+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Ribosome-dependent activation of stringent control. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 534, Issue 7606, Page 277-280, Year 2016 |
| Publish date | Jun 9, 2016 |
 Authors Authors | Alan Brown / Israel S Fernández / Yuliya Gordiyenko / V Ramakrishnan /  |
| PubMed Abstract | In order to survive, bacteria continually sense, and respond to, environmental fluctuations. Stringent control represents a key bacterial stress response to nutrient starvation that leads to rapid ...In order to survive, bacteria continually sense, and respond to, environmental fluctuations. Stringent control represents a key bacterial stress response to nutrient starvation that leads to rapid and comprehensive reprogramming of metabolic and transcriptional patterns. In general, transcription of genes for growth and proliferation is downregulated, while those important for survival and virulence are upregulated. Amino acid starvation is sensed by depletion of the aminoacylated tRNA pools, and this results in accumulation of ribosomes stalled with non-aminoacylated (uncharged) tRNA in the ribosomal A site. RelA is recruited to stalled ribosomes and activated to synthesize a hyperphosphorylated guanosine analogue, (p)ppGpp, which acts as a pleiotropic secondary messenger. However, structural information about how RelA recognizes stalled ribosomes and discriminates against aminoacylated tRNAs is missing. Here we present the cryo-electron microscopy structure of RelA bound to the bacterial ribosome stalled with uncharged tRNA. The structure reveals that RelA utilizes a distinct binding site compared to the translational factors, with a multi-domain architecture that wraps around a highly distorted A-site tRNA. The TGS (ThrRS, GTPase and SpoT) domain of RelA binds the CCA tail to orient the free 3' hydroxyl group of the terminal adenosine towards a β-strand, such that an aminoacylated tRNA at this position would be sterically precluded. The structure supports a model in which association of RelA with the ribosome suppresses auto-inhibition to activate synthesis of (p)ppGpp and initiate the stringent response. Since stringent control is responsible for the survival of pathogenic bacteria under stress conditions, and contributes to chronic infections and antibiotic tolerance, RelA represents a good target for the development of novel antibacterial therapeutics. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:27279228 / PubMed:27279228 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.0 - 3.6 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-8107: Structure of RelA bound to the 70S ribosome (overall map, class 1) 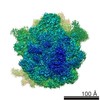 EMDB-8108: 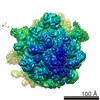 EMDB-8109:  EMDB-8110:  EMDB-8111:  EMDB-8112:  EMDB-8113:  EMDB-8114:  EMDB-8115: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-ZN: 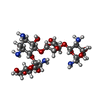 ChemComp-PAR: 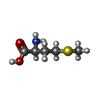 ChemComp-MET:  ChemComp-HOH: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords |  RIBOSOME / RIBOSOME /  tRNA / tRNA /  RelA / ppGpp RelA / ppGpp |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers