[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-6320: Structure of bacterial chemotaxis signaling CheA2-hexamer core co... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-6320 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
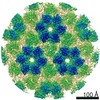
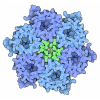
| Title | Structure of bacterial chemotaxis signaling CheA2-hexamer core complex by cryo-electron tomography and subvolume averaging | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Structure of bacterial chemotaxis signaling CheA2-hexamer core complex by cryo-electron tomography and subvolume averaging | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Bacterial chemotaxis /  Signal transduction / Signal transduction /  cryo-Electron Tomography / cryo-Electron Tomography /  Molecular dynamics simulation / all-atom Molecular dynamics simulation / all-atom | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of protein modification process / detection of chemical stimulus / methyl accepting chemotaxis protein complex / protein histidine kinase binding / positive regulation of post-translational protein modification / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent swimming motility / cell tip / regulation of bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility /  aerotaxis / protein histidine kinase activity ...negative regulation of protein modification process / detection of chemical stimulus / methyl accepting chemotaxis protein complex / protein histidine kinase binding / positive regulation of post-translational protein modification / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent swimming motility / cell tip / regulation of bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / aerotaxis / protein histidine kinase activity ...negative regulation of protein modification process / detection of chemical stimulus / methyl accepting chemotaxis protein complex / protein histidine kinase binding / positive regulation of post-translational protein modification / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent swimming motility / cell tip / regulation of bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility /  aerotaxis / protein histidine kinase activity / aerotaxis / protein histidine kinase activity /  regulation of chemotaxis / regulation of chemotaxis /  thermotaxis / signal complex assembly / thermotaxis / signal complex assembly /  histidine kinase / phosphorelay sensor kinase activity / phosphorelay signal transduction system / establishment of localization in cell / cellular response to amino acid stimulus / protein homooligomerization / histidine kinase / phosphorelay sensor kinase activity / phosphorelay signal transduction system / establishment of localization in cell / cellular response to amino acid stimulus / protein homooligomerization /  chemotaxis / transmembrane signaling receptor activity / protein domain specific binding / chemotaxis / transmembrane signaling receptor activity / protein domain specific binding /  phosphorylation / phosphorylation /  signal transduction / protein homodimerization activity / signal transduction / protein homodimerization activity /  ATP binding / identical protein binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding /  plasma membrane / plasma membrane /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) | |||||||||
| Method | subtomogram averaging /  cryo EM / Resolution: 17.5 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 17.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Cassidy CK / Himes BA / Alvarez FJ / Ma J / Zhou G / Perilla JR / Schulten K / Zhang P | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2015 Journal: Elife / Year: 2015Title: CryoEM and computer simulations reveal a novel kinase conformational switch in bacterial chemotaxis signaling. Authors: C Keith Cassidy / Benjamin A Himes / Frances J Alvarez / Jun Ma / Gongpu Zhao / Juan R Perilla / Klaus Schulten / Peijun Zhang /  Abstract: Chemotactic responses in bacteria require large, highly ordered arrays of sensory proteins to mediate the signal transduction that ultimately controls cell motility. A mechanistic understanding of ...Chemotactic responses in bacteria require large, highly ordered arrays of sensory proteins to mediate the signal transduction that ultimately controls cell motility. A mechanistic understanding of the molecular events underlying signaling, however, has been hampered by the lack of a high-resolution structural description of the extended array. Here, we report a novel reconstitution of the array, involving the receptor signaling domain, histidine kinase CheA, and adaptor protein CheW, as well as a density map of the core-signaling unit at 11.3 Å resolution, obtained by cryo-electron tomography and sub-tomogram averaging. Extracting key structural constraints from our density map, we computationally construct and refine an atomic model of the core array structure, exposing novel interfaces between the component proteins. Using all-atom molecular dynamics simulations, we further reveal a distinctive conformational change in CheA. Mutagenesis and chemical cross-linking experiments confirm the importance of the conformational dynamics of CheA for chemotactic function. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_6320.map.gz emd_6320.map.gz | 3.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-6320-v30.xml emd-6320-v30.xml emd-6320.xml emd-6320.xml | 13.4 KB 13.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_6320_fsc.xml emd_6320_fsc.xml | 3.8 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_6320.png emd_6320.png | 354.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6320 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6320 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6320 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6320 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_6320.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_6320.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Structure of bacterial chemotaxis signaling CheA2-hexamer core complex by cryo-electron tomography and subvolume averaging | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 3.01 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : tarCF CheA CheW
| Entire | Name: tarCF CheA CheW |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: tarCF CheA CheW
| Supramolecule | Name: tarCF CheA CheW / type: sample / ID: 1000 Oligomeric state: Hexamer of (CheA dimer, dimer of tarCF trimers of dimers, 2 CheW subunits) Number unique components: 3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 3.32 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Chemotaxis protein CheA
| Macromolecule | Name: Chemotaxis protein CheA / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: Bacterial Chemotaxis Histidine Kinase CheA / Number of copies: 12 / Oligomeric state: Dimer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Location in cell: Inner Membrane Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Location in cell: Inner Membrane |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 71.384 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Recombinant strain: RP3098 / Recombinant plasmid: pKJ9 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Recombinant strain: RP3098 / Recombinant plasmid: pKJ9 |
| Sequence | UniProtKB:  Chemotaxis protein CheA Chemotaxis protein CheA |
-Macromolecule #2: Chemotaxis protein CheW
| Macromolecule | Name: Chemotaxis protein CheW / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Oligomeric state: monomeric / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Location in cell: Inner Membrane Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Location in cell: Inner Membrane |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.083 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Recombinant strain: RP3098 / Recombinant plasmid: PPA770 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Recombinant strain: RP3098 / Recombinant plasmid: PPA770 |
| Sequence | UniProtKB:  Chemotaxis protein CheW Chemotaxis protein CheW |
-Macromolecule #3: Methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein II
| Macromolecule | Name: Methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein II / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Name.synonym: tarCF Details: Cytoplasmic fragment of wild-type aspartate receptor Number of copies: 6 / Oligomeric state: trimer of dimers / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Location in cell: Inner Membrane Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Location in cell: Inner Membrane |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 31.209 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Recombinant strain: RP3098 / Recombinant plasmid: pHTCF Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Recombinant strain: RP3098 / Recombinant plasmid: pHTCF |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: Methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein II |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | subtomogram averaging |
| Aggregation state | 2D array |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 / Details: 75 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Details: Perforated R2/2 Quantifoil grids precoated with 10 nm fiducial gold beads on the backside of the grid |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER Method: Single-sided blotting to avoid disruption of the monolayer |
| Details | Pseudo-crystalline 2D monolayer reconstituted on a lipid monolayer |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI POLARA 300 |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 49834 / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 8.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 4.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 39000 Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 8.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 4.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 39000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: OTHER / Tilt series - Axis1 - Min angle: -70 ° / Tilt series - Axis1 - Max angle: 70 ° |
| Date | Jan 7, 2009 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: GATAN ULTRASCAN 4000 (4k x 4k) / Number real images: 60 / Average electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Bits/pixel: 16 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller