[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-1263: Following the signal sequence from ribosomal tunnel exit to signa... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-1263 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
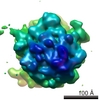
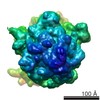
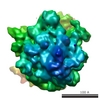
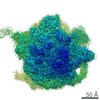
| Title | Following the signal sequence from ribosomal tunnel exit to signal recognition particle. | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | w | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationabsorption of visible light / G protein-coupled opsin signaling pathway / signal recognition particle / photoreceptor inner segment membrane / 11-cis retinal binding / G protein-coupled photoreceptor activity / signal-recognition-particle GTPase / 7S RNA binding / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / protein targeting to membrane ...absorption of visible light / G protein-coupled opsin signaling pathway / signal recognition particle / photoreceptor inner segment membrane / 11-cis retinal binding / G protein-coupled photoreceptor activity / signal-recognition-particle GTPase / 7S RNA binding / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / protein targeting to membrane / negative regulation of cytoplasmic translational initiation / photoreceptor outer segment membrane / stringent response / transcriptional attenuation / endoribonuclease inhibitor activity / RNA-binding transcription regulator activity / positive regulation of ribosome biogenesis / negative regulation of cytoplasmic translation / translational termination / DnaA-L2 complex / translation repressor activity / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / visual perception / mRNA regulatory element binding translation repressor activity / ribosome assembly / assembly of large subunit precursor of preribosome / cytosolic ribosome assembly / ribosomal large subunit assembly / response to reactive oxygen species / translational initiation / regulation of cell growth / DNA-templated transcription termination / response to radiation / mRNA 5'-UTR binding / photoreceptor disc membrane / large ribosomal subunit / ribosome binding / transferase activity / 5S rRNA binding / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / tRNA binding / rRNA binding / negative regulation of translation / ribosome / structural constituent of ribosome / translation / ribonucleoprotein complex / response to antibiotic / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / GTPase activity / mRNA binding / GTP binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / DNA binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / membrane / metal ion binding / plasma membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 9.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Halic M / Blau M / Becker T / Mielke T / Pool MR / Wild K / Sinning I / Beckmann R | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2006 Journal: Nature / Year: 2006Title: Following the signal sequence from ribosomal tunnel exit to signal recognition particle. Authors: Mario Halic / Michael Blau / Thomas Becker / Thorsten Mielke / Martin R Pool / Klemens Wild / Irmgard Sinning / Roland Beckmann /  Abstract: Membrane and secretory proteins can be co-translationally inserted into or translocated across the membrane. This process is dependent on signal sequence recognition on the ribosome by the signal ...Membrane and secretory proteins can be co-translationally inserted into or translocated across the membrane. This process is dependent on signal sequence recognition on the ribosome by the signal recognition particle (SRP), which results in targeting of the ribosome-nascent-chain complex to the protein-conducting channel at the membrane. Here we present an ensemble of structures at subnanometre resolution, revealing the signal sequence both at the ribosomal tunnel exit and in the bacterial and eukaryotic ribosome-SRP complexes. Molecular details of signal sequence interaction in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic complexes were obtained by fitting high-resolution molecular models. The signal sequence is presented at the ribosomal tunnel exit in an exposed position ready for accommodation in the hydrophobic groove of the rearranged SRP54 M domain. Upon ribosome binding, the SRP54 NG domain also undergoes a conformational rearrangement, priming it for the subsequent docking reaction with the NG domain of the SRP receptor. These findings provide the structural basis for improving our understanding of the early steps of co-translational protein sorting. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_1263.map.gz emd_1263.map.gz | 12 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-1263-v30.xml emd-1263-v30.xml emd-1263.xml emd-1263.xml | 7.3 KB 7.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  1263.gif 1263.gif | 43 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1263 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1263 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1263 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1263 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_1263_validation.pdf.gz emd_1263_validation.pdf.gz | 250.5 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_1263_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_1263_full_validation.pdf.gz | 249.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_1263_validation.xml.gz emd_1263_validation.xml.gz | 6.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1263 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1263 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1263 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1263 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
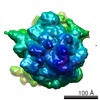
| Related structure data |  2j28MC  1261C 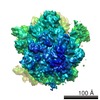 1262C 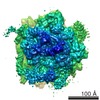 1264C  2j37C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_1263.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 94.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_1263.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 94.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | w | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.23 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : E. coli signal recognition particle bound to ribosome nascent cha...
| Entire | Name: E. coli signal recognition particle bound to ribosome nascent chain complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: E. coli signal recognition particle bound to ribosome nascent cha...
| Supramolecule | Name: E. coli signal recognition particle bound to ribosome nascent chain complex type: sample / ID: 1000 / Number unique components: 1 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #1: ribosome
| Supramolecule | Name: ribosome / type: complex / ID: 1 / Details: nascent chain / Recombinant expression: No / Ribosome-details: ribosome-prokaryote: ALL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
|---|
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F30 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Category: FILM / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM / Digitization - Scanner: PRIMESCAN / Average electron dose: 20 e/Å2 / Bits/pixel: 16 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.9 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: f / Specimen holder model: OTHER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F30 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 9.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: spider |
|---|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller