+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structural changes in isometrically contracting insect flight muscle trapped following a mechanical perturbation. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | PLoS One, Vol. 7, Issue 6, Page e39422, Year 2012 |
| Publish date | Jun 25, 2012 |
 Authors Authors | Shenping Wu / Jun Liu / Mary C Reedy / Robert J Perz-Edwards / Richard T Tregear / Hanspeter Winkler / Clara Franzini-Armstrong / Hiroyuki Sasaki / Carmen Lucaveche / Yale E Goldman / Michael K Reedy / Kenneth A Taylor /  |
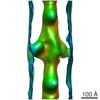
| PubMed Abstract | The application of rapidly applied length steps to actively contracting muscle is a classic method for synchronizing the response of myosin cross-bridges so that the average response of the ensemble ...The application of rapidly applied length steps to actively contracting muscle is a classic method for synchronizing the response of myosin cross-bridges so that the average response of the ensemble can be measured. Alternatively, electron tomography (ET) is a technique that can report the structure of the individual members of the ensemble. We probed the structure of active myosin motors (cross-bridges) by applying 0.5% changes in length (either a stretch or a release) within 2 ms to isometrically contracting insect flight muscle (IFM) fibers followed after 5-6 ms by rapid freezing against a liquid helium cooled copper mirror. ET of freeze-substituted fibers, embedded and thin-sectioned, provides 3-D cross-bridge images, sorted by multivariate data analysis into ~40 classes, distinct in average structure, population size and lattice distribution. Individual actin subunits are resolved facilitating quasi-atomic modeling of each class average to determine its binding strength (weak or strong) to actin. ~98% of strong-binding acto-myosin attachments present after a length perturbation are confined to "target zones" of only two actin subunits located exactly midway between successive troponin complexes along each long-pitch helical repeat of actin. Significant changes in the types, distribution and structure of actin-myosin attachments occurred in a manner consistent with the mechanical transients. Most dramatic is near disappearance, after either length perturbation, of a class of weak-binding cross-bridges, attached within the target zone, that are highly likely to be precursors of strong-binding cross-bridges. These weak-binding cross-bridges were originally observed in isometrically contracting IFM. Their disappearance following a quick stretch or release can be explained by a recent kinetic model for muscle contraction, as behaviour consistent with their identification as precursors of strong-binding cross-bridges. The results provide a detailed model for contraction in IFM that may be applicable to contraction in other types of muscle. |
 External links External links |  PLoS One / PLoS One /  PubMed:22761792 / PubMed:22761792 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (subtomogram averaging) / EM (helical sym.) / EM (tomography) |
| Resolution | 35 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-1584: Electron tomography of isometrically contracting insect flight muscle quick frozen after a quick release step EMDB-1585: Electron tomography of isometrically contracting insect flight muscle quick frozen after a rapid stretch transient |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords |  CONTRACTILE PROTEIN / CONTRACTILE PROTEIN /  METHYLATION / ATP-BINDING / METHYLATION / ATP-BINDING /  ISOMETRIC CONTRACTION / ISOMETRIC CONTRACTION /  MICROTOMY / FREEZE SUBSTITUTION / MICROTOMY / FREEZE SUBSTITUTION /  MUSCLE PROTEIN / CALMODULIN-BINDING / MUSCLE PROTEIN / CALMODULIN-BINDING /  MOTOR PROTEIN / ACTIN-BINDING / MOTOR PROTEIN / ACTIN-BINDING /  TROPOMYOSIN / LIGHT CHAINS / TROPOMYOSIN / LIGHT CHAINS /  THIN FILAMENT / THIN FILAMENT /  THICK FILAMENT THICK FILAMENT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers