16.U4 fragment of antibody (Fab). Different from most other antibodies directed against surface loops, H16.U4 monoclonal antibody is unique in targeting the C-terminal arm of the L1 protein. This monoclonal antibody (MAb) is used throughout the HPV research community in HPV serological and vaccine development and to define mechanisms of HPV uptake. The unique binding mode of H16.U4 defined here shows important conformation-dependent interactions within the HPV16 capsid. By targeting an important structural and conformational epitope, H16.U4 may identify subtle conformational changes in different maturation stages of the HPV capsid and provide a key probe to analyze the mechanisms of HPV uptake during the early stages of virus infection. Our analyses precisely define important conformational epitopes on HPV16 capsids that are key targets for successful HPV prophylactic vaccines. |
 External links External links |  J Virol / J Virol /  PubMed:26401038 / PubMed:26401038 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 12.0 - 13.0 Å |
| Structure data |  EMDB-6423: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | VIRUS/IMMUNE SYSTEM /  HPV16 / HPV16 /  antibody / U4 / neutralization / antibody / U4 / neutralization /  Fab / VIRUS-IMMUNE SYSTEM complex Fab / VIRUS-IMMUNE SYSTEM complex |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers