[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-5343: Molecular architecture of the human VP16-Mediator-RNA polymerase ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-5343 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
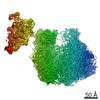
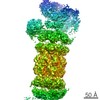
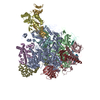
| Title | Molecular architecture of the human VP16-Mediator-RNA polymerase II-TFIIF assembly | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | none | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  transcription / Mediator / transcription / Mediator /  RNA polymerase II / RNA polymerase II /  TFIIF / activator TFIIF / activator | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRPB4-RPB7 complex / : / nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, deadenylation-dependent decay / : / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / positive regulation of nuclear-transcribed mRNA poly(A) tail shortening / Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA / : / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 2 Promoter / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE ...RPB4-RPB7 complex / : / nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, deadenylation-dependent decay / : / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / positive regulation of nuclear-transcribed mRNA poly(A) tail shortening / Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA / : / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 2 Promoter / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / mRNA Capping / termination of RNA polymerase II transcription / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / maintenance of transcriptional fidelity during transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / RNA-templated transcription / termination of RNA polymerase III transcription / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / Dual incision in TC-NER /  RNA polymerase I activity / termination of RNA polymerase I transcription / RNA polymerase I activity / termination of RNA polymerase I transcription /  transcription initiation at RNA polymerase III promoter / tRNA transcription by RNA polymerase III / nucleolar large rRNA transcription by RNA polymerase I / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase III promoter / tRNA transcription by RNA polymerase III / nucleolar large rRNA transcription by RNA polymerase I / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER /  transcription initiation at RNA polymerase I promoter / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase I promoter /  RNA polymerase II activity / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase I / positive regulation of translational initiation / transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair / RNA polymerase II activity / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase I / positive regulation of translational initiation / transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair /  translesion synthesis / translesion synthesis /  RNA polymerase I complex / RNA polymerase I complex /  RNA polymerase III complex / transcription by RNA polymerase I / transcription by RNA polymerase III / RNA polymerase III complex / transcription by RNA polymerase I / transcription by RNA polymerase III /  RNA polymerase II, core complex / RNA polymerase II, core complex /  translation initiation factor binding / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / translation initiation factor binding / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II /  P-body / DNA-templated transcription initiation / P-body / DNA-templated transcription initiation /  transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter /  ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed 5'-3' RNA polymerase activity / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed 5'-3' RNA polymerase activity /  DNA-directed RNA polymerase / cytoplasmic stress granule / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / cytoplasmic stress granule /  single-stranded DNA binding / single-stranded DNA binding /  ribosome biogenesis / transcription by RNA polymerase II / ribosome biogenesis / transcription by RNA polymerase II /  single-stranded RNA binding / single-stranded RNA binding /  nucleic acid binding / nucleic acid binding /  protein dimerization activity / protein dimerization activity /  nucleotide binding / nucleotide binding /  mRNA binding / mRNA binding /  nucleolus / nucleolus /  mitochondrion / mitochondrion /  DNA binding / zinc ion binding / DNA binding / zinc ion binding /  nucleoplasm / nucleoplasm /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  nucleus / nucleus /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / cryo EM /  negative staining / Resolution: 36.0 Å negative staining / Resolution: 36.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Bernecky C / Grob P / Ebmeier CC / Nogales E / Taatjes DJ | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: PLoS Biol / Year: 2011 Journal: PLoS Biol / Year: 2011Title: Molecular architecture of the human Mediator-RNA polymerase II-TFIIF assembly. Authors: Carrie Bernecky / Patricia Grob / Christopher C Ebmeier / Eva Nogales / Dylan J Taatjes /  Abstract: The macromolecular assembly required to initiate transcription of protein-coding genes, known as the Pre-Initiation Complex (PIC), consists of multiple protein complexes and is approximately 3.5 MDa ...The macromolecular assembly required to initiate transcription of protein-coding genes, known as the Pre-Initiation Complex (PIC), consists of multiple protein complexes and is approximately 3.5 MDa in size. At the heart of this assembly is the Mediator complex, which helps regulate PIC activity and interacts with the RNA polymerase II (pol II) enzyme. The structure of the human Mediator-pol II interface is not well-characterized, whereas attempts to structurally define the Mediator-pol II interaction in yeast have relied on incomplete assemblies of Mediator and/or pol II and have yielded inconsistent interpretations. We have assembled the complete, 1.9 MDa human Mediator-pol II-TFIIF complex from purified components and have characterized its structural organization using cryo-electron microscopy and single-particle reconstruction techniques. The orientation of pol II within this assembly was determined by crystal structure docking and further validated with projection matching experiments, allowing the structural organization of the entire human PIC to be envisioned. Significantly, pol II orientation within the Mediator-pol II-TFIIF assembly can be reconciled with past studies that determined the location of other PIC components relative to pol II itself. Pol II surfaces required for interacting with TFIIB, TFIIE, and promoter DNA (i.e., the pol II cleft) are exposed within the Mediator-pol II-TFIIF structure; RNA exit is unhindered along the RPB4/7 subunits; upstream and downstream DNA is accessible for binding additional factors; and no major structural re-organization is necessary to accommodate the large, multi-subunit TFIIH or TFIID complexes. The data also reveal how pol II binding excludes Mediator-CDK8 subcomplex interactions and provide a structural basis for Mediator-dependent control of PIC assembly and function. Finally, parallel structural analysis of Mediator-pol II complexes lacking TFIIF reveal that TFIIF plays a key role in stabilizing pol II orientation within the assembly. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_5343.map.gz emd_5343.map.gz | 14.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-5343-v30.xml emd-5343-v30.xml emd-5343.xml emd-5343.xml | 12.3 KB 12.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_5343_1.png emd_5343_1.png | 70.4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-5343 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-5343 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-5343 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-5343 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 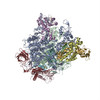 3j0kMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_5343.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 15.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_5343.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 15.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | none | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 4.29 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Assembly of VP16-bound human Mediator, RNA polymerase II, and TFIIF
| Entire | Name: Assembly of VP16-bound human Mediator, RNA polymerase II, and TFIIF |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Assembly of VP16-bound human Mediator, RNA polymerase II, and TFIIF
| Supramolecule | Name: Assembly of VP16-bound human Mediator, RNA polymerase II, and TFIIF type: sample / ID: 1000 Oligomeric state: one Mediator complex binds one pol II-TFIIF Number unique components: 3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.9 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: core Mediator
| Macromolecule | Name: core Mediator / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: Mediator / Details: bound to GST-VP16 (residues 411 - 490) / Oligomeric state: 26 subunit complex / Recombinant expression: No / Database: NCBI |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: human / Cell: HeLa / Organelle: Nucleus Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: human / Cell: HeLa / Organelle: Nucleus |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.2 MDa |
-Macromolecule #2: RNA polymerase II
| Macromolecule | Name: RNA polymerase II / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Name.synonym: pol II / Details: unphosphorylated / Oligomeric state: 12-subunit complex / Recombinant expression: No / Database: NCBI |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human / Cell: HeLa / Organelle: Nucleus Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human / Cell: HeLa / Organelle: Nucleus |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 520 KDa |
-Macromolecule #3: TFIIF
| Macromolecule | Name: TFIIF / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Name.synonym: TFIIF / Details: RAP74 and RAP30 expressed separately then combined / Oligomeric state: Dimer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 10 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  negative staining, negative staining,  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.9 Details: 20 mM HEPES, 0.10 mM EDTA, 150 mM KCl, 0.02% NP-40, 35% glycerol |
|---|---|
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE Details: grids with adsorbed protein washed 3x with buffer containing 5% trehalose, 20 mM HEPES, 100 mM KCl, and 0.10 mM EDTA, then subjected to cryo-negative staining in a saturated solution (1.2M) ...Details: grids with adsorbed protein washed 3x with buffer containing 5% trehalose, 20 mM HEPES, 100 mM KCl, and 0.10 mM EDTA, then subjected to cryo-negative staining in a saturated solution (1.2M) of ammonium molybdate (pH 7.5) |
| Grid | Details: thin carbon-coated holey carbon 400 mesh copper grid |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber temperature: 90 K / Instrument: OTHER Method: blot for 2 seconds, dry for 3 seconds before plunging |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 4.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 29000 Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 4.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 29000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: side entry / Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Category: FILM / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM / Digitization - Scanner: OTHER / Digitization - Sampling interval: 12.9 µm / Number real images: 106 / Average electron dose: 15 e/Å2 / Od range: 1 / Bits/pixel: 16 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Details: each micrograph |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 36.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: Spider / Number images used: 3146 |
| Details | The particles were selected interactively at the computer terminal. |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Software | Name: Situs |
| Details | Protocol: rigid body. the TFIIS chain S was removed before fitting |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Target criteria: contour-based Laplacian correlation |
| Output model |  PDB-3j0k: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller