+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structures of tweety homolog proteins TTYH2 and TTYH3 reveal a Ca-dependent switch from intra- to intermembrane dimerization. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Commun, Vol. 12, Issue 1, Page 6913, Year 2021 |
| Publish date | Nov 25, 2021 |
 Authors Authors | Baobin Li / Christopher M Hoel / Stephen G Brohawn /  |
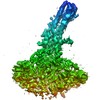
| PubMed Abstract | Tweety homologs (TTYHs) comprise a conserved family of transmembrane proteins found in eukaryotes with three members (TTYH1-3) in vertebrates. They are widely expressed in mammals including at high ...Tweety homologs (TTYHs) comprise a conserved family of transmembrane proteins found in eukaryotes with three members (TTYH1-3) in vertebrates. They are widely expressed in mammals including at high levels in the nervous system and have been implicated in cancers and other diseases including epilepsy, chronic pain, and viral infections. TTYHs have been reported to form Ca- and cell volume-regulated anion channels structurally distinct from any characterized protein family with potential roles in cell adhesion, migration, and developmental signaling. To provide insight into TTYH family structure and function, we determined cryo-EM structures of Mus musculus TTYH2 and TTYH3 in lipid nanodiscs. TTYH2 and TTYH3 adopt a previously unobserved fold which includes an extended extracellular domain with a partially solvent exposed pocket that may be an interaction site for hydrophobic molecules. In the presence of Ca, TTYH2 and TTYH3 form homomeric cis-dimers bridged by extracellularly coordinated Ca. Strikingly, in the absence of Ca, TTYH2 forms trans-dimers that span opposing membranes across a ~130 Å intermembrane space as well as a monomeric state. All TTYH structures lack ion conducting pathways and we do not observe TTYH2-dependent channel activity in cells. We conclude TTYHs are not pore forming subunits of anion channels and their function may involve Ca-dependent changes in quaternary structure, interactions with hydrophobic molecules near the extracellular membrane surface, and/or association with additional protein partners. |
 External links External links |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:34824283 / PubMed:34824283 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.23 - 3.96 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-24688, PDB-7rtt: EMDB-24689, PDB-7rtu: EMDB-24690, PDB-7rtv: EMDB-24691, PDB-7rtw: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-CA:  ChemComp-NAG: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords |  MEMBRANE PROTEIN / TTYH2 / Cisdimer / MEMBRANE PROTEIN / TTYH2 / Cisdimer /  monomer / momomer monomer / momomer |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers