+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-8244 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
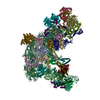
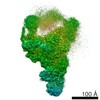
| Title | Rigor myosin X co-complexed with an actin filament | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Rigor myosin X co-complexed with an actin filament | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | myosin molecular motors cytoskeletal motility /  MOTOR PROTEIN MOTOR PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationplus-end directed microfilament motor activity / Netrin-1 signaling / positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion / filopodium tip / cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport /  regulation of filopodium assembly / filopodium membrane / regulation of filopodium assembly / filopodium membrane /  myosin complex / cytoskeletal motor activator activity / microfilament motor activity ...plus-end directed microfilament motor activity / Netrin-1 signaling / positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion / filopodium tip / cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport / myosin complex / cytoskeletal motor activator activity / microfilament motor activity ...plus-end directed microfilament motor activity / Netrin-1 signaling / positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion / filopodium tip / cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport /  regulation of filopodium assembly / filopodium membrane / regulation of filopodium assembly / filopodium membrane /  myosin complex / cytoskeletal motor activator activity / microfilament motor activity / myosin complex / cytoskeletal motor activator activity / microfilament motor activity /  spectrin binding / spectrin binding /  tropomyosin binding / tropomyosin binding /  myosin heavy chain binding / mesenchyme migration / myosin heavy chain binding / mesenchyme migration /  troponin I binding / actin filament bundle / filamentous actin / phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding / actin filament bundle assembly / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin monomer binding / skeletal muscle fiber development / troponin I binding / actin filament bundle / filamentous actin / phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding / actin filament bundle assembly / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin monomer binding / skeletal muscle fiber development /  stress fiber / stress fiber /  titin binding / ruffle / actin filament polymerization / titin binding / ruffle / actin filament polymerization /  filopodium / filopodium /  actin filament / FCGR3A-mediated phagocytosis / actin filament / FCGR3A-mediated phagocytosis /  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / Regulation of actin dynamics for phagocytic cup formation / calcium-dependent protein binding / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / Regulation of actin dynamics for phagocytic cup formation / calcium-dependent protein binding /  actin filament binding / actin filament binding /  lamellipodium / lamellipodium /  cell body / cell body /  cell cortex / regulation of cell shape / cell cortex / regulation of cell shape /  calmodulin binding / calmodulin binding /  hydrolase activity / neuron projection / protein domain specific binding / neuronal cell body / hydrolase activity / neuron projection / protein domain specific binding / neuronal cell body /  calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression /  nucleolus / magnesium ion binding / nucleolus / magnesium ion binding /  signal transduction / signal transduction /  ATP binding / identical protein binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding /  plasma membrane / plasma membrane /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 9.1 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 9.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Sindelar CV / Houdusse A | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2016 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2016Title: The myosin X motor is optimized for movement on actin bundles. Authors: Virginie Ropars / Zhaohui Yang / Tatiana Isabet / Florian Blanc / Kaifeng Zhou / Tianming Lin / Xiaoyan Liu / Pascale Hissier / Frédéric Samazan / Béatrice Amigues / Eric D Yang / Hyokeun ...Authors: Virginie Ropars / Zhaohui Yang / Tatiana Isabet / Florian Blanc / Kaifeng Zhou / Tianming Lin / Xiaoyan Liu / Pascale Hissier / Frédéric Samazan / Béatrice Amigues / Eric D Yang / Hyokeun Park / Olena Pylypenko / Marco Cecchini / Charles V Sindelar / H Lee Sweeney / Anne Houdusse /    Abstract: Myosin X has features not found in other myosins. Its structure must underlie its unique ability to generate filopodia, which are essential for neuritogenesis, wound healing, cancer metastasis and ...Myosin X has features not found in other myosins. Its structure must underlie its unique ability to generate filopodia, which are essential for neuritogenesis, wound healing, cancer metastasis and some pathogenic infections. By determining high-resolution structures of key components of this motor, and characterizing the in vitro behaviour of the native dimer, we identify the features that explain the myosin X dimer behaviour. Single-molecule studies demonstrate that a native myosin X dimer moves on actin bundles with higher velocities and takes larger steps than on single actin filaments. The largest steps on actin bundles are larger than previously reported for artificially dimerized myosin X constructs or any other myosin. Our model and kinetic data explain why these large steps and high velocities can only occur on bundled filaments. Thus, myosin X functions as an antiparallel dimer in cells with a unique geometry optimized for movement on actin bundles. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_8244.map.gz emd_8244.map.gz | 7.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-8244-v30.xml emd-8244-v30.xml emd-8244.xml emd-8244.xml | 18.4 KB 18.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_8244_fsc.xml emd_8244_fsc.xml | 5.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_8244.png emd_8244.png | 217.3 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_8244_msk_1.map emd_8244_msk_1.map | 8 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-8244.cif.gz emd-8244.cif.gz | 6.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_8244_half_map_1.map.gz emd_8244_half_map_1.map.gz emd_8244_half_map_2.map.gz emd_8244_half_map_2.map.gz | 7.4 MB 7.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8244 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8244 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8244 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8244 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5kg8MC  5hmoC  5hmpC  5i0hC  5i0iC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_8244.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_8244.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Rigor myosin X co-complexed with an actin filament | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.868 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
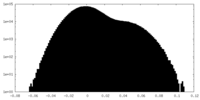
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_8244_msk_1.map emd_8244_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Rigor myosin X co-complexed with an actin filament, half map #1
| File | emd_8244_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Rigor myosin X co-complexed with an actin filament, half map #1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Rigor myosin X co-complexed with an actin filament, half map #2
| File | emd_8244_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Rigor myosin X co-complexed with an actin filament, half map #2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Actin filament decorated by the myosin X motor domain
| Entire | Name: Actin filament decorated by the myosin X motor domain |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Actin filament decorated by the myosin X motor domain
| Supramolecule | Name: Actin filament decorated by the myosin X motor domain / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: Unconventional myosin-X
| Macromolecule | Name: Unconventional myosin-X / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 85.083086 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: NFFTEGTRVW LRENGQHFPS TVNSCAEGIV VFRTDYGQVF TYKQSTITHQ KVTAMHPTNE EGVDDMASLT ELHGGSIMYN LFQRYKRNQ IYTYIGSILA SVNPYQPIAG LYEPATMEQY SRRHLGELPP HIFAIANECY RCLWKRHDNQ CILISGESGA G KTESTKLI ...String: NFFTEGTRVW LRENGQHFPS TVNSCAEGIV VFRTDYGQVF TYKQSTITHQ KVTAMHPTNE EGVDDMASLT ELHGGSIMYN LFQRYKRNQ IYTYIGSILA SVNPYQPIAG LYEPATMEQY SRRHLGELPP HIFAIANECY RCLWKRHDNQ CILISGESGA G KTESTKLI LKFLSVISQQ SLELSLKEKT SCVERAILES SPIMEAFGNA KTVYNNNSSR FGKFVQLNIC QKGNIQGGRI VD YLLEKNR VVRQNPGERN YHIFYALLAG LEHEEREEFY LSTPENYHYL NQSGCVEDKT ISDQESFREV ITAMDVMQFS KEE VREVSR LLAGILHLGN IEFITAGGAQ VSFKTALGRS AELLGLDPTQ LTDALTQRSM FLRGEEILTP LNVQQAVDSR DSLA MALYA CCFEWVIKKI NSRIKGNEDF KSIGILDIFG FENFEVNHFE QFNINYANEK LQEYFNKHIF SLEQLEYSRE GLVWE DIDW IDNGECLDLI EKKLGLLALI NEESHFPQAT DSTLLEKLHS QHANNHFYVK PRVAVNNFGV KHYAGEVQYD VRGILE KNR DTFRDDLLNL LRESRFDFIY DLFEHVSSRN NQDAAAAAAA ARRPTVSSQF KDSLHSLMAT LSSSNPFFVR CIKPNMQ KM PDQFDQAVVL NQLRYSGMLE TVRIRKAGYA VRRPFQDFYK RYKVLMRNLA LPEDVRGKCT SLLQLYDASN SEWQLGKT K VFLRESLEQK LEKRREEE UniProtKB: Unconventional myosin-X |
-Macromolecule #2: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.827609 KDa |
| Sequence | String: DEDETTALVC DNGSGLVKAG FAGDDAPRAV FPSIVGRPRH QGVMVGMGQK DSYVGDEAQS KRGILTLKYP IECGIITNWD DMEKIWHHT FYNELRVAPE EHPTLLTEAP LNPKANREKM TQIMFETFNV PAMYVAIQAV LSLYASGRTT GIVLDSGDGV T HNVPIYEG ...String: DEDETTALVC DNGSGLVKAG FAGDDAPRAV FPSIVGRPRH QGVMVGMGQK DSYVGDEAQS KRGILTLKYP IECGIITNWD DMEKIWHHT FYNELRVAPE EHPTLLTEAP LNPKANREKM TQIMFETFNV PAMYVAIQAV LSLYASGRTT GIVLDSGDGV T HNVPIYEG YALPHAIMRL DLAGRDLTDY LMKILTERGY SFVTTAEREI VRDIKEKLCY VALDFENEMA TAASSSSLEK SY ELPDGQV ITIGNERFRC PETLFQPSFI GMESAGIHET TYNSIMKCDI DIRKDLYANN VMSGGTTMYP GIADRMQKEI TAL APSTMK IKIIAPPERK YSVWIGGSIL ASLSTFQQMW ITKQEYDEAG PSIVHRKCF UniProtKB:  Actin, alpha skeletal muscle Actin, alpha skeletal muscle |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.7 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 6.8 / Component - Concentration: 5.0 mM / Component - Name: MOPS |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Calibrated defocus max: 5.251 µm / Calibrated defocus min: 1.438 µm / Calibrated magnification: 26780 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 5.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 5.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: GATAN 626 SINGLE TILT LIQUID NITROGEN CRYO TRANSFER HOLDER Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Number grids imaged: 2 / Number real images: 154 / Average exposure time: 13.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller















 Z
Z Y
Y X
X