+Search query
-Structure paper
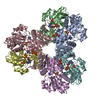
| Title | Human PRPS1 filaments stabilize allosteric sites to regulate activity. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Struct Mol Biol, Vol. 30, Issue 3, Page 391-402, Year 2023 |
| Publish date | Feb 6, 2023 |
 Authors Authors | Kelli L Hvorecny / Kenzee Hargett / Joel D Quispe / Justin M Kollman /  |
| PubMed Abstract | The universally conserved enzyme phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase (PRPS) assembles filaments in evolutionarily diverse organisms. PRPS is a key regulator of nucleotide metabolism, and ...The universally conserved enzyme phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase (PRPS) assembles filaments in evolutionarily diverse organisms. PRPS is a key regulator of nucleotide metabolism, and mutations in the human enzyme PRPS1 lead to a spectrum of diseases. Here we determine structures of human PRPS1 filaments in active and inhibited states, with fixed assembly contacts accommodating both conformations. The conserved assembly interface stabilizes the binding site for the essential activator phosphate, increasing activity in the filament. Some disease mutations alter assembly, supporting the link between filament stability and activity. Structures of active PRPS1 filaments turning over substrate also reveal coupling of catalysis in one active site with product release in an adjacent site. PRPS1 filaments therefore provide an additional layer of allosteric control, conserved throughout evolution, with likely impact on metabolic homeostasis. Stabilization of allosteric binding sites by polymerization adds to the growing diversity of assembly-based enzyme regulatory mechanisms. |
 External links External links |  Nat Struct Mol Biol / Nat Struct Mol Biol /  PubMed:36747094 / PubMed:36747094 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.0 - 3.2 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-27279, PDB-8dbc: EMDB-27280, PDB-8dbd: EMDB-27281, PDB-8dbe: EMDB-27282, PDB-8dbf: EMDB-27283, PDB-8dbg: EMDB-27284, PDB-8dbh: EMDB-27285, PDB-8dbi: EMDB-27286, PDB-8dbj: EMDB-27287, PDB-8dbk:  EMDB-27288: Human PRPS1 with Phosphate, ATP, and R5P; Hexamer with resolved catalytic loops EMDB-27289, PDB-8dbl: EMDB-27290, PDB-8dbm: EMDB-27291, PDB-8dbn:  EMDB-27292: Human PRPS1-E307A engineered mutation with Phosphate, ATP, and R5P; Symmetry-expanded Hexamer EMDB-27293, PDB-8dbo:  EMDB-27294: Human PRPS1-E307A engineered mutation with ADP; Symmetry-expanded Hexamer 1  EMDB-27295: Human PRPS1-E307A engineered mutation with ADP; Symmetry-expanded Hexamer 2 |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-PO4:  ChemComp-HSX:  ChemComp-ADP:  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-ATP:  ChemComp-PRP: 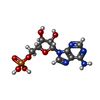 ChemComp-AMP: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords |  TRANSFERASE / TRANSFERASE /  phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase / phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase /  phosphate / phosphate activator / ADP inhibitor / ATP substrate / ATP and R5P substrates / catalytic loop / PRPP product / ATP/R5P substrate / Filament-breaking mutation phosphate / phosphate activator / ADP inhibitor / ATP substrate / ATP and R5P substrates / catalytic loop / PRPP product / ATP/R5P substrate / Filament-breaking mutation |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers