+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Variable microtubule architecture in the malaria parasite. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Commun, Vol. 14, Issue 1, Page 1216, Year 2023 |
| Publish date | Mar 3, 2023 |
 Authors Authors | Josie L Ferreira / Vojtěch Pražák / Daven Vasishtan / Marc Siggel / Franziska Hentzschel / Annika M Binder / Emma Pietsch / Jan Kosinski / Friedrich Frischknecht / Tim W Gilberger / Kay Grünewald /   |
| PubMed Abstract | Microtubules are a ubiquitous eukaryotic cytoskeletal element typically consisting of 13 protofilaments arranged in a hollow cylinder. This arrangement is considered the canonical form and is adopted ...Microtubules are a ubiquitous eukaryotic cytoskeletal element typically consisting of 13 protofilaments arranged in a hollow cylinder. This arrangement is considered the canonical form and is adopted by most organisms, with rare exceptions. Here, we use in situ electron cryo-tomography and subvolume averaging to analyse the changing microtubule cytoskeleton of Plasmodium falciparum, the causative agent of malaria, throughout its life cycle. Unexpectedly, different parasite forms have distinct microtubule structures coordinated by unique organising centres. In merozoites, the most widely studied form, we observe canonical microtubules. In migrating mosquito forms, the 13 protofilament structure is further reinforced by interrupted luminal helices. Surprisingly, gametocytes contain a wide distribution of microtubule structures ranging from 13 to 18 protofilaments, doublets and triplets. Such a diversity of microtubule structures has not been observed in any other organism to date and is likely evidence of a distinct role in each life cycle form. This data provides a unique view into an unusual microtubule cytoskeleton of a relevant human pathogen. |
 External links External links |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:36869034 / PubMed:36869034 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (subtomogram averaging) |
| Resolution | 20.0 - 34.0 Å |
| Structure data |  EMDB-15532: Plasmodium falciparum sporozoite subpellicular microtubule with interrupted luminal helix determined in situ  EMDB-15534: Plasmodium falciparum gametocyte subpellicular microtubule with 13 protofilaments determined in situ 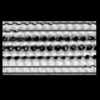 EMDB-15535: Plasmodium falciparum gametocyte subpellicular microtubule with 14 protofilaments determined in situ  EMDB-15536: Plasmodium falciparum gametocyte subpellicular microtubule with 15 protofilaments determined in situ 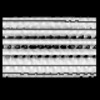 EMDB-15537: Plasmodium falciparum gametocyte subpellicular microtubule with 16 protofilaments determined in situ 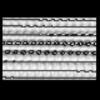 EMDB-15538: Plasmodium falciparum gametocyte subpellicular microtubule with 17 protofilaments determined in situ 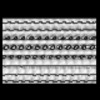 EMDB-15539: Plasmodium falciparum gametocyte subpellicular microtubule with 18 protofilaments determined in situ |
| Source |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




 Plasmodium falciparum NF54 (eukaryote)
Plasmodium falciparum NF54 (eukaryote)