[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-5201: The electron cryo-microscopic structure of Shigella phage Sf6 rev... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-5201 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | The electron cryo-microscopic structure of Shigella phage Sf6 reveals novel cementing proteins | |||||||||
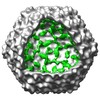
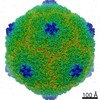
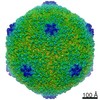
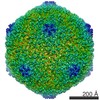
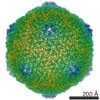
 Map data Map data | Electron cryo-microscopic reconstruction of Shigella phage Sf6. The image is viewed approximately down the icosahedral 3-fold axis, and an octant of the capsid was removed to show the internal density (colored in green) that corresponds to the two host-derived cementing proteins. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  virus assembly / cementing protein / virus assembly / cementing protein /  bacteriophage / Sf6 / bacteriophage / Sf6 /  Shigella Shigella | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationouter membrane protein complex / monoatomic ion transmembrane transporter activity / detection of virus / outer membrane /  porin activity / pore complex / monoatomic ion transport / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / cell outer membrane / virus receptor activity ...outer membrane protein complex / monoatomic ion transmembrane transporter activity / detection of virus / outer membrane / porin activity / pore complex / monoatomic ion transport / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / cell outer membrane / virus receptor activity ...outer membrane protein complex / monoatomic ion transmembrane transporter activity / detection of virus / outer membrane /  porin activity / pore complex / monoatomic ion transport / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / cell outer membrane / virus receptor activity / outer membrane-bounded periplasmic space / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / symbiont entry into host cell / DNA damage response / porin activity / pore complex / monoatomic ion transport / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / cell outer membrane / virus receptor activity / outer membrane-bounded periplasmic space / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / symbiont entry into host cell / DNA damage response /  membrane / identical protein binding / membrane / identical protein binding /  metal ion binding metal ion bindingSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Bacillus phage SF6 (virus) Bacillus phage SF6 (virus) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 19.0 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 19.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhao H / Sequeira RD / Galeva NA / Tang L | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Virology / Year: 2011 Journal: Virology / Year: 2011Title: The host outer membrane proteins OmpA and OmpC are associated with the Shigella phage Sf6 virion. Authors: Haiyan Zhao / Reuben D Sequeira / Nadezhda A Galeva / Liang Tang /  Abstract: Assembly of dsDNA bacteriophage is a precisely programmed process. Potential roles of host cell components in phage assembly haven't been well understood. It was previously reported that two ...Assembly of dsDNA bacteriophage is a precisely programmed process. Potential roles of host cell components in phage assembly haven't been well understood. It was previously reported that two unidentified proteins were present in bacteriophage Sf6 virion (Casjens et al, 2004, J.Mol.Biol. 339, 379-394, Fig. 2A). Using tandem mass spectrometry, we have identified the two proteins as outer membrane proteins (OMPs) OmpA and OmpC from its host Shigella flexneri. The transmission electron cryo-microscopy structure of Sf6 shows significant density at specific sites at the phage capsid inner surface. This density fit well with the characteristic beta-barrel domains of OMPs, thus may be due to the two host proteins. Locations of this density suggest a role in Sf6 morphogenesis reminiscent of phage-encoded cementing proteins. These data indicate a new, OMP-related phage:host linkage, adding to previous knowledge that some lambdoid bacteriophage genomes contain OmpC-like genes that express phage-encoded porins in the lysogenic state. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_5201.map.gz emd_5201.map.gz | 4.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-5201-v30.xml emd-5201-v30.xml emd-5201.xml emd-5201.xml | 10.7 KB 10.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_5201_1.jpg emd_5201_1.jpg | 62.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-5201 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-5201 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-5201 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-5201 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3nb3MC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_5201.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 29.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_5201.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 29.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Electron cryo-microscopic reconstruction of Shigella phage Sf6. The image is viewed approximately down the icosahedral 3-fold axis, and an octant of the capsid was removed to show the internal density (colored in green) that corresponds to the two host-derived cementing proteins. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 3.9284 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : bacteriophage Sf6
| Entire | Name:  bacteriophage Sf6 (virus) bacteriophage Sf6 (virus) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: bacteriophage Sf6
| Supramolecule | Name: bacteriophage Sf6 / type: sample / ID: 1000 / Oligomeric state: icosahedral / Number unique components: 60 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 19.2 MDa |
-Supramolecule #1: Bacillus phage SF6
| Supramolecule | Name: Bacillus phage SF6 / type: virus / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: Sf6 / Details: purified infectious virion / NCBI-ID: 10773 / Sci species name: Bacillus phage SF6 / Database: NCBI / Virus type: VIRION / Virus isolate: SPECIES / Virus enveloped: No / Virus empty: No / Syn species name: Sf6 |
|---|---|
| Host (natural) | Organism:   Shigella flexneri (bacteria) / synonym: BACTERIA(EUBACTERIA) Shigella flexneri (bacteria) / synonym: BACTERIA(EUBACTERIA) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 19.2 MDa |
| Virus shell | Shell ID: 1 / Name: gp5 / Diameter: 680 Å / T number (triangulation number): 7 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 / Details: 10 mM Tric-HCl, pH 7.4, 10mM MgCl2 |
| Grid | Details: 300 mech holey copper grid |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Details: Vitrification instrument: home-made plunger / Method: blot for 3-4 seconds before plunging |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 1.06 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.471 µm / Nominal magnification: 39000 Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 1.06 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.471 µm / Nominal magnification: 39000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: Side entry liquid nitrogen-cooled cryo specimen holder Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN |
| Temperature | Average: 89 K |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: GENERIC CCD (2k x 2k) / Number real images: 79 / Average electron dose: 20 e/Å2 / Bits/pixel: 8 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final angle assignment | Details: SPIDER: theta 31.72, phi 180 |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 19.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: SPIDER / Number images used: 3232 |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - Chain ID: A |
|---|---|
| Details | PDBEntryID_givenInChain. The coordinates were fitted by manual docking using program O and UCSF Chimera |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
| Output model |  PDB-3nb3: |
-Atomic model buiding 2
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - Chain ID: A |
|---|---|
| Details | PDBEntryID_givenInChain. The coordinates were fitted by manual docking using program O and UCSF Chimera |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
| Output model |  PDB-3nb3: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller