[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-8246: Structural model of 53BP1 bound to a ubiquitylated and methylated... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-8246 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
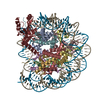
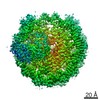
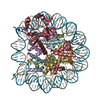
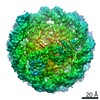
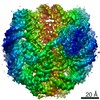
| Title | Structural model of 53BP1 bound to a ubiquitylated and methylated nucleosome, at 4.5 A resolution | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | 53BP1 bound to a ubiquitylated and methylated nucleosome | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationubiquitin-modified histone reader activity / positive regulation of isotype switching / cellular response to X-ray / double-strand break repair via classical nonhomologous end joining /  DNA repair complex / hypothalamus gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neuron development / female meiosis I / positive regulation of protein monoubiquitination / mitochondrion transport along microtubule / fat pad development ...ubiquitin-modified histone reader activity / positive regulation of isotype switching / cellular response to X-ray / double-strand break repair via classical nonhomologous end joining / DNA repair complex / hypothalamus gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neuron development / female meiosis I / positive regulation of protein monoubiquitination / mitochondrion transport along microtubule / fat pad development ...ubiquitin-modified histone reader activity / positive regulation of isotype switching / cellular response to X-ray / double-strand break repair via classical nonhomologous end joining /  DNA repair complex / hypothalamus gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neuron development / female meiosis I / positive regulation of protein monoubiquitination / mitochondrion transport along microtubule / fat pad development / negative regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / telomeric DNA binding / female gonad development / seminiferous tubule development / male meiosis I / SUMOylation of transcription factors / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / DNA repair complex / hypothalamus gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neuron development / female meiosis I / positive regulation of protein monoubiquitination / mitochondrion transport along microtubule / fat pad development / negative regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / telomeric DNA binding / female gonad development / seminiferous tubule development / male meiosis I / SUMOylation of transcription factors / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus /  energy homeostasis / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / regulation of neuron apoptotic process / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Maturation of protein E / Maturation of protein E / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Myoclonic epilepsy of Lafora / FLT3 signaling by CBL mutants / Prevention of phagosomal-lysosomal fusion / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex / Alpha-protein kinase 1 signaling pathway / energy homeostasis / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / regulation of neuron apoptotic process / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Maturation of protein E / Maturation of protein E / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Myoclonic epilepsy of Lafora / FLT3 signaling by CBL mutants / Prevention of phagosomal-lysosomal fusion / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex / Alpha-protein kinase 1 signaling pathway /  Glycogen synthesis / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Membrane binding and targetting of GAG proteins / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants / NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / PTK6 Regulates RTKs and Their Effectors AKT1 and DOK1 / Negative regulation of FLT3 / TICAM1,TRAF6-dependent induction of TAK1 complex / TICAM1-dependent activation of IRF3/IRF7 / methylated histone binding / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Meiotic synapsis / Downregulation of ERBB4 signaling / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation in TLR7/8 or 9 signaling / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / PINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / TRAF6-mediated induction of TAK1 complex within TLR4 complex / InlA-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cells / Pexophagy / Regulation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA / VLDLR internalisation and degradation / histone reader activity / Downregulation of ERBB2:ERBB3 signaling / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Regulation of PTEN localization / Translesion synthesis by POLK / Glycogen synthesis / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Membrane binding and targetting of GAG proteins / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants / NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / PTK6 Regulates RTKs and Their Effectors AKT1 and DOK1 / Negative regulation of FLT3 / TICAM1,TRAF6-dependent induction of TAK1 complex / TICAM1-dependent activation of IRF3/IRF7 / methylated histone binding / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Meiotic synapsis / Downregulation of ERBB4 signaling / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation in TLR7/8 or 9 signaling / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / PINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / TRAF6-mediated induction of TAK1 complex within TLR4 complex / InlA-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cells / Pexophagy / Regulation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA / VLDLR internalisation and degradation / histone reader activity / Downregulation of ERBB2:ERBB3 signaling / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Regulation of PTEN localization / Translesion synthesis by POLK /  Regulation of BACH1 activity / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / MAP3K8 (TPL2)-dependent MAPK1/3 activation / TICAM1, RIP1-mediated IKK complex recruitment / Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling / Josephin domain DUBs / Activation of IRF3, IRF7 mediated by TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE) / Regulation of BACH1 activity / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / MAP3K8 (TPL2)-dependent MAPK1/3 activation / TICAM1, RIP1-mediated IKK complex recruitment / Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling / Josephin domain DUBs / Activation of IRF3, IRF7 mediated by TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE) /  DNA methylation / Regulation of activated PAK-2p34 by proteasome mediated degradation / InlB-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cell / IKK complex recruitment mediated by RIP1 / JNK (c-Jun kinases) phosphorylation and activation mediated by activated human TAK1 / neuron projection morphogenesis / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential / TGF-beta receptor signaling in EMT (epithelial to mesenchymal transition) / HCMV Late Events / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / DNA methylation / Regulation of activated PAK-2p34 by proteasome mediated degradation / InlB-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cell / IKK complex recruitment mediated by RIP1 / JNK (c-Jun kinases) phosphorylation and activation mediated by activated human TAK1 / neuron projection morphogenesis / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential / TGF-beta receptor signaling in EMT (epithelial to mesenchymal transition) / HCMV Late Events / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) /  replication fork / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / replication fork / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C /  innate immune response in mucosa / TNFR1-induced NF-kappa-B signaling pathway / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA innate immune response in mucosa / TNFR1-induced NF-kappa-B signaling pathway / PRC2 methylates histones and DNASimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species | unclassified (unknown) / synthetic construct (others) /   Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) | ||||||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 4.54 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 4.54 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Benlekbir S / Wilson MD / Sicheri F / Rubinstein JL / Durocher D | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 3 items Canada, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2016 Journal: Nature / Year: 2016Title: The structural basis of modified nucleosome recognition by 53BP1. Abstract: DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) elicit a histone modification cascade that controls DNA repair. This pathway involves the sequential ubiquitination of histones H1 and H2A by the E3 ubiquitin ligases ...DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) elicit a histone modification cascade that controls DNA repair. This pathway involves the sequential ubiquitination of histones H1 and H2A by the E3 ubiquitin ligases RNF8 and RNF168, respectively. RNF168 ubiquitinates H2A on lysine 13 and lysine 15 (refs 7, 8) (yielding H2AK13ub and H2AK15ub, respectively), an event that triggers the recruitment of 53BP1 (also known as TP53BP1) to chromatin flanking DSBs. 53BP1 binds specifically to H2AK15ub-containing nucleosomes through a peptide segment termed the ubiquitination-dependent recruitment motif (UDR), which requires the simultaneous engagement of histone H4 lysine 20 dimethylation (H4K20me2) by its tandem Tudor domain. How 53BP1 interacts with these two histone marks in the nucleosomal context, how it recognizes ubiquitin, and how it discriminates between H2AK13ub and H2AK15ub is unknown. Here we present the electron cryomicroscopy (cryo-EM) structure of a dimerized human 53BP1 fragment bound to a H4K20me2-containing and H2AK15ub-containing nucleosome core particle (NCP-ubme) at 4.5 Å resolution. The structure reveals that H4K20me2 and H2AK15ub recognition involves intimate contacts with multiple nucleosomal elements including the acidic patch. Ubiquitin recognition by 53BP1 is unusual and involves the sandwiching of the UDR segment between ubiquitin and the NCP surface. The selectivity for H2AK15ub is imparted by two arginine fingers in the H2A amino-terminal tail, which straddle the nucleosomal DNA and serve to position ubiquitin over the NCP-bound UDR segment. The structure of the complex between NCP-ubme and 53BP1 reveals the basis of 53BP1 recruitment to DSB sites and illuminates how combinations of histone marks and nucleosomal elements cooperate to produce highly specific chromatin responses, such as those elicited following chromosome breaks. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_8246.map.gz emd_8246.map.gz | 7.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-8246-v30.xml emd-8246-v30.xml emd-8246.xml emd-8246.xml | 34.2 KB 34.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_8246_fsc.xml emd_8246_fsc.xml | 4.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_8246.png emd_8246.png | 84.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8246 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8246 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8246 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8246 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5kgfMC 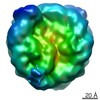 8247C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_8246.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_8246.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | 53BP1 bound to a ubiquitylated and methylated nucleosome | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.45 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : NCP-ubme/GST-53BP1 complex
+Supramolecule #1: NCP-ubme/GST-53BP1 complex
+Supramolecule #2: NCP-ubme
+Supramolecule #3: Widom-601 DNA
+Supramolecule #4: GST-53BP1
+Supramolecule #5: Ubiquitylated methylated histone octamer
+Supramolecule #6: Histone H4kc20Me2
+Supramolecule #7: Histone H3
+Supramolecule #8: Histone H2B.1
+Supramolecule #9: Histone H2A.1 K13RK36R
+Supramolecule #10: Ubiquitin
+Macromolecule #1: Histone H3.2
+Macromolecule #2: Histone H4
+Macromolecule #3: Histone H2A type 1
+Macromolecule #4: Histone H2B type 1-C/E/F/G/I
+Macromolecule #7: Tumor suppressor p53-binding protein 1
+Macromolecule #8: Ubiquitin
+Macromolecule #5: DNA (145-MER)
+Macromolecule #6: DNA (145-MER)
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.6 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
Details: High concentration NCP-ubme/GST-53BP1 complex at 200 mM salt was diluted just prior to grid freezing. | |||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: electron micrsocopy sciences / Material: COPPER/RHODIUM / Mesh: 400 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Support film - Film thickness: 20.0 nm / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Pretreatment - Pressure: 0.039 kPa | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III Details: Plunged into liquid ethane-propane (FEI VITROBOT MARK III). |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 30.0 µm / Calibrated magnification: 34483 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal magnification: 25000 Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal magnification: 25000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: GATAN 626 SINGLE TILT LIQUID NITROGEN CRYO TRANSFER HOLDER Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-30 / Number grids imaged: 2 / Number real images: 319 / Average exposure time: 0.5 sec. / Average electron dose: 36.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Details | The atomic models of Widom-601 DNA (PDB ID 3LZ0), octameric histones (PDB ID 1KX5), ubiquitin (PDB ID 1UBI), and H4K20me2/53BP1 tandem Tudor domain (PDB ID 2IG0) were fitted without allowing flexibility into the 3D maps using UCSF Chimera. Segmentation was performed in UCSF Chimera. For the NCP-ubme structure the ubiquitin segmentation was further modified to remove obvious NCP density from the ubiquitin segment. The H2A/H2B sequence was mutated to the human H2AK13R/K36R and H2B manually in UCSF Chimera. A polyalanine model of the UDR was built within the UDR density in Coot, which compared well to predicted structures generated by Rosetta. The UDR model was mutated and fitted using UCSF Chimera, followed by iterative rounds of real-space refinement in PHENIX and model optimization in Coot. All figures were prepared in UCSF Chimera. |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Overall B value: 207.5 |
| Output model |  PDB-5kgf: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)
























