[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
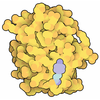
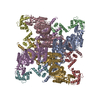
Yorodumi- PDB-5k7l: Single particle cryo-EM structure of the voltage-gated K+ channel... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5k7l | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Single particle cryo-EM structure of the voltage-gated K+ channel Eag1 bound to the channel inhibitor calmodulin | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | METAL TRANSPORT/CALCIUM BINDING PROTEIN /  Voltage-gated potassium channel / Voltage-gated potassium channel /  calmodulin / calmodulin /  Cryoelectron microscopy / Eag1 / METAL TRANSPORT-CALCIUM BINDING PROTEIN complex Cryoelectron microscopy / Eag1 / METAL TRANSPORT-CALCIUM BINDING PROTEIN complex | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationVoltage gated Potassium channels /  potassium channel complex / regulation of presynaptic cytosolic calcium ion concentration / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / : / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / establishment of protein localization to mitochondrial membrane / type 3 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synapse / potassium channel complex / regulation of presynaptic cytosolic calcium ion concentration / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / : / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / establishment of protein localization to mitochondrial membrane / type 3 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synapse /  CaM pathway ...Voltage gated Potassium channels / CaM pathway ...Voltage gated Potassium channels /  potassium channel complex / regulation of presynaptic cytosolic calcium ion concentration / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / : / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / establishment of protein localization to mitochondrial membrane / type 3 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synapse / potassium channel complex / regulation of presynaptic cytosolic calcium ion concentration / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / : / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / establishment of protein localization to mitochondrial membrane / type 3 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synapse /  CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / nuclear inner membrane / Calmodulin induced events / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / nuclear inner membrane / Calmodulin induced events / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis /  phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate binding / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / PKA activation / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / organelle localization by membrane tethering / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / autophagosome membrane docking / response to corticosterone / positive regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate binding / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / PKA activation / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / organelle localization by membrane tethering / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / autophagosome membrane docking / response to corticosterone / positive regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission /  nitric-oxide synthase binding / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / nitric-oxide synthase binding / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction /  startle response / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / negative regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / protein phosphatase activator activity / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / positive regulation of cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity / positive regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity / startle response / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / negative regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / protein phosphatase activator activity / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / positive regulation of cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity / positive regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity /  Long-term potentiation / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / Long-term potentiation / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins /  adenylate cyclase binding / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / adenylate cyclase binding / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity /  catalytic complex / DARPP-32 events / catalytic complex / DARPP-32 events /  axolemma / detection of calcium ion / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Smooth Muscle Contraction / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / calcium channel inhibitor activity / cellular response to interferon-beta / positive regulation of DNA binding / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / axolemma / detection of calcium ion / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Smooth Muscle Contraction / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / calcium channel inhibitor activity / cellular response to interferon-beta / positive regulation of DNA binding / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion /  Protein methylation / enzyme regulator activity / Protein methylation / enzyme regulator activity /  voltage-gated potassium channel complex / voltage-gated potassium channel complex /  phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / eNOS activation / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / positive regulation of protein dephosphorylation / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / eNOS activation / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / positive regulation of protein dephosphorylation /  titin binding / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / Ion homeostasis / positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation / potassium ion transmembrane transport / sperm midpiece / response to amphetamine / titin binding / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / Ion homeostasis / positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation / potassium ion transmembrane transport / sperm midpiece / response to amphetamine /  calcium channel complex / activation of adenylate cyclase activity / substantia nigra development / cellular response to calcium ion / adenylate cyclase activator activity / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor / calcium channel complex / activation of adenylate cyclase activity / substantia nigra development / cellular response to calcium ion / adenylate cyclase activator activity / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor /  regulation of membrane potential / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / regulation of membrane potential / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport /  regulation of heart rate / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / regulation of heart rate / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity /  sarcomere / FCERI mediated Ca+2 mobilization / FCGR3A-mediated IL10 synthesis / 14-3-3 protein binding / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / Antigen activates B Cell Receptor (BCR) leading to generation of second messengers sarcomere / FCERI mediated Ca+2 mobilization / FCGR3A-mediated IL10 synthesis / 14-3-3 protein binding / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / Antigen activates B Cell Receptor (BCR) leading to generation of second messengersSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.78 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.78 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Whicher, J.R. / MacKinnon, R. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2016 Journal: Science / Year: 2016Title: Structure of the voltage-gated K⁺ channel Eag1 reveals an alternative voltage sensing mechanism. Authors: Jonathan R Whicher / Roderick MacKinnon /  Abstract: Voltage-gated potassium (K(v)) channels are gated by the movement of the transmembrane voltage sensor, which is coupled, through the helical S4-S5 linker, to the potassium pore. We determined the ...Voltage-gated potassium (K(v)) channels are gated by the movement of the transmembrane voltage sensor, which is coupled, through the helical S4-S5 linker, to the potassium pore. We determined the single-particle cryo-electron microscopy structure of mammalian K(v)10.1, or Eag1, bound to the channel inhibitor calmodulin, at 3.78 angstrom resolution. Unlike previous K(v) structures, the S4-S5 linker of Eag1 is a five-residue loop and the transmembrane segments are not domain swapped, which suggest an alternative mechanism of voltage-dependent gating. Additionally, the structure and position of the S4-S5 linker allow calmodulin to bind to the intracellular domains and to close the potassium pore, independent of voltage-sensor position. The structure reveals an alternative gating mechanism for K(v) channels and provides a template to further understand the gating properties of Eag1 and related channels. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5k7l.cif.gz 5k7l.cif.gz | 171.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5k7l.ent.gz pdb5k7l.ent.gz | 130.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5k7l.json.gz 5k7l.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/k7/5k7l https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/k7/5k7l ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/k7/5k7l ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/k7/5k7l | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8215MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | 
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 | 
|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: (Schoenflies symbol : C4 (4 fold cyclic : C4 (4 fold cyclic )) )) |
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 97359.766 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: UNP residues 1-773, 888-962 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) / Gene: Kcnh1, Eag / Plasmid: pEG BacMam / Cell line (production host): HEK293 GnTI- / Production host: Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) / Gene: Kcnh1, Eag / Plasmid: pEG BacMam / Cell line (production host): HEK293 GnTI- / Production host:   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q63472 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q63472 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein |  / CaM / CaMMass: 16852.545 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: CALM1, CALM, CAM, CAM1, CALM2, CAM2, CAMB, CALM3, CALML2, CAM3, CAMC, CAMIII Plasmid: pEG BacMam / Cell line (production host): HEK293 GnTI- / Production host:   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P62158, UniProt: P0DP23*PLUS Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P62158, UniProt: P0DP23*PLUS |
| #3: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG /  N-Acetylglucosamine N-Acetylglucosamine |
| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-Y01 / |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 4 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 86 % / Details: Plunged into liquid ethane (FEI VITROBOT MARK IV) |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 1.8 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 1657 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: REFMAC / Version: 5.8.0088 / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 240000 Details: Particles were auto-picked and manually inspected in RELION. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C4 (4 fold cyclic : C4 (4 fold cyclic ) ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.78 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 145000 Details: 2D classification, 3D classification, and refinement were performed in RELION. Final map generation was performed in FREALIGN. Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: RECIPROCAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Resolution: 3.78→165 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.979 / SU B: 61.954 / SU ML: 0.725 / ESU R: 0.687 Stereochemistry target values: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD WITH PHASES Details: HYDROGENS HAVE BEEN ADDED IN THE RIDING POSITIONS
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Ion probe radii: 0.8 Å / Shrinkage radii: 0.8 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.2 Å / Solvent model: MASK | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 301.016 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj