+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structure of lactococcal phage p2 baseplate and its mechanism of activation. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Vol. 107, Issue 15, Page 6852-6857, Year 2010 |
| Publish date | Apr 13, 2010 |
 Authors Authors | Giuliano Sciara / Cecilia Bebeacua / Patrick Bron / Denise Tremblay / Miguel Ortiz-Lombardia / Julie Lichière / Marin van Heel / Valérie Campanacci / Sylvain Moineau / Christian Cambillau /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Siphoviridae is the most abundant viral family on earth which infects bacteria as well as archaea. All known siphophages infecting gram+ Lactococcus lactis possess a baseplate at the tip of their ...Siphoviridae is the most abundant viral family on earth which infects bacteria as well as archaea. All known siphophages infecting gram+ Lactococcus lactis possess a baseplate at the tip of their tail involved in host recognition and attachment. Here, we report analysis of the p2 phage baseplate structure by X-ray crystallography and electron microscopy and propose a mechanism for the baseplate activation during attachment to the host cell. This approximately 1 MDa, Escherichia coli-expressed baseplate is composed of three protein species, including six trimers of the receptor-binding protein (RBP). RBPs host-recognition domains point upwards, towards the capsid, in agreement with the electron-microscopy map of the free virion. In the presence of Ca(2+), a cation mandatory for infection, the RBPs rotated 200 degrees downwards, presenting their binding sites to the host, and a channel opens at the bottom of the baseplate for DNA passage. These conformational changes reveal a novel siphophage activation and host-recognition mechanism leading ultimately to DNA ejection. |
 External links External links |  Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A /  PubMed:20351260 / PubMed:20351260 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 2.6 - 26.0 Å |
| Structure data | 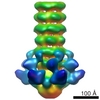 EMDB-1699: 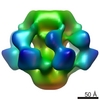 EMDB-1706:  PDB-2wzp:  PDB-2x53:  PDB-4v5i: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-SR:  ChemComp-CA: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords |  VIRAL PROTEIN / VIRAL PROTEIN /  BASEPLATE / BASEPLATE /  SIPHOVIRIDAE / SIPHOVIRIDAE /  LACTOCOCCUS LACTIS LACTOCOCCUS LACTIS |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers



 lactococcus phage p2 (virus)
lactococcus phage p2 (virus)
