+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-5439 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
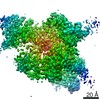
| Title | Structural basis for microtubule binding and release by dynein | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Construct of the high affinity dynein microtubule-binding domain fused to seryl-tRNA synthase-monomer | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  dynein / microtubule bound / high affinity microtubule binding domain dynein / microtubule bound / high affinity microtubule binding domain | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationCOPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / cilium movement / Aggrephagy / positive regulation of intracellular transport / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion ...COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / cilium movement / Aggrephagy / positive regulation of intracellular transport / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / regulation of metaphase plate congression / establishment of spindle localization / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / positive regulation of spindle assembly / Separation of Sister Chromatids / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / manchette /  Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition /  P-body assembly / P-body assembly /  dynein complex / MHC class II antigen presentation / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / dynein complex / MHC class II antigen presentation / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity /  cytoplasmic dynein complex / retrograde axonal transport / dynein light intermediate chain binding / nuclear migration / positive regulation of axon guidance / dynein intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic microtubule / microtubule-based process / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / cytoplasmic dynein complex / retrograde axonal transport / dynein light intermediate chain binding / nuclear migration / positive regulation of axon guidance / dynein intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic microtubule / microtubule-based process / cytoplasmic microtubule organization /  stress granule assembly / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / axon cytoplasm / cellular response to interleukin-4 / Neutrophil degranulation / mitotic spindle organization / stress granule assembly / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / axon cytoplasm / cellular response to interleukin-4 / Neutrophil degranulation / mitotic spindle organization /  filopodium / filopodium /  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / microtubule cytoskeleton / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / microtubule cytoskeleton /  double-stranded RNA binding / mitotic cell cycle / double-stranded RNA binding / mitotic cell cycle /  nuclear envelope / nuclear envelope /  nervous system development / positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / nervous system development / positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis /  cell cortex / cell cortex /  microtubule / protein heterodimerization activity / microtubule / protein heterodimerization activity /  cell division / cell division /  axon / axon /  GTPase activity / GTPase activity /  centrosome / neuronal cell body / centrosome / neuronal cell body /  ubiquitin protein ligase binding / GTP binding / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / GTP binding /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Mus musculus (house mouse) / Mus musculus (house mouse) /   Bos taurus (cattle) Bos taurus (cattle) | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 9.7 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 9.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Redwine WB / Hernandez-Lopez R / Zou S / Huang J / Reck-Peterson SL / Leschziner AE | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2012 Journal: Science / Year: 2012Title: Structural basis for microtubule binding and release by dynein. Authors: W B Redwine / R Hernandez-Lopez / S Zou / J Huang / S L Reck-Peterson / A E Leschziner /  Abstract: Cytoplasmic dynein is a microtubule-based motor required for intracellular transport and cell division. Its movement involves coupling cycles of track binding and release with cycles of force- ...Cytoplasmic dynein is a microtubule-based motor required for intracellular transport and cell division. Its movement involves coupling cycles of track binding and release with cycles of force-generating nucleotide hydrolysis. How this is accomplished given the ~25 nanometers separating dynein's track- and nucleotide-binding sites is not understood. Here, we present a subnanometer-resolution structure of dynein's microtubule-binding domain bound to microtubules by cryo-electron microscopy that was used to generate a pseudo-atomic model of the complex with molecular dynamics. We identified large rearrangements triggered by track binding and specific interactions, confirmed by mutagenesis and single-molecule motility assays, which tune dynein's affinity for microtubules. Our results provide a molecular model for how dynein's binding to microtubules is communicated to the rest of the motor. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_5439.map.gz emd_5439.map.gz | 336.1 KB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-5439-v30.xml emd-5439-v30.xml emd-5439.xml emd-5439.xml | 12.3 KB 12.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_5439.png emd_5439.png | 151.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-5439 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-5439 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-5439 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-5439 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3j1tMC  3j1uMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_5439.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 492.2 KB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_5439.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 492.2 KB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Construct of the high affinity dynein microtubule-binding domain fused to seryl-tRNA synthase-monomer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.988 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : high affinity construct of dynein microtubule-binding domain fuse...
| Entire | Name: high affinity construct of dynein microtubule-binding domain fused to seryl-tRNA synthase monomer |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: high affinity construct of dynein microtubule-binding domain fuse...
| Supramolecule | Name: high affinity construct of dynein microtubule-binding domain fused to seryl-tRNA synthase monomer type: sample / ID: 1000 / Number unique components: 2 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: High affinity dynein microtubule binding domain
| Macromolecule | Name: High affinity dynein microtubule binding domain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Mus musculus (house mouse) / synonym: mouse Mus musculus (house mouse) / synonym: mouse |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
-Macromolecule #2: tubulin
| Macromolecule | Name: tubulin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Recombinant expression: No / Database: NCBI |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Bos taurus (cattle) Bos taurus (cattle) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 15 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 / Details: 50 mM Tris-HCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA, 1 mM DTT |
| Grid | Details: C-flat 2/2-2C holey carbon grids (Protochips) were glow-discharged for 20 seconds at 30 mA in an Edwards carbon evaporator. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 120 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV Method: The solution was blotted manually, and the process of addition and blotting of SRS-MTBD was repeated a total of three times. The final blotting was done inside the humidity chamber of a ...Method: The solution was blotted manually, and the process of addition and blotting of SRS-MTBD was repeated a total of three times. The final blotting was done inside the humidity chamber of a Vitrobot Mark IV (FEI) at 22 Celsius. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 120 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 63377 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.2 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 62000 Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.2 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 62000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN |
| Temperature | Average: 100 K |
| Date | Apr 10, 2011 |
| Image recording | Category: FILM / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM / Digitization - Scanner: OTHER / Digitization - Sampling interval: 6.35 µm / Number real images: 225 / Average electron dose: 15 e/Å2 / Bits/pixel: 8 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Details: each particle |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δz: 9.26 Å Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δ&Phi: 25.76 ° Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 9.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: Frealign |
| Details | Particles were aligned using customized scripts in SPIDER and 3D reconstruction was done using Frealign. |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - Chain ID: A |
|---|---|
| Software | Name:  Chimera Chimera |
| Details | Protocol: Rigid Body. The components of the complex were separately fitted by manual docking |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
| Output model |  PDB-3j1t:  PDB-3j1u: |
-Atomic model buiding 2
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - #0 - Chain ID: A / Chain - #1 - Chain ID: B |
|---|---|
| Software | Name:  Chimera Chimera |
| Details | Protocol: Rigid Body. The components of the complex were separately fitted by manual docking |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
| Output model |  PDB-3j1t:  PDB-3j1u: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller