[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-6188: High-resolution structures of kinesin on microtubules provide a b... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-6188 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | High-resolution structures of kinesin on microtubules provide a basis for nucleotide-gated force generation | |||||||||
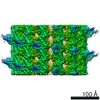
 Map data Map data | Microtubule decorated with monomeric human kinesin (K349 construct) having ADP aluminum fluoride complex bound in the nucleotide pocket. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcytoplasm organization / cytolytic granule membrane / plus-end-directed vesicle transport along microtubule / anterograde neuronal dense core vesicle transport / anterograde dendritic transport of neurotransmitter receptor complex / mitocytosis / retrograde neuronal dense core vesicle transport / anterograde axonal protein transport / vesicle transport along microtubule / lysosome localization ...cytoplasm organization / cytolytic granule membrane / plus-end-directed vesicle transport along microtubule / anterograde neuronal dense core vesicle transport / anterograde dendritic transport of neurotransmitter receptor complex / mitocytosis / retrograde neuronal dense core vesicle transport / anterograde axonal protein transport / vesicle transport along microtubule / lysosome localization / positive regulation of potassium ion transport / natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Hedgehog 'off' state /  Cilium Assembly / Cilium Assembly /  Intraflagellar transport / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / RHOH GTPase cycle / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Kinesins / PKR-mediated signaling / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / Kinesins / Separation of Sister Chromatids / The role of GTSE1 in G2/M progression after G2 checkpoint / Aggrephagy / plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / RHO GTPases activate KTN1 / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / MHC class II antigen presentation / stress granule disassembly / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / mitochondrion transport along microtubule / Intraflagellar transport / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / RHOH GTPase cycle / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Kinesins / PKR-mediated signaling / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / Kinesins / Separation of Sister Chromatids / The role of GTSE1 in G2/M progression after G2 checkpoint / Aggrephagy / plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / RHO GTPases activate KTN1 / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / MHC class II antigen presentation / stress granule disassembly / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / mitochondrion transport along microtubule /  ciliary rootlet / centrosome localization / ciliary rootlet / centrosome localization /  kinesin complex / synaptic vesicle transport / kinesin complex / synaptic vesicle transport /  microtubule motor activity / microtubule-based movement / Insulin processing / centriolar satellite / Signaling by ALK fusions and activated point mutants / Nuclear events stimulated by ALK signaling in cancer / microtubule-based process / phagocytic vesicle / axon cytoplasm / MHC class II antigen presentation / dendrite cytoplasm / microtubule motor activity / microtubule-based movement / Insulin processing / centriolar satellite / Signaling by ALK fusions and activated point mutants / Nuclear events stimulated by ALK signaling in cancer / microtubule-based process / phagocytic vesicle / axon cytoplasm / MHC class II antigen presentation / dendrite cytoplasm /  regulation of membrane potential / regulation of membrane potential /  axon guidance / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, GABAergic / positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / axon guidance / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, GABAergic / positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane /  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / cellular response to type II interferon / microtubule cytoskeleton / mitotic cell cycle / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / cellular response to type II interferon / microtubule cytoskeleton / mitotic cell cycle /  microtubule binding / vesicle / microtubule binding / vesicle /  microtubule / microtubule /  cadherin binding / cadherin binding /  GTPase activity / protein-containing complex binding / GTP binding / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / GTPase activity / protein-containing complex binding / GTP binding / perinuclear region of cytoplasm /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  mitochondrion / mitochondrion /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  membrane / identical protein binding / membrane / identical protein binding /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /   Sus scrofa (pig) Sus scrofa (pig) | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 5.0 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 5.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Shang ZG / Zhou KF / Xu C / Csencsits R / Cochran JC / Sindelar CV | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2014 Journal: Elife / Year: 2014Title: High-resolution structures of kinesin on microtubules provide a basis for nucleotide-gated force-generation. Authors: Zhiguo Shang / Kaifeng Zhou / Chen Xu / Roseann Csencsits / Jared C Cochran / Charles V Sindelar /  Abstract: Microtubule-based transport by the kinesin motors, powered by ATP hydrolysis, is essential for a wide range of vital processes in eukaryotes. We obtained insight into this process by developing ...Microtubule-based transport by the kinesin motors, powered by ATP hydrolysis, is essential for a wide range of vital processes in eukaryotes. We obtained insight into this process by developing atomic models for no-nucleotide and ATP states of the monomeric kinesin motor domain on microtubules from cryo-EM reconstructions at 5-6 Å resolution. By comparing these models with existing X-ray structures of ADP-bound kinesin, we infer a mechanistic scheme in which microtubule attachment, mediated by a universally conserved 'linchpin' residue in kinesin (N255), triggers a clamshell opening of the nucleotide cleft and accompanying release of ADP. Binding of ATP re-closes the cleft in a manner that tightly couples to translocation of cargo, via kinesin's 'neck linker' element. These structural transitions are reminiscent of the analogous nucleotide-exchange steps in the myosin and F1-ATPase motors and inform how the two heads of a kinesin dimer 'gate' each other to promote coordinated stepping along microtubules. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_6188.map.gz emd_6188.map.gz | 12.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-6188-v30.xml emd-6188-v30.xml emd-6188.xml emd-6188.xml | 12.5 KB 12.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  400_6188.gif 400_6188.gif 80_6188.gif 80_6188.gif | 86.1 KB 5.3 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6188 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6188 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6188 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6188 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3j8yMC  6187C  3j8xC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_6188.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 34.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_6188.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 34.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Microtubule decorated with monomeric human kinesin (K349 construct) having ADP aluminum fluoride complex bound in the nucleotide pocket. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.097 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Microtubule decorated with monomeric human kinesin (K349 construc...
| Entire | Name: Microtubule decorated with monomeric human kinesin (K349 construct) having ADP aluminum fluoride complex bound in the nucleotide pocket. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Microtubule decorated with monomeric human kinesin (K349 construc...
| Supramolecule | Name: Microtubule decorated with monomeric human kinesin (K349 construct) having ADP aluminum fluoride complex bound in the nucleotide pocket. type: sample / ID: 1000 / Details: Microtubule decorated with monomeric human kinesin Oligomeric state: One monomer of kinesin binds to one heterodimer of tubulin Number unique components: 2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 135 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: monomeric kinesin-1A
| Macromolecule | Name: monomeric kinesin-1A / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Details: K349 / Number of copies: 1 / Oligomeric state: monomer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: human Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: human |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 38 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Recombinant strain: BL21(DE3) / Recombinant plasmid: pHB40p Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Recombinant strain: BL21(DE3) / Recombinant plasmid: pHB40p |
| Sequence | UniProtKB:  Kinesin-1 heavy chain Kinesin-1 heavy chain |
-Macromolecule #2: tubulin
| Macromolecule | Name: tubulin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Oligomeric state: heterodimer / Recombinant expression: No / Database: NCBI |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Sus scrofa (pig) / synonym: pig Sus scrofa (pig) / synonym: pig |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 6.8 / Details: 25 mM PIPES, 25 mM NaCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA |
|---|---|
| Grid | Details: 300 mesh copper grid with homemade holey carbon |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER Method: No glow discharged applied; after sample application to grid, liquid was mostly 'wicked' away by edgewise application of filter paper. Subsequently, blotting and plunge freezing were ...Method: No glow discharged applied; after sample application to grid, liquid was mostly 'wicked' away by edgewise application of filter paper. Subsequently, blotting and plunge freezing were performed with a ~0.5 second delay after blotting but prior to plunging. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 23859.4 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN |
| Details | 4K x 4K counting mode was used; 24 frames total were collected. |
| Date | Jun 2, 2013 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: GATAN ULTRASCAN 4000 (4k x 4k) / Number real images: 51 / Average electron dose: 15 e/Å2 Details: Each image was collected as a stack of 24 movie frames. |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Details: done within FREALIGN |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δz: 9.455 Å Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δ&Phi: 25.71 ° Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Axial symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 5.0 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: SPIDER, FREALIGN Details: Approximately 33,600 asymmetric units were averaged in the final reconstruction. |
| Details | Initial alignment was done using customized SPIDER scripts. Reconstruction and subsequent refinement were done by FREALIGN. |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - #0 - Chain ID: K / Chain - #1 - Chain ID: A / Chain - #2 - Chain ID: B |
|---|---|
| Software | Name: MDFF |
| Details | MDFF was performed using explicit solvation. Side chains were removed from the MDFF target potential. Following several equilibration steps, the relative strength of the EM map potential (GSCALE term) was slowly increased from 0 to 1 over the course of 10 nanoseconds. The t = 1.2 ns time point was selected to represent the final fitted model, based on the approximate convergence of the RMSD from the starting structure. |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT Target criteria: RMSD from the starting structure was monitored for convergence |
| Output model |  PDB-3j8y: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller