[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-2bcw: Coordinates of the N-terminal domain of ribosomal protein L11,C-t... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 2bcw | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
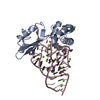
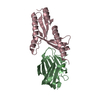
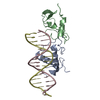
| Title | Coordinates of the N-terminal domain of ribosomal protein L11,C-terminal domain of ribosomal protein L7/L12 and a portion of the G' domain of elongation factor G, as fitted into cryo-em map of an Escherichia coli 70S*EF-G*GDP*fusidic acid complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  RIBOSOME / Components involved in interaction between EF-G AND L7/L12 stalk base of the ribosome RIBOSOME / Components involved in interaction between EF-G AND L7/L12 stalk base of the ribosome | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtranslational elongation /  translation elongation factor activity / GDP binding / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / translation elongation factor activity / GDP binding / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding /  ribosome binding / large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome binding / large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / structural constituent of ribosome /  translation ...translational elongation / translation ...translational elongation /  translation elongation factor activity / GDP binding / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / translation elongation factor activity / GDP binding / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding /  ribosome binding / large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome binding / large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / structural constituent of ribosome /  translation / translation /  mRNA binding / mRNA binding /  GTPase activity / GTP binding / magnesium ion binding / protein homodimerization activity / GTPase activity / GTP binding / magnesium ion binding / protein homodimerization activity /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |    Thermotoga maritima (bacteria) Thermotoga maritima (bacteria)  Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli)   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 11.2 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 11.2 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Datta, P.P. / Sharma, M.R. / Qi, L. / Frank, J. / Agrawal, R.K. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2005 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2005Title: Interaction of the G' domain of elongation factor G and the C-terminal domain of ribosomal protein L7/L12 during translocation as revealed by cryo-EM. Authors: Partha P Datta / Manjuli R Sharma / Li Qi / Joachim Frank / Rajendra K Agrawal /  Abstract: During tRNA translocation on the ribosome, an arc-like connection (ALC) is formed between the G' domain of elongation factor G (EF-G) and the L7/L12-stalk base of the large ribosomal subunit in the ...During tRNA translocation on the ribosome, an arc-like connection (ALC) is formed between the G' domain of elongation factor G (EF-G) and the L7/L12-stalk base of the large ribosomal subunit in the GDP state. To delineate the boundary of EF-G within the ALC, we tagged an amino acid residue near the tip of the G' domain of EF-G with undecagold, which was then visualized with three-dimensional cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). Two distinct positions for the undecagold, observed in the GTP-state and GDP-state cryo-EM maps of the ribosome bound EF-G, allowed us to determine the movement of the labeled amino acid. Molecular analyses of the cryo-EM maps show: (1) that three structural components, the N-terminal domain of ribosomal protein L11, the C-terminal domain of ribosomal protein L7/L12, and the G' domain of EF-G, participate in formation of the ALC; and (2) that both EF-G and the ribosomal protein L7/L12 undergo large conformational changes to form the ALC. #1:  Journal: Cell / Year: 1999 Journal: Cell / Year: 1999Title: A detailed view of a ribosomal active site: the structure of the L11-RNA complex. Authors: B T Wimberly / R Guymon / J P McCutcheon / S W White / V Ramakrishnan /  Abstract: We report the crystal structure of a 58 nucleotide fragment of 23S ribosomal RNA bound to ribosomal protein L11. This highly conserved ribonucleoprotein domain is the target for the thiostrepton ...We report the crystal structure of a 58 nucleotide fragment of 23S ribosomal RNA bound to ribosomal protein L11. This highly conserved ribonucleoprotein domain is the target for the thiostrepton family of antibiotics that disrupt elongation factor function. The highly compact RNA has both familiar and novel structural motifs. While the C-terminal domain of L11 binds RNA tightly, the N-terminal domain makes only limited contacts with RNA and is proposed to function as a switch that reversibly associates with an adjacent region of RNA. The sites of mutations conferring resistance to thiostrepton and micrococcin line a narrow cleft between the RNA and the N-terminal domain. These antibiotics are proposed to bind in this cleft, locking the putative switch and interfering with the function of elongation factors. #2:  Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 1987 Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 1987Title: Structure of the C-terminal domain of the ribosomal protein L7/L12 from Escherichia coli at 1.7 A. Authors: M Leijonmarck / A Liljas /  Abstract: The structure of a C-terminal fragment of the ribosomal protein L7/L12 from Escherichia coli has been refined using crystallographic data to 1.7 A resolution. The R-value is 17.4%. Six residues at ...The structure of a C-terminal fragment of the ribosomal protein L7/L12 from Escherichia coli has been refined using crystallographic data to 1.7 A resolution. The R-value is 17.4%. Six residues at the N terminus are too disordered in the structure to be localized. These residues are probably part of a hinge in the complete L7/L12 molecule. The possibility that a 2-fold crystallographic axis is a molecular 2-fold axis is discussed. A patch of invariant residues on the surface of the dimer is probably involved in functional interactions with elongation factors. #3:  Journal: EMBO J / Year: 1994 Journal: EMBO J / Year: 1994Title: Three-dimensional structure of the ribosomal translocase: elongation factor G from Thermus thermophilus. Authors: A AEvarsson / E Brazhnikov / M Garber / J Zheltonosova / Y Chirgadze / S al-Karadaghi / L A Svensson / A Liljas /  Abstract: The crystal structure of Thermus thermophilus elongation factor G without guanine nucleotide was determined to 2.85 A. This GTPase has five domains with overall dimensions of 50 x 60 x 118 A. The GTP ...The crystal structure of Thermus thermophilus elongation factor G without guanine nucleotide was determined to 2.85 A. This GTPase has five domains with overall dimensions of 50 x 60 x 118 A. The GTP binding domain has a core common to other GTPases with a unique subdomain which probably functions as an intrinsic nucleotide exchange factor. Domains I and II are homologous to elongation factor Tu and their arrangement, both with and without GDP, is more similar to elongation factor Tu in complex with a GTP analogue than with GDP. Domains III and V show structural similarities to ribosomal proteins. Domain IV protrudes from the main body of the protein and has an extraordinary topology with a left-handed cross-over connection between two parallel beta-strands. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  2bcw.cif.gz 2bcw.cif.gz | 18.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb2bcw.ent.gz pdb2bcw.ent.gz | 7.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  2bcw.json.gz 2bcw.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bc/2bcw https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bc/2bcw ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bc/2bcw ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bc/2bcw | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein |  / Coordinate model: Cα atoms only / Coordinate model: Cα atoms onlyMass: 7021.266 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: N-terminal domain / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermotoga maritima (bacteria) / References: UniProt: P29395 Thermotoga maritima (bacteria) / References: UniProt: P29395 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein |  Ribosome / L8 / Coordinate model: Cα atoms only Ribosome / L8 / Coordinate model: Cα atoms onlyMass: 6942.973 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: C-terminal domain / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P0A7K2 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P0A7K2 |
| #3: Protein |  EF-G / EF-G / Coordinate model: Cα atoms only EF-G / EF-G / Coordinate model: Cα atoms onlyMass: 6710.497 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: A portion of G' domain' / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / References: UniProt: P13551 Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / References: UniProt: P13551 |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer solution | Name: 20mM HEPES-KOH (pH 7.5), 6mM MgCl2, and 150 mM NH4Cl, 2mM spermidine, 0.4 mM spermine pH: 7.5 Details: 20mM HEPES-KOH (pH 7.5), 6mM MgCl2, and 150 mM NH4Cl, 2mM spermidine, 0.4 mM spermine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.03 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: QUANTIFOIL HOLEY CARBON FILM GRIDS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Details: RAPID-FREEZING IN LIQUID ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F20 / Date: Nov 9, 2004 |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 50000 X / Calibrated magnification: 50760 X / Nominal defocus max: -3.5 nm / Nominal defocus min: -0.7 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 50000 X / Calibrated magnification: 50760 X / Nominal defocus max: -3.5 nm / Nominal defocus min: -0.7 nm / Cs : 2 mm : 2 mm |
| Specimen holder | Temperature: 93 K / Tilt angle max: 0 ° / Tilt angle min: 0 ° |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 20 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Relative weight: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Details: CTF CORRECTION OF 3D MAPS BY WIENER FILTRATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Method: REFERENCE BASED ALIGNMENT / Resolution: 11.2 Å / Actual pixel size: 2.76 Å / Magnification calibration: TMV / Details: PROJECTION MATCHING USING SPIDER PACKAGE / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL Target criteria: The X-ray crystallographic structure of the EF-G individual domains were fitted into the cryo-EM map of the 70S*EF-G-UG*GDP*Fusidic acid complex using O. The G' domain within domain ...Target criteria: The X-ray crystallographic structure of the EF-G individual domains were fitted into the cryo-EM map of the 70S*EF-G-UG*GDP*Fusidic acid complex using O. The G' domain within domain I was separately fitted, using a combination of manual rigid-body docking and flexible docking approaches, and taking into consideration both the cryo-EM envelope and the positional constraints imposed by the UG density. X-ray crystallographic structures of the N-terminal domain of protein L11 and C-terminal domain of protein L7/L12 were fitted as rigid bodies. Details: METHOD--A COMBINATION OF MANUAL RIGID-BODY DOCKING AND FLEXIBLE DOCKING REFINEMENT PROTOCOL--A COMBINATION OF MANUAL RIGID-BODY DOCKING AND FLEXIBLE DOCKING | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 PDBj
PDBj








