[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-3ja6: Cryo-electron Tomography and All-atom Molecular Dynamics Simulati... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 3ja6 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
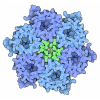
| Title | Cryo-electron Tomography and All-atom Molecular Dynamics Simulations Reveal a Novel Kinase Conformational Switch in Bacterial Chemotaxis Signaling | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  SIGNALING PROTEIN / bacterial chemotaxis / core-signaling unit / adaptor protein / SIGNALING PROTEIN / bacterial chemotaxis / core-signaling unit / adaptor protein /  histidine kinase / histidine kinase /  chemoreceptor chemoreceptor | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information histidine kinase / phosphorelay sensor kinase activity / histidine kinase / phosphorelay sensor kinase activity /  chemotaxis / transmembrane signaling receptor activity / protein domain specific binding / chemotaxis / transmembrane signaling receptor activity / protein domain specific binding /  signal transduction / signal transduction /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  plasma membrane / plasma membrane /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  electron tomography / electron tomography /  cryo EM / Resolution: 12.7 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 12.7 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Cassidy, C.K. / Himes, B.A. / Alvarez, F.J. / Ma, J. / Zhao, G. / Perilla, J.R. / Schulten, K. / Zhang, P. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2015 Journal: Elife / Year: 2015Title: CryoEM and computer simulations reveal a novel kinase conformational switch in bacterial chemotaxis signaling. Authors: C Keith Cassidy / Benjamin A Himes / Frances J Alvarez / Jun Ma / Gongpu Zhao / Juan R Perilla / Klaus Schulten / Peijun Zhang /  Abstract: Chemotactic responses in bacteria require large, highly ordered arrays of sensory proteins to mediate the signal transduction that ultimately controls cell motility. A mechanistic understanding of ...Chemotactic responses in bacteria require large, highly ordered arrays of sensory proteins to mediate the signal transduction that ultimately controls cell motility. A mechanistic understanding of the molecular events underlying signaling, however, has been hampered by the lack of a high-resolution structural description of the extended array. Here, we report a novel reconstitution of the array, involving the receptor signaling domain, histidine kinase CheA, and adaptor protein CheW, as well as a density map of the core-signaling unit at 11.3 Å resolution, obtained by cryo-electron tomography and sub-tomogram averaging. Extracting key structural constraints from our density map, we computationally construct and refine an atomic model of the core array structure, exposing novel interfaces between the component proteins. Using all-atom molecular dynamics simulations, we further reveal a distinctive conformational change in CheA. Mutagenesis and chemical cross-linking experiments confirm the importance of the conformational dynamics of CheA for chemotactic function. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  3ja6.cif.gz 3ja6.cif.gz | 1.5 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb3ja6.ent.gz pdb3ja6.ent.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  3ja6.json.gz 3ja6.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ja/3ja6 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ja/3ja6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ja/3ja6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ja/3ja6 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6319MC  3234C  6320C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein |  Mass: 15718.318 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Fragment: SEE REMARK 999 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Plasmid: PPA770 / Production host: Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Plasmid: PPA770 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): RP3098 / References: UniProt: Q56311*PLUS Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): RP3098 / References: UniProt: Q56311*PLUS#2: Protein |  Mass: 42489.328 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Fragment: dimerization domain, kinase domain, and regulatory domain (SEE REMARK 999) Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Plasmid: pKJ9 / Production host: Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Plasmid: pKJ9 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): RP3098 / References: UniProt: Q56310*PLUS Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): RP3098 / References: UniProt: Q56310*PLUS#3: Protein | Mass: 33398.828 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Fragment: cytoplasmic domain (SEE REMARK 999) Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Plasmid: pHTCF / Production host: Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Plasmid: pHTCF / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): RP3098 / References: UniProt: Q9X0M7*PLUS Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): RP3098 / References: UniProt: Q9X0M7*PLUS#4: Protein | Mass: 33225.594 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Fragment: cytoplasmic domain (SEE REMARK 999) Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Plasmid: pHTCF / Production host: Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Plasmid: pHTCF / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): RP3098 / References: UniProt: Q9X0M7*PLUS Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): RP3098 / References: UniProt: Q9X0M7*PLUSSequence details | THE IMAGED PROTEINS WERE FROM ESCHERICHI | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  electron tomography electron tomography |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 1.66 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | Name: 75 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2 / pH: 7.4 / Details: 75 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: Perforated R2/2 Quantifoil grids precoated with 10 nm fiducial gold beads on the backside of the grid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Cryogen name: ETHANE Details: Single-sided blotting (to avoid disruption of the monolayer) before plunging into liquid ethane Method: Single-sided blotting to avoid disruption of the monolayer |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI POLARA 300 / Date: Jan 7, 2009 |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 39000 X / Calibrated magnification: 49834 X / Nominal defocus max: 8000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 4000 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 39000 X / Calibrated magnification: 49834 X / Nominal defocus max: 8000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 4000 nm / Cs : 2 mm : 2 mm |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: OTHER / Specimen holder type: Polara cartridge / Tilt angle max: 70 ° / Tilt angle min: -70 ° |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN ULTRASCAN 4000 (4k x 4k) |
| Image scans | Num. digital images: 60 |
- Processing
Processing
CTF correction | Details: TomoCTF (strip-based periodogram) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C2 (2 fold cyclic : C2 (2 fold cyclic ) ) | ||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Method: SIRT Sirte / Resolution: 12.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 4000 / Nominal pixel size: 3.01 Å / Actual pixel size: 3.01 Å / Details: Gold-standard refinement / Refinement type: HALF-MAPS REFINED INDEPENDENTLY / Symmetry type: 2D CRYSTAL Sirte / Resolution: 12.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 4000 / Nominal pixel size: 3.01 Å / Actual pixel size: 3.01 Å / Details: Gold-standard refinement / Refinement type: HALF-MAPS REFINED INDEPENDENTLY / Symmetry type: 2D CRYSTAL | ||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL / Details: REFINEMENT PROTOCOL--FLEXIBLE | ||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 1QU7 Accession code: 1QU7 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj