[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-3j7e: Electron cryo-microscopy of human papillomavirus 16 and H16.V5 Fa... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 3j7e | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Electron cryo-microscopy of human papillomavirus 16 and H16.V5 Fab fragments | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  IMMUNE SYSTEM / HPV16.V5 Fab variable domain / HI and FG loops / HPV16 capsid / virus-Fab complex / neutralization antibody / maturation IMMUNE SYSTEM / HPV16.V5 Fab variable domain / HI and FG loops / HPV16 capsid / virus-Fab complex / neutralization antibody / maturation | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationImmunoglobulin V-Type /  Immunoglobulin V-set domain / Immunoglobulin V-set domain /  Immunoglobulin V-set domain / Immunoglobulin subtype / Immunoglobulin V-set domain / Immunoglobulin subtype /  Immunoglobulin / Ig-like domain profile. / Immunoglobulin-like domain / Immunoglobulin-like domain superfamily / Immunoglobulin-like fold Immunoglobulin / Ig-like domain profile. / Immunoglobulin-like domain / Immunoglobulin-like domain superfamily / Immunoglobulin-like foldSimilarity search - Domain/homology | ||||||
| Biological species |   Mus musculus (house mouse) Mus musculus (house mouse) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 13.6 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 13.6 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Lee, H. / Brendle, S.A. / Bywaters, S.M. / Christensen, N.D. / Hafenstein, S. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Virol / Year: 2015 Journal: J Virol / Year: 2015Title: A cryo-electron microscopy study identifies the complete H16.V5 epitope and reveals global conformational changes initiated by binding of the neutralizing antibody fragment. Authors: Hyunwook Lee / Sarah A Brendle / Stephanie M Bywaters / Jian Guan / Robert E Ashley / Joshua D Yoder / Alexander M Makhov / James F Conway / Neil D Christensen / Susan Hafenstein /  Abstract: Human papillomavirus 16 (HPV16) is a worldwide health threat and an etiologic agent of cervical cancer. To understand the antigenic properties of HPV16, we pursued a structural study to elucidate HPV ...Human papillomavirus 16 (HPV16) is a worldwide health threat and an etiologic agent of cervical cancer. To understand the antigenic properties of HPV16, we pursued a structural study to elucidate HPV capsids and antibody interactions. The cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of a mature HPV16 particle and an altered capsid particle were solved individually and as complexes with fragment of antibody (Fab) from the neutralizing antibody H16.V5. Fitted crystal structures provided a pseudoatomic model of the virus-Fab complex, which identified a precise footprint of H16.V5, including previously unrecognized residues. The altered-capsid-Fab complex map showed that binding of the Fab induced significant conformational changes that were not seen in the altered-capsid structure alone. These changes included more ordered surface loops, consolidated so-called "invading-arm" structures, and tighter intercapsomeric connections at the capsid floor. The H16.V5 Fab preferentially bound hexavalent capsomers likely with a stabilizing effect that directly correlated with the number of bound Fabs. Additional cryo-EM reconstructions of the virus-Fab complex for different incubation times and structural analysis provide a model for a hyperstabilization of the capsomer by H16.V5 Fab and showed that the Fab distinguishes subtle differences between antigenic sites. IMPORTANCE: Our analysis of the cryo-EM reconstructions of the HPV16 capsids and virus-Fab complexes has identified the entire HPV.V5 conformational epitope and demonstrated a detailed neutralization ...IMPORTANCE: Our analysis of the cryo-EM reconstructions of the HPV16 capsids and virus-Fab complexes has identified the entire HPV.V5 conformational epitope and demonstrated a detailed neutralization mechanism of this clinically important monoclonal antibody against HPV16. The Fab bound and ordered the apical loops of HPV16. This conformational change was transmitted to the lower region of the capsomer, resulting in enhanced intercapsomeric interactions evidenced by the more ordered capsid floor and "invading-arm" structures. This study advances the understanding of the neutralization mechanism used by H16.V5. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  3j7e.cif.gz 3j7e.cif.gz | 165.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb3j7e.ent.gz pdb3j7e.ent.gz | 133.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  3j7e.json.gz 3j7e.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j7/3j7e https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j7/3j7e ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j7/3j7e ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j7/3j7e | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5994MC  5991C  5992C  5993C  6118C  6119C 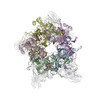 3j7gC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | x 60
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 | x 5
|
| 4 | x 6
|
| 5 | 
|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: (Schoenflies symbol : I (icosahedral : I (icosahedral )) )) |
- Components
Components
| #1: Antibody | Mass: 12623.161 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Fragment: variable domain / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Mus musculus (house mouse) / Cell: hybridoma Mus musculus (house mouse) / Cell: hybridoma#2: Antibody | Mass: 13497.968 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Fragment: variable domain / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Mus musculus (house mouse) / Cell: hybridoma / References: UniProt: K7TH34*PLUS Mus musculus (house mouse) / Cell: hybridoma / References: UniProt: K7TH34*PLUS |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 42 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details of virus | Empty: NO / Enveloped: NO / Host category: VERTEBRATES / Isolate: OTHER / Type: VIRION | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural host | Organism: Homo sapiens | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | Name: 137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 10 mM Na2HPO4, 1.8 mM KH2PO4 / pH: 7.4 Details: 137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 10 mM Na2HPO4, 1.8 mM KH2PO4 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: glow-discharged holey carbon Quantifoil grids | ||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: GATAN CRYOPLUNGE 3 / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Temp: 102 K / Humidity: 90 % Details: Blot for 0.7 seconds before plunging into liquid ethane (GATAN CRYOPLUNGE 3). Method: Blot for 0.7 seconds before plunging |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: JEOL 2100 / Date: Oct 30, 2013 |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source : LAB6 / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN : LAB6 / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 80000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3990 nm / Nominal defocus min: 690 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 80000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3990 nm / Nominal defocus min: 690 nm / Cs : 2 mm : 2 mm |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN / Temperature: 95 K / Tilt angle max: 0 ° / Tilt angle min: 0 ° |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 15 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN ULTRASCAN 4000 (4k x 4k) |
| Image scans | Num. digital images: 411 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Relative weight: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Details: Each particle | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : I (icosahedral : I (icosahedral ) ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Method: Cross-common lines / Resolution: 13.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 2075 / Nominal pixel size: 1.48 Å / Actual pixel size: 1.48 Å Details: Semi-automatic particle selection was performed using e2boxer.py to obtain the particle coordinates, followed by particle boxing, linearization, normalization, and apodization of the images ...Details: Semi-automatic particle selection was performed using e2boxer.py to obtain the particle coordinates, followed by particle boxing, linearization, normalization, and apodization of the images using Robem. Defocus and astigmatism values to perform contrast transfer function (CTF) correction were assessed using Robem for the extracted particles. The icosahedrally averaged reconstructions were initiated using a random model generated with setup_rmc and reached 14 A resolution estimated at a Fourier Shell Correlation (FSC) of 0.5. For the last step of refinement, the final maps were CTF-corrected using a B factor of 200 A2. (Single particle--Applied symmetry: I) Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL / Details: REFINEMENT PROTOCOL--flexible | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj

