+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Functional domains of the 50S subunit mature late in the assembly process. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nucleic Acids Res, Vol. 42, Issue 5, Page 3419-3435, Year 2014 |
| Publish date | Dec 13, 2013 |
 Authors Authors | Ahmad Jomaa / Nikhil Jain / Joseph H Davis / James R Williamson / Robert A Britton / Joaquin Ortega /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Despite the identification of many factors that facilitate ribosome assembly, the molecular mechanisms by which they drive ribosome biogenesis are poorly understood. Here, we analyze the late stages ...Despite the identification of many factors that facilitate ribosome assembly, the molecular mechanisms by which they drive ribosome biogenesis are poorly understood. Here, we analyze the late stages of assembly of the 50S subunit using Bacillus subtilis cells depleted of RbgA, a highly conserved GTPase. We found that RbgA-depleted cells accumulate late assembly intermediates bearing sub-stoichiometric quantities of ribosomal proteins L16, L27, L28, L33a, L35 and L36. Using a novel pulse labeling/quantitative mass spectrometry technique, we show that this particle is physiologically relevant and is capable of maturing into a complete 50S particle. Cryo-electron microscopy and chemical probing revealed that the central protuberance, the GTPase associating region and tRNA-binding sites in this intermediate are unstructured. These findings demonstrate that key functional sites of the 50S subunit remain unstructured until late stages of maturation, preventing the incomplete subunit from prematurely engaging in translation. Finally, structural and biochemical analysis of a ribosome particle depleted of L16 indicate that L16 binding is necessary for the stimulation of RbgA GTPase activity and, in turn, release of this co-factor, and for conversion of the intermediate to a complete 50S subunit. |
 External links External links |  Nucleic Acids Res / Nucleic Acids Res /  PubMed:24335279 / PubMed:24335279 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 11.0 - 13.0 Å |
| Structure data | 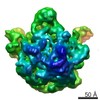 EMDB-5787: 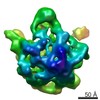 EMDB-5788: 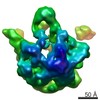 EMDB-5789:  EMDB-5790: 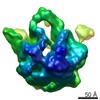 EMDB-5791:  EMDB-5792: |
| Source |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




 Bacillus subtilis (bacteria)
Bacillus subtilis (bacteria)