+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-6124 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
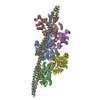
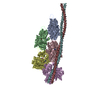
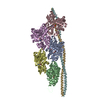
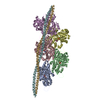
| Title | Structure of the F-actin-tropomyosin complex | |||||||||
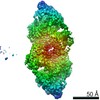
 Map data Map data | Reconstruction of F-actin tropomyosin complex | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  F-actin / F-actin /  tropomyosin / tropomyosin /  filament / protein polymers / filament / protein polymers /  muscle / muscle /  thin filament / thin filament /  cytoskeleton cytoskeleton | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of heart rate by epinephrine / muscle thin filament tropomyosin / Striated Muscle Contraction / Smooth Muscle Contraction / bleb / negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration / muscle filament sliding / actin filament capping / ruffle organization / sarcomere organization ...positive regulation of heart rate by epinephrine / muscle thin filament tropomyosin / Striated Muscle Contraction / Smooth Muscle Contraction / bleb / negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration / muscle filament sliding / actin filament capping / ruffle organization / sarcomere organization / cytoskeletal motor activator activity / ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis /  tropomyosin binding / tropomyosin binding /  myofibril / myofibril /  myosin heavy chain binding / mesenchyme migration / myosin heavy chain binding / mesenchyme migration /  troponin I binding / actin filament bundle / filamentous actin / negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation / actin filament bundle assembly / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin monomer binding / positive regulation of cell adhesion / skeletal muscle fiber development / troponin I binding / actin filament bundle / filamentous actin / negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation / actin filament bundle assembly / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin monomer binding / positive regulation of cell adhesion / skeletal muscle fiber development /  stress fiber / stress fiber /  titin binding / cardiac muscle contraction / positive regulation of stress fiber assembly / titin binding / cardiac muscle contraction / positive regulation of stress fiber assembly /  cytoskeletal protein binding / actin filament polymerization / negative regulation of cell migration / cytoskeletal protein binding / actin filament polymerization / negative regulation of cell migration /  filopodium / actin filament organization / filopodium / actin filament organization /  actin filament / actin filament /  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement /  wound healing / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / ruffle membrane / calcium-dependent protein binding / disordered domain specific binding / wound healing / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / ruffle membrane / calcium-dependent protein binding / disordered domain specific binding /  actin filament binding / actin filament binding /  actin cytoskeleton / actin cytoskeleton /  lamellipodium / lamellipodium /  cell body / cell body /  actin binding / regulation of cell shape / in utero embryonic development / actin binding / regulation of cell shape / in utero embryonic development /  hydrolase activity / protein heterodimerization activity / protein domain specific binding / hydrolase activity / protein heterodimerization activity / protein domain specific binding /  calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / magnesium ion binding / protein homodimerization activity / protein-containing complex / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / magnesium ion binding / protein homodimerization activity / protein-containing complex /  ATP binding / identical protein binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) /   Mus musculus (house mouse) Mus musculus (house mouse) | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | von der Ecken J / Mueller M / Lehman W / Manstein DJ / Penczek PA / Raunser S | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2015 Journal: Nature / Year: 2015Title: Structure of the F-actin-tropomyosin complex. Authors: Julian von der Ecken / Mirco Müller / William Lehman / Dietmar J Manstein / Pawel A Penczek / Stefan Raunser /   Abstract: Filamentous actin (F-actin) is the major protein of muscle thin filaments, and actin microfilaments are the main component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. Mutations in different actin isoforms lead ...Filamentous actin (F-actin) is the major protein of muscle thin filaments, and actin microfilaments are the main component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. Mutations in different actin isoforms lead to early-onset autosomal dominant non-syndromic hearing loss, familial thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections, and multiple variations of myopathies. In striated muscle fibres, the binding of myosin motors to actin filaments is mainly regulated by tropomyosin and troponin. Tropomyosin also binds to F-actin in smooth muscle and in non-muscle cells and stabilizes and regulates the filaments there in the absence of troponin. Although crystal structures for monomeric actin (G-actin) are available, a high-resolution structure of F-actin is still missing, hampering our understanding of how disease-causing mutations affect the function of thin muscle filaments and microfilaments. Here we report the three-dimensional structure of F-actin at a resolution of 3.7 Å in complex with tropomyosin at a resolution of 6.5 Å, determined by electron cryomicroscopy. The structure reveals that the D-loop is ordered and acts as a central region for hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions that stabilize the F-actin filament. We clearly identify map density corresponding to ADP and Mg(2+) and explain the possible effect of prominent disease-causing mutants. A comparison of F-actin with G-actin reveals the conformational changes during filament formation and identifies the D-loop as their key mediator. We also confirm that negatively charged tropomyosin interacts with a positively charged groove on F-actin. Comparison of the position of tropomyosin in F-actin-tropomyosin with its position in our previously determined F-actin-tropomyosin-myosin structure reveals a myosin-induced transition of tropomyosin. Our results allow us to understand the role of individual mutations in the genesis of actin- and tropomyosin-related diseases and will serve as a strong foundation for the targeted development of drugs. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_6124.map.gz emd_6124.map.gz | 5.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-6124-v30.xml emd-6124-v30.xml emd-6124.xml emd-6124.xml | 11.7 KB 11.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_6124.jpg emd_6124.jpg | 210.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6124 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6124 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6124 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6124 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3j8aMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_6124.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 6.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_6124.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 6.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Reconstruction of F-actin tropomyosin complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.12 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : F-actin-tropomyosin complex
| Entire | Name: F-actin-tropomyosin complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: F-actin-tropomyosin complex
| Supramolecule | Name: F-actin-tropomyosin complex / type: sample / ID: 1000 / Oligomeric state: filament / Number unique components: 2 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: F-actin (alpha)
| Macromolecule | Name: F-actin (alpha) / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 5 / Oligomeric state: filament / Recombinant expression: No / Database: NCBI |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / synonym: rabbit / Tissue: muscle Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / synonym: rabbit / Tissue: muscle |
| Sequence | UniProtKB:  Actin, alpha skeletal muscle Actin, alpha skeletal muscle |
-Macromolecule #2: tropomyosin (alpha)
| Macromolecule | Name: tropomyosin (alpha) / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Oligomeric state: filament (dimer) / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Mus musculus (house mouse) / synonym: mouse / Tissue: muscle Mus musculus (house mouse) / synonym: mouse / Tissue: muscle |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: Tropomyosin alpha-1 chain |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 / Details: 5 mM Tris, 1 mM DTT, 100 mM KCL, 2 mM MgCl2 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Details: C-flats 2/1 copper 300 mesh, Protochips, glow-discharged |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 106 K / Instrument: GATAN CRYOPLUNGE 3 Method: Sample was applied to grid, incubated for 10 seconds, and manually blotted for 3 seconds from the backside with filter paper. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.6 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm / Nominal magnification: 59000 / Cs: mm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.6 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm / Nominal magnification: 59000 / Cs: mm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Cs | 0 |
| Details | Cs-corrected microscope |
| Date | Oct 17, 2013 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Number real images: 1311 / Average electron dose: 14.6 e/Å2 Details: Every image is the average of seven frames recorded by the direct electron detector after beam-induced motion correction. Only 689 images were used for the refinement. |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Details: each micrograph |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δz: 27.5 Å Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δ&Phi: 166.4 ° Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Axial symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.7 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: SPARX Details: The tropomyosin map filtered to 6.5 Angstrom was merged with the final F-actin map (3.7 Angstrom) to obtain a map of the entire F-actin tropomyosin complex. |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - #0 - Chain ID: A / Chain - #1 - Chain ID: B / Chain - #2 - Chain ID: C / Chain - #3 - Chain ID: D / Chain - #4 - Chain ID: E |
|---|---|
| Software | Name: SPARX, PHENIX, COOT |
| Refinement | Space: RECIPROCAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Overall B value: 55.4 / Target criteria: R-factor |
| Output model |  PDB-3j8a: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller