[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-3j0j: Fitted atomic models of Thermus thermophilus V-ATPase subunits in... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 3j0j | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Fitted atomic models of Thermus thermophilus V-ATPase subunits into cryo-EM map | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  HYDROLASE / flexible fitting / rigid body fitting / HYDROLASE / flexible fitting / rigid body fitting /  membrane protein complex membrane protein complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, catalytic domain / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis /  H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  metal ion binding metal ion bindingSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 9.7 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 9.7 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Lau, W.C.Y. / Rubinstein, J.L. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2011 Journal: Nature / Year: 2011Title: Subnanometre-resolution structure of the intact Thermus thermophilus H+-driven ATP synthase. Authors: Wilson C Y Lau / John L Rubinstein /  Abstract: Ion-translocating rotary ATPases serve either as ATP synthases, using energy from a transmembrane ion motive force to create the cell's supply of ATP, or as transmembrane ion pumps that are powered ...Ion-translocating rotary ATPases serve either as ATP synthases, using energy from a transmembrane ion motive force to create the cell's supply of ATP, or as transmembrane ion pumps that are powered by ATP hydrolysis. The members of this family of enzymes each contain two rotary motors: one that couples ion translocation to rotation and one that couples rotation to ATP synthesis or hydrolysis. During ATP synthesis, ion translocation through the membrane-bound region of the complex causes rotation of a central rotor that drives conformational changes and ATP synthesis in the catalytic region of the complex. There are no structural models available for the intact membrane region of any ion-translocating rotary ATPase. Here we present a 9.7 Å resolution map of the H(+)-driven ATP synthase from Thermus thermophilus obtained by electron cryomicroscopy of single particles in ice. The 600-kilodalton complex has an overall subunit composition of A(3)B(3)CDE(2)FG(2)IL(12). The membrane-bound motor consists of a ring of L subunits and the carboxy-terminal region of subunit I, which are equivalent to the c and a subunits of most other rotary ATPases, respectively. The map shows that the ring contains 12 L subunits and that the I subunit has eight transmembrane helices. The L(12) ring and I subunit have a surprisingly small contact area in the middle of the membrane, with helices from the I subunit making contacts with two different L subunits. The transmembrane helices of subunit I form bundles that could serve as half-channels across the membrane, with the first half-channel conducting protons from the periplasm to the L(12) ring and the second half-channel conducting protons from the L(12) ring to the cytoplasm. This structure therefore suggests the mechanism by which a transmembrane proton motive force is converted to rotation in rotary ATPases. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  3j0j.cif.gz 3j0j.cif.gz | 594.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb3j0j.ent.gz pdb3j0j.ent.gz | 429.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  3j0j.json.gz 3j0j.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j0/3j0j https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j0/3j0j ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j0/3j0j ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j0/3j0j | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 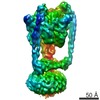 5335MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-V-type ATP synthase ... , 6 types, 11 molecules ABCDEFGHJLM
| #1: Protein | Mass: 63699.980 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579References: UniProt: Q56403,  H+-transporting two-sector ATPase H+-transporting two-sector ATPase#2: Protein | Mass: 53219.500 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / References: UniProt: Q56404 Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / References: UniProt: Q56404#3: Protein | | Mass: 24715.566 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / References: UniProt: O87880 Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / References: UniProt: O87880#4: Protein | | Mass: 11294.904 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / References: UniProt: P74903 Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / References: UniProt: P74903#6: Protein | Mass: 20699.693 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / References: UniProt: P74901 Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / References: UniProt: P74901#7: Protein | | Mass: 35968.570 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / References: UniProt: P74902 Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / References: UniProt: P74902 |
|---|
-Protein / Non-polymers , 2 types, 4 molecules IK

| #5: Protein | Mass: 11621.355 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / References: UniProt: Q5SIT5 Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / References: UniProt: Q5SIT5#8: Chemical |  Adenosine diphosphate Adenosine diphosphate |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer solution | Name: 50 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.02% DDM, pH 8.0 pH: 8 Details: 50 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.02% DDM, pH 8.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 2.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: Quantifoil R2/2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Details: Vitrification from 4 degree Celsius environment / Method: Blot 20 seconds before plunging |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F20 / Date: Jan 1, 2010 |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 50000 X / Calibrated magnification: 50000 X / Nominal defocus max: 4500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 2500 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 50000 X / Calibrated magnification: 50000 X / Nominal defocus max: 4500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 2500 nm / Cs : 2 mm : 2 mm |
| Specimen holder | Temperature: 100 K / Tilt angle max: 0 ° / Tilt angle min: 0 ° |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 0.18 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GENERIC FILM / Details: Scanned with Intergraph Photoscan densitometer |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Relative weight: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Details: Each particle | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Method: Fourier sinc interpolation (Build_fspace) / Resolution: 9.7 Å / Num. of particles: 46105 / Nominal pixel size: 1.4 Å / Actual pixel size: 1.4 Å Magnification calibration: Graphite imaging and Rosenthal apoferritin method (Publication In Preparation) Details: Frealign and new software used for refinement and reconstruction Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj






