+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Targeted selection of HIV-specific antibody mutations by engineering B cell maturation. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Science, Vol. 366, Issue 6470, Year 2019 |
| Publish date | Dec 6, 2019 |
 Authors Authors | Kevin O Saunders / Kevin Wiehe / Ming Tian / Priyamvada Acharya / Todd Bradley / S Munir Alam / Eden P Go / Richard Scearce / Laura Sutherland / Rory Henderson / Allen L Hsu / Mario J Borgnia / Haiyan Chen / Xiaozhi Lu / Nelson R Wu / Brian Watts / Chuancang Jiang / David Easterhoff / Hwei-Ling Cheng / Kelly McGovern / Peyton Waddicor / Aimee Chapdelaine-Williams / Amanda Eaton / Jinsong Zhang / Wes Rountree / Laurent Verkoczy / Mark Tomai / Mark G Lewis / Heather R Desaire / Robert J Edwards / Derek W Cain / Mattia Bonsignori / David Montefiori / Frederick W Alt / Barton F Haynes /  |
| PubMed Abstract | INTRODUCTION: A major goal of HIV-1 vaccine development is the design of immunogens that induce broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs). However, vaccination of humans has not resulted in the ...INTRODUCTION: A major goal of HIV-1 vaccine development is the design of immunogens that induce broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs). However, vaccination of humans has not resulted in the induction of affinity-matured and potent HIV-1 bnAbs. To devise effective vaccine strategies, we previously determined the maturation pathway of select HIV-1 bnAbs from acute infection through neutralizing antibody development. During their evolution, bnAbs acquire an abundance of improbable amino acid substitutions as a result of nucleotide mutations at variable region sequences rarely targeted by activation-induced cytidine deaminase, the enzyme responsible for antibody mutation. A subset of improbable mutations is essential for broad neutralization activity, and their acquisition represents a key roadblock to bnAb development. RATIONALE: Current bnAb lineage-based vaccine strategies can initiate bnAb lineage development in animal models but have not specifically elicited the improbable mutations required for neutralization breadth. Induction of bnAbs requires vaccine strategies that specifically engage bnAb precursors and subsequently select for improbable mutations required for broadly neutralizing activity. We hypothesized that vaccination with immunogens that bind with moderate to high affinity to bnAb B cell precursors, and with higher affinity to precursors that have acquired improbable mutations, could initiate bnAb B cell lineages and select for key improbable mutations required for bnAb development. RESULTS: We elicited serum neutralizing HIV-1 antibodies in human bnAb precursor knock-in mice and wild-type macaques vaccinated with immunogens designed to select for improbable mutations. We designed two HIV-1 envelope immunogens that bound precursor B cells of either a CD4 binding site or V3-glycan bnAb lineage. In vitro, these immunogens bound more strongly to bnAb precursors once the precursor acquired the desired improbable mutations. Vaccination of macaques with the CD4 binding site–targeting immunogen induced CD4 binding site serum neutralizing antibodies. Antibody sequences elicited in human bnAb precursor knock-in mice encoded functional improbable mutations critical for bnAb development. In bnAb precursor knock-in mice, we isolated a vaccine-elicited monoclonal antibody bearing functional improbable mutations that was capable of neutralizing multiple HIV-1 global isolates. Structures of a bnAb precursor, a bnAb, and the vaccine-elicited antibody revealed the precise roles that acquired improbable mutations played in recognizing the HIV-1 envelope. Thus, our immunogens elicited antibody responses in macaques and knock-in mice that exhibited the mutational patterns, structural characteristics, or neutralization profiles of nascent broadly neutralizing antibodies. CONCLUSION: Our study represents a proof of concept for targeted selection of improbable mutations to guide antibody affinity maturation. Moreover, this study demonstrates a rational strategy for sequential immunogen design to circumvent the difficult roadblocks in HIV-1 bnAb induction by vaccination. We show that immunogens should exhibit differences in affinity across antibody maturation stages where improbable mutations are necessary for the desired antibody function. This strategy of selection of specific antibody nucleotides by immunogen design can be applied to B cell lineages targeting other pathogens where guided affinity maturation is needed for a protective antibody response. |
 External links External links |  Science / Science /  PubMed:31806786 / PubMed:31806786 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
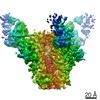
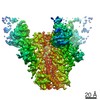
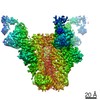
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.5 - 4.3 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-20817, PDB-6um5: EMDB-20818, PDB-6um6: EMDB-20819, PDB-6um7: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-NAG: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords |  VIRAL PROTEIN/immune system / V3-glycan site / unmutated common ancestor / DH270 lineage / VIRAL PROTEIN/immune system / V3-glycan site / unmutated common ancestor / DH270 lineage /  VIRAL PROTEIN / VIRAL PROTEIN /  VIRAL PROTEIN-immune system complex VIRAL PROTEIN-immune system complex |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers