[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
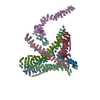
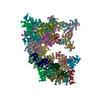
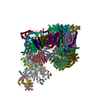
Yorodumi- PDB-5flc: Architecture of human mTOR Complex 1 - 5.9 Angstrom reconstruction -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5flc | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Architecture of human mTOR Complex 1 - 5.9 Angstrom reconstruction | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  TRANSFERASE / TRANSFERASE /  RAPAMYCIN / RAPAMYCIN /  MTORC1 MTORC1 | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRNA polymerase III type 2 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / positive regulation of cytoplasmic translational initiation / RNA polymerase III type 1 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / positive regulation of pentose-phosphate shunt / T-helper 1 cell lineage commitment / regulation of locomotor rhythm / positive regulation of wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells / cellular response to leucine starvation / TFIIIC-class transcription factor complex binding /  TORC2 complex ...RNA polymerase III type 2 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / positive regulation of cytoplasmic translational initiation / RNA polymerase III type 1 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / positive regulation of pentose-phosphate shunt / T-helper 1 cell lineage commitment / regulation of locomotor rhythm / positive regulation of wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells / cellular response to leucine starvation / TFIIIC-class transcription factor complex binding / TORC2 complex ...RNA polymerase III type 2 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / positive regulation of cytoplasmic translational initiation / RNA polymerase III type 1 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / positive regulation of pentose-phosphate shunt / T-helper 1 cell lineage commitment / regulation of locomotor rhythm / positive regulation of wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells / cellular response to leucine starvation / TFIIIC-class transcription factor complex binding /  TORC2 complex / heart valve morphogenesis / TORC2 complex / heart valve morphogenesis /  regulation of membrane permeability / negative regulation of lysosome organization / RNA polymerase III type 3 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / regulation of membrane permeability / negative regulation of lysosome organization / RNA polymerase III type 3 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding /  TORC1 complex / positive regulation of transcription of nucleolar large rRNA by RNA polymerase I / calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade / TORC1 complex / positive regulation of transcription of nucleolar large rRNA by RNA polymerase I / calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade /  regulation of autophagosome assembly / TORC1 signaling / voluntary musculoskeletal movement / regulation of osteoclast differentiation / positive regulation of keratinocyte migration / cellular response to L-leucine / MTOR signalling / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / cellular response to nutrient / energy reserve metabolic process / Energy dependent regulation of mTOR by LKB1-AMPK / nucleus localization / ruffle organization / negative regulation of cell size / cellular response to osmotic stress / regulation of autophagosome assembly / TORC1 signaling / voluntary musculoskeletal movement / regulation of osteoclast differentiation / positive regulation of keratinocyte migration / cellular response to L-leucine / MTOR signalling / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / cellular response to nutrient / energy reserve metabolic process / Energy dependent regulation of mTOR by LKB1-AMPK / nucleus localization / ruffle organization / negative regulation of cell size / cellular response to osmotic stress /  anoikis / cardiac muscle cell development / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III / negative regulation of protein localization to nucleus / anoikis / cardiac muscle cell development / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III / negative regulation of protein localization to nucleus /  regulation of myelination / negative regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade / regulation of myelination / negative regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade /  Macroautophagy / Macroautophagy /  regulation of cell size / negative regulation of macroautophagy / lysosome organization / positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation / positive regulation of actin filament polymerization / positive regulation of myotube differentiation / behavioral response to pain / regulation of cell size / negative regulation of macroautophagy / lysosome organization / positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation / positive regulation of actin filament polymerization / positive regulation of myotube differentiation / behavioral response to pain /  TOR signaling / oligodendrocyte differentiation / mTORC1-mediated signalling / germ cell development / Constitutive Signaling by AKT1 E17K in Cancer / cellular response to nutrient levels / CD28 dependent PI3K/Akt signaling / positive regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity / positive regulation of translational initiation / neuronal action potential / HSF1-dependent transactivation / positive regulation of TOR signaling / positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition / TOR signaling / oligodendrocyte differentiation / mTORC1-mediated signalling / germ cell development / Constitutive Signaling by AKT1 E17K in Cancer / cellular response to nutrient levels / CD28 dependent PI3K/Akt signaling / positive regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity / positive regulation of translational initiation / neuronal action potential / HSF1-dependent transactivation / positive regulation of TOR signaling / positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition /  regulation of macroautophagy / regulation of macroautophagy /  endomembrane system / 'de novo' pyrimidine nucleobase biosynthetic process / response to amino acid / positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process / phagocytic vesicle / positive regulation of lamellipodium assembly / heart morphogenesis / regulation of cellular response to heat / cytoskeleton organization / cardiac muscle contraction / positive regulation of stress fiber assembly / cellular response to amino acid starvation / T cell costimulation / cellular response to starvation / positive regulation of glycolytic process / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / negative regulation of autophagy / response to nutrient levels / post-embryonic development / response to nutrient / positive regulation of translation / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / Regulation of PTEN gene transcription / endomembrane system / 'de novo' pyrimidine nucleobase biosynthetic process / response to amino acid / positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process / phagocytic vesicle / positive regulation of lamellipodium assembly / heart morphogenesis / regulation of cellular response to heat / cytoskeleton organization / cardiac muscle contraction / positive regulation of stress fiber assembly / cellular response to amino acid starvation / T cell costimulation / cellular response to starvation / positive regulation of glycolytic process / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / negative regulation of autophagy / response to nutrient levels / post-embryonic development / response to nutrient / positive regulation of translation / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / Regulation of PTEN gene transcription /  regulation of cell growth / regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization / cellular response to amino acid stimulus / TP53 Regulates Metabolic Genes / regulation of cell growth / regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization / cellular response to amino acid stimulus / TP53 Regulates Metabolic Genes /  macroautophagy / macroautophagy /  phosphoprotein binding / protein catabolic process / multicellular organism growth / protein destabilization / phosphoprotein binding / protein catabolic process / multicellular organism growth / protein destabilization /  regulation of circadian rhythm / PML body / cellular response to insulin stimulus / rhythmic process / positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / Regulation of TP53 Degradation / regulation of circadian rhythm / PML body / cellular response to insulin stimulus / rhythmic process / positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / Regulation of TP53 Degradation /  ribosome binding ribosome bindingSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   HOMO SAPIENS (human) HOMO SAPIENS (human)  SPODOPTERA FRUGIPERDA (fall armyworm) SPODOPTERA FRUGIPERDA (fall armyworm) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 5.9 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 5.9 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Aylett, C.H.S. / Sauer, E. / Imseng, S. / Boehringer, D. / Hall, M.N. / Ban, N. / Maier, T. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2016 Journal: Science / Year: 2016Title: Architecture of human mTOR complex 1. Authors: Christopher H S Aylett / Evelyn Sauer / Stefan Imseng / Daniel Boehringer / Michael N Hall / Nenad Ban / Timm Maier /  Abstract: Target of rapamycin (TOR), a conserved protein kinase and central controller of cell growth, functions in two structurally and functionally distinct complexes: TORC1 and TORC2. Dysregulation of ...Target of rapamycin (TOR), a conserved protein kinase and central controller of cell growth, functions in two structurally and functionally distinct complexes: TORC1 and TORC2. Dysregulation of mammalian TOR (mTOR) signaling is implicated in pathologies that include diabetes, cancer, and neurodegeneration. We resolved the architecture of human mTORC1 (mTOR with subunits Raptor and mLST8) bound to FK506 binding protein (FKBP)-rapamycin, by combining cryo-electron microscopy at 5.9 angstrom resolution with crystallographic studies of Chaetomium thermophilum Raptor at 4.3 angstrom resolution. The structure explains how FKBP-rapamycin and architectural elements of mTORC1 limit access to the recessed active site. Consistent with a role in substrate recognition and delivery, the conserved amino-terminal domain of Raptor is juxtaposed to the kinase active site. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5flc.cif.gz 5flc.cif.gz | 1010.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5flc.ent.gz pdb5flc.ent.gz | 832.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5flc.json.gz 5flc.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fl/5flc https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fl/5flc ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fl/5flc ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fl/5flc | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3213MC 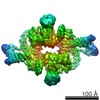 3212C 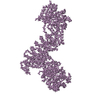 5ef5C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 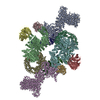
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-SERINE/THREONINE-PROTEIN KINASE ... , 3 types, 6 molecules 1324BF
| #1: Protein | Mass: 52357.672 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: HORN DOMAIN Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line (production host): Sf21 / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line (production host): Sf21 / Production host:   SPODOPTERA FRUGIPERDA (fall armyworm) / References: SPODOPTERA FRUGIPERDA (fall armyworm) / References:  non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase#2: Protein | Mass: 31081.197 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: BRIDGE DOMAIN Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line (production host): Sf21 / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line (production host): Sf21 / Production host:   SPODOPTERA FRUGIPERDA (fall armyworm) / References: SPODOPTERA FRUGIPERDA (fall armyworm) / References:  non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase#4: Protein | Mass: 134036.641 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: FAT AND PIKK DOMAINS Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line (production host): Sf21 / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line (production host): Sf21 / Production host:   SPODOPTERA FRUGIPERDA (fall armyworm) SPODOPTERA FRUGIPERDA (fall armyworm)References: UniProt: P42345,  non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase |
|---|
-Protein , 3 types, 6 molecules AECGDH
| #3: Protein | Mass: 87589.977 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line (production host): Sf21 / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line (production host): Sf21 / Production host:   SPODOPTERA FRUGIPERDA (fall armyworm) SPODOPTERA FRUGIPERDA (fall armyworm)#5: Protein |  Mass: 9124.238 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   SPODOPTERA FRUGIPERDA (fall armyworm) SPODOPTERA FRUGIPERDA (fall armyworm)#6: Protein |  MTOR / TORC SUBUNIT LST8 / G PROTEIN BETA SUBUNIT-LIKE / GABLE / PROTEIN GBETAL / MAMMALIAN LETHAL WITH ...TORC SUBUNIT LST8 / G PROTEIN BETA SUBUNIT-LIKE / GABLE / PROTEIN GBETAL / MAMMALIAN LETHAL WITH SEC13 PROTEIN 8 / MLST8 MTOR / TORC SUBUNIT LST8 / G PROTEIN BETA SUBUNIT-LIKE / GABLE / PROTEIN GBETAL / MAMMALIAN LETHAL WITH ...TORC SUBUNIT LST8 / G PROTEIN BETA SUBUNIT-LIKE / GABLE / PROTEIN GBETAL / MAMMALIAN LETHAL WITH SEC13 PROTEIN 8 / MLST8Mass: 35910.090 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line (production host): Sf21 / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line (production host): Sf21 / Production host:   SPODOPTERA FRUGIPERDA (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: Q9BVC4 SPODOPTERA FRUGIPERDA (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: Q9BVC4 |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 1 types, 2 molecules 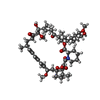
| #7: Chemical |  Sirolimus Sirolimus |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: HUMAN MTOR COMPLEX 1 MTORC1 / Type: COMPLEX MTORC1 / Type: COMPLEX |
|---|---|
| Buffer solution | Name: 100 MM NACL, 10 MM NABICINE, 1 MM TCEP / pH: 8 / Details: 100 MM NACL, 10 MM NABICINE, 1 MM TCEP |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
| Specimen support | Details: CARBON |
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK I / Cryogen name: ETHANE Details: VITRIFICATION 1 -- CRYOGEN- ETHANE, HUMIDITY- 100, TEMPERATURE- 120, INSTRUMENT- FEI VITROBOT MARK I, METHOD- 4 SECOND BLOTTING, |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS / Date: May 5, 2015 |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 59000 X / Calibrated magnification: 100719 X / Nominal defocus max: 4000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1900 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 59000 X / Calibrated magnification: 100719 X / Nominal defocus max: 4000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1900 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm : 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Temperature: 100 K |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 25 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Details: EACH IMAGE | ||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C2 (2 fold cyclic : C2 (2 fold cyclic ) ) | ||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Method: MAXIMUM A POSTERIORI PROJECTION MATCHING / Resolution: 5.9 Å / Num. of particles: 309792 / Nominal pixel size: 1.39 Å / Actual pixel size: 1.39 Å Details: THE UNK CHAINS (A, E, C, G, 1-4) CORRESPONDING TO RAPTOR (A,E), SF FKBP AND RAPAMYCIN (C,G) AND THE N-TERMINAL HEAT REPEATS OF MTOR (1-4), HAVE BEEN NUMBERED FROM 100 AT EACH BREAK TO ...Details: THE UNK CHAINS (A, E, C, G, 1-4) CORRESPONDING TO RAPTOR (A,E), SF FKBP AND RAPAMYCIN (C,G) AND THE N-TERMINAL HEAT REPEATS OF MTOR (1-4), HAVE BEEN NUMBERED FROM 100 AT EACH BREAK TO INDICATE LACK OF SEQUENCE - DENSITY CERTAINTY. CHAINS 1-4 CORRESPOND TO THE N-TERMINAL HEAT REPEAT DOMAINS OF MTOR. WE PROPOSE A TOPOLOGY IN THE CORRESPONDING PAPER (1-2-B AND 3-4-F), BUT GIVEN THE FACT THAT THEIR TOPOLOGY CANNOT BE ASSIGNED DEFINITIVELY THEY ARE REPRESENTED AS A SEPARATE CHAIN FOR EACH DOMAIN. THE FITTING OF CRYSTAL STRUCTURES FOR THE MTOR FAT AND PIKK DOMAINS, MLST8, RAPTOR AND FKBP ALLOWS THEIR DENSITY TO BE ASSIGNED DEFINITIVELY, AND THEIR CHAINS ARE THEREFORE LETTERED. SUBMISSION BASED ON EXPERIMENTAL DATA FROM EMDB EMD-3213. (DEPOSITION ID: 13912). Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Target criteria: FSC / Details: METHOD--RIGID BODY | ||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 5.9 Å | ||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Highest resolution: 5.9 Å
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj