+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-2161 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the yeast F1Fo-ATP synthase dimer | |||||||||
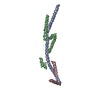
 Map data Map data | Subtomgram average of Yeast ATP synthase dimers in mitochondrial membranes | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  Mitochondria / Subtomogram average Mitochondria / Subtomogram average | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase, central stalk / Formation of ATP by chemiosmotic coupling / Cristae formation / mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase, catalytic core / mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase, stator stalk / mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, coupling factor F(o) / mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, catalytic sector F(1) / mitochondrial nucleoid / proton motive force-driven mitochondrial ATP synthesis ...mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase, central stalk / Formation of ATP by chemiosmotic coupling / Cristae formation / mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase, catalytic core / mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase, stator stalk / mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, coupling factor F(o) / mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, catalytic sector F(1) / mitochondrial nucleoid / proton motive force-driven mitochondrial ATP synthesis / proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis / proton transmembrane transporter activity / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, catalytic core F(1) /  H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism /  ADP binding / ADP binding /  mitochondrial intermembrane space / mitochondrial intermembrane space /  mitochondrial inner membrane / mitochondrial inner membrane /  lipid binding / lipid binding /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  mitochondrion / mitochondrion /  ATP binding / identical protein binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding /  plasma membrane / plasma membrane /  cytosol cytosolSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Saccharomyces cerevisiae W303 (yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae W303 (yeast) | |||||||||
| Method | subtomogram averaging /  cryo EM / Resolution: 37.0 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 37.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Davies KM / Kuehlbrandt W | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2012 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2012Title: Structure of the yeast F1Fo-ATP synthase dimer and its role in shaping the mitochondrial cristae. Authors: Karen M Davies / Claudio Anselmi / Ilka Wittig / José D Faraldo-Gómez / Werner Kühlbrandt /  Abstract: We used electron cryotomography of mitochondrial membranes from wild-type and mutant Saccharomyces cerevisiae to investigate the structure and organization of ATP synthase dimers in situ. Subtomogram ...We used electron cryotomography of mitochondrial membranes from wild-type and mutant Saccharomyces cerevisiae to investigate the structure and organization of ATP synthase dimers in situ. Subtomogram averaging of the dimers to 3.7 nm resolution revealed a V-shaped structure of twofold symmetry, with an angle of 86° between monomers. The central and peripheral stalks are well resolved. The monomers interact within the membrane at the base of the peripheral stalks. In wild-type mitochondria ATP synthase dimers are found in rows along the highly curved cristae ridges, and appear to be crucial for membrane morphology. Strains deficient in the dimer-specific subunits e and g or the first transmembrane helix of subunit 4 lack both dimers and lamellar cristae. Instead, cristae are either absent or balloon-shaped, with ATP synthase monomers distributed randomly in the membrane. Computer simulations indicate that isolated dimers induce a plastic deformation in the lipid bilayer, which is partially relieved by their side-by-side association. We propose that the assembly of ATP synthase dimer rows is driven by the reduction in the membrane elastic energy, rather than by direct protein contacts, and that the dimer rows enable the formation of highly curved ridges in mitochondrial cristae. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_2161.map.gz emd_2161.map.gz | 538.9 KB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-2161-v30.xml emd-2161-v30.xml emd-2161.xml emd-2161.xml | 14.1 KB 14.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  EMD-2161.png EMD-2161.png emd_2161.png emd_2161.png | 1.1 MB 1.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2161 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2161 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2161 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2161 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  4b2qMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_2161.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 619.1 KB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_2161.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 619.1 KB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Subtomgram average of Yeast ATP synthase dimers in mitochondrial membranes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 5.76 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : ATP synthase dimer from mitochondria of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
| Entire | Name: ATP synthase dimer from mitochondria of Saccharomyces cerevisiae |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: ATP synthase dimer from mitochondria of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
| Supramolecule | Name: ATP synthase dimer from mitochondria of Saccharomyces cerevisiae type: sample / ID: 1000 Details: Average of subvolumes extracted from tomograms of mitochondrial membrane fragments Number unique components: 1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.2 MDa |
-Supramolecule #1: F1Fo-ATP synthase
| Supramolecule | Name: F1Fo-ATP synthase / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Recombinant expression: No / Database: NCBI |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae W303 (yeast) / Strain: W303 / Organelle: Mitochondria / Location in cell: Cristae membranes Saccharomyces cerevisiae W303 (yeast) / Strain: W303 / Organelle: Mitochondria / Location in cell: Cristae membranes |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.2 MDa |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | subtomogram averaging |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 / Details: 250mM Trehalose, 10nm Tris-HCl pH7.4 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Details: 300 mesh copper grid with quantifoil support film (R2/2), glow discharged |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber temperature: 100 K / Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Method: Single side manual blotting for 5 seconds. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI POLARA 300 |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 24500 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2 mm / Nominal defocus max: 7.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 7.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 41000 Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2 mm / Nominal defocus max: 7.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 7.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 41000 |
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Tridiem 863 / Energy filter - Lower energy threshold: 0.0 eV / Energy filter - Upper energy threshold: 20.0 eV |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: OTHER / Tilt series - Axis1 - Min angle: -50 ° / Tilt series - Axis1 - Max angle: 60 ° |
| Temperature | Average: 80 K |
| Alignment procedure | Legacy - Astigmatism: Standard procedure |
| Date | Mar 11, 2009 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: GATAN ULTRASCAN 1000 (2k x 2k) / Average electron dose: 160 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 37.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name:  IMOD / Details: Final map calculated from 121 subvolumes IMOD / Details: Final map calculated from 121 subvolumes |
|---|---|
| Details | Tomogram reconstruction performed in IMOD. Average number of tilts used in the 3D reconstructions: 75. Average tomographic tilt angle increment: 1.5. |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - #0 - Chain ID: A / Chain - #1 - Chain ID: B / Chain - #2 - Chain ID: C / Chain - #3 - Chain ID: D / Chain - #4 - Chain ID: E / Chain - #5 - Chain ID: F / Chain - #6 - Chain ID: G / Chain - #7 - Chain ID: H / Chain - #8 - Chain ID: I / Chain - #9 - Chain ID: J / Chain - #10 - Chain ID: K / Chain - #11 - Chain ID: L / Chain - #12 - Chain ID: M / Chain - #13 - Chain ID: N / Chain - #14 - Chain ID: O / Chain - #15 - Chain ID: P / Chain - #16 - Chain ID: Q / Chain - #17 - Chain ID: R / Chain - #18 - Chain ID: S |
|---|---|
| Software | Name:  Chimera Chimera |
| Details | Protocol: Rigid body |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
| Output model |  PDB-4b2q: |
-Atomic model buiding 2
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - #0 - Chain ID: A / Chain - #1 - Chain ID: B / Chain - #2 - Chain ID: C |
|---|---|
| Software | Name:  Chimera Chimera |
| Details | Protocol: Rigid body with sequential fit command. Chain A extended using residues 180-207 of chain T from 2WSS |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
| Output model |  PDB-4b2q: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller