+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-2650 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the mammalian ribosome-Sec61 complex | |||||||||
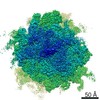
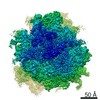
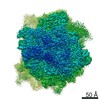
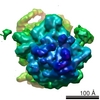
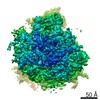
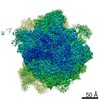
 Map data Map data | Final map for mammalian ribosome in complex with Sec61 in idle configuration with the large subunit masked along refinement | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  translation / translation /  ribosome / ribosome /  mammalian / mammalian /  sec61 sec61 | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information : / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / VLDLR internalisation and degradation / Interferon alpha/beta signaling / Negative regulators of DDX58/IFIH1 signaling / RAS processing / Inactivation of CSF3 (G-CSF) signaling / : / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / VLDLR internalisation and degradation / Interferon alpha/beta signaling / Negative regulators of DDX58/IFIH1 signaling / RAS processing / Inactivation of CSF3 (G-CSF) signaling /  Regulation of BACH1 activity / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway ... Regulation of BACH1 activity / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway ... : / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / VLDLR internalisation and degradation / Interferon alpha/beta signaling / Negative regulators of DDX58/IFIH1 signaling / RAS processing / Inactivation of CSF3 (G-CSF) signaling / : / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / VLDLR internalisation and degradation / Interferon alpha/beta signaling / Negative regulators of DDX58/IFIH1 signaling / RAS processing / Inactivation of CSF3 (G-CSF) signaling /  Regulation of BACH1 activity / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway / Regulation of NF-kappa B signaling / GSK3B and BTRC:CUL1-mediated-degradation of NFE2L2 / regulation of cell cycle => GO:0051726 / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / Translesion Synthesis by POLH / Oxygen-dependent proline hydroxylation of Hypoxia-inducible Factor Alpha / Downregulation of ERBB4 signaling / Spry regulation of FGF signaling / Downregulation of ERBB2:ERBB3 signaling / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / APC/C:Cdh1 mediated degradation of Cdc20 and other APC/C:Cdh1 targeted proteins in late mitosis/early G1 / Cdc20:Phospho-APC/C mediated degradation of Cyclin A / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / EGFR downregulation / SCF(Skp2)-mediated degradation of p27/p21 / Degradation of beta-catenin by the destruction complex / TCF dependent signaling in response to WNT / Downstream TCR signaling / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / Downregulation of SMAD2/3:SMAD4 transcriptional activity / SMAD2/SMAD3:SMAD4 heterotrimer regulates transcription / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / Stimuli-sensing channels / FCERI mediated NF-kB activation / Regulation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA / Autodegradation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 / Deactivation of the beta-catenin transactivating complex / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / activated TAK1 mediates p38 MAPK activation / JNK (c-Jun kinases) phosphorylation and activation mediated by activated human TAK1 / AUF1 (hnRNP D0) binds and destabilizes mRNA / Asymmetric localization of PCP proteins / Degradation of AXIN / Degradation of DVL / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / Regulation of TNFR1 signaling / TNFR1-induced NF-kappa-B signaling pathway / Hedgehog ligand biogenesis / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) signaling / Degradation of GLI1 by the proteasome / GLI3 is processed to GLI3R by the proteasome / Hedgehog 'on' state / Negative regulation of FGFR1 signaling / Negative regulation of FGFR2 signaling / Negative regulation of FGFR3 signaling / Negative regulation of FGFR4 signaling / Translesion synthesis by POLK / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Termination of translesion DNA synthesis / Regulation of RAS by GAPs / TNFR2 non-canonical NF-kB pathway / Negative regulation of MAPK pathway / Regulation of necroptotic cell death / MAP3K8 (TPL2)-dependent MAPK1/3 activation / HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) / MAPK6/MAPK4 signaling / UCH proteinases / Josephin domain DUBs / Ub-specific processing proteases / Ovarian tumor domain proteases / Metalloprotease DUBs / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / DNA Damage Recognition in GG-NER / Formation of Incision Complex in GG-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / Dual Incision in GG-NER / Fanconi Anemia Pathway / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Phosphorylation / Regulation of TP53 Degradation / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Methylation / Negative regulation of MET activity / Orc1 removal from chromatin / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / Cyclin D associated events in G1 / G2/M Checkpoints / Ubiquitin Mediated Degradation of Phosphorylated Cdc25A / Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Cyclin D / PTK6 Regulates RTKs and Their Effectors AKT1 and DOK1 / FBXL7 down-regulates AURKA during mitotic entry and in early mitosis / Cargo recognition for clathrin-mediated endocytosis / Downregulation of ERBB2 signaling / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs Regulation of BACH1 activity / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway / Regulation of NF-kappa B signaling / GSK3B and BTRC:CUL1-mediated-degradation of NFE2L2 / regulation of cell cycle => GO:0051726 / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / Translesion Synthesis by POLH / Oxygen-dependent proline hydroxylation of Hypoxia-inducible Factor Alpha / Downregulation of ERBB4 signaling / Spry regulation of FGF signaling / Downregulation of ERBB2:ERBB3 signaling / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / APC/C:Cdh1 mediated degradation of Cdc20 and other APC/C:Cdh1 targeted proteins in late mitosis/early G1 / Cdc20:Phospho-APC/C mediated degradation of Cyclin A / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / EGFR downregulation / SCF(Skp2)-mediated degradation of p27/p21 / Degradation of beta-catenin by the destruction complex / TCF dependent signaling in response to WNT / Downstream TCR signaling / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / Downregulation of SMAD2/3:SMAD4 transcriptional activity / SMAD2/SMAD3:SMAD4 heterotrimer regulates transcription / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / Stimuli-sensing channels / FCERI mediated NF-kB activation / Regulation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA / Autodegradation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 / Deactivation of the beta-catenin transactivating complex / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / activated TAK1 mediates p38 MAPK activation / JNK (c-Jun kinases) phosphorylation and activation mediated by activated human TAK1 / AUF1 (hnRNP D0) binds and destabilizes mRNA / Asymmetric localization of PCP proteins / Degradation of AXIN / Degradation of DVL / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / Regulation of TNFR1 signaling / TNFR1-induced NF-kappa-B signaling pathway / Hedgehog ligand biogenesis / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) signaling / Degradation of GLI1 by the proteasome / GLI3 is processed to GLI3R by the proteasome / Hedgehog 'on' state / Negative regulation of FGFR1 signaling / Negative regulation of FGFR2 signaling / Negative regulation of FGFR3 signaling / Negative regulation of FGFR4 signaling / Translesion synthesis by POLK / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Termination of translesion DNA synthesis / Regulation of RAS by GAPs / TNFR2 non-canonical NF-kB pathway / Negative regulation of MAPK pathway / Regulation of necroptotic cell death / MAP3K8 (TPL2)-dependent MAPK1/3 activation / HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) / MAPK6/MAPK4 signaling / UCH proteinases / Josephin domain DUBs / Ub-specific processing proteases / Ovarian tumor domain proteases / Metalloprotease DUBs / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / DNA Damage Recognition in GG-NER / Formation of Incision Complex in GG-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / Dual Incision in GG-NER / Fanconi Anemia Pathway / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Phosphorylation / Regulation of TP53 Degradation / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Methylation / Negative regulation of MET activity / Orc1 removal from chromatin / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / Cyclin D associated events in G1 / G2/M Checkpoints / Ubiquitin Mediated Degradation of Phosphorylated Cdc25A / Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Cyclin D / PTK6 Regulates RTKs and Their Effectors AKT1 and DOK1 / FBXL7 down-regulates AURKA during mitotic entry and in early mitosis / Cargo recognition for clathrin-mediated endocytosis / Downregulation of ERBB2 signaling / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCsSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Sus scrofa domesticus (domestic pig) Sus scrofa domesticus (domestic pig) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Voorhees RM / Fernandez IS / Scheres SHW / Hegde R | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2014 Journal: Cell / Year: 2014Title: Structure of the mammalian ribosome-Sec61 complex to 3.4 Å resolution. Authors: Rebecca M Voorhees / Israel S Fernández / Sjors H W Scheres / Ramanujan S Hegde /  Abstract: Cotranslational protein translocation is a universally conserved process for secretory and membrane protein biosynthesis. Nascent polypeptides emerging from a translating ribosome are either ...Cotranslational protein translocation is a universally conserved process for secretory and membrane protein biosynthesis. Nascent polypeptides emerging from a translating ribosome are either transported across or inserted into the membrane via the ribosome-bound Sec61 channel. Here, we report structures of a mammalian ribosome-Sec61 complex in both idle and translating states, determined to 3.4 and 3.9 Å resolution. The data sets permit building of a near-complete atomic model of the mammalian ribosome, visualization of A/P and P/E hybrid-state tRNAs, and analysis of a nascent polypeptide in the exit tunnel. Unprecedented chemical detail is observed for both the ribosome-Sec61 interaction and the conformational state of Sec61 upon ribosome binding. Comparison of the maps from idle and translating complexes suggests how conformational changes to the Sec61 channel could facilitate translocation of a secreted polypeptide. The high-resolution structure of the mammalian ribosome-Sec61 complex provides a valuable reference for future functional and structural studies. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_2650.map.gz emd_2650.map.gz | 31.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-2650-v30.xml emd-2650-v30.xml emd-2650.xml emd-2650.xml | 8.6 KB 8.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  EMD-2650.png EMD-2650.png | 307.4 KB | ||
| Others |  60S_idle_half1_unfil.map 60S_idle_half1_unfil.map 60S_idle_half2_unfil.map 60S_idle_half2_unfil.map | 282.6 MB 282.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2650 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2650 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2650 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2650 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3j7qMC 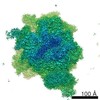 2644C 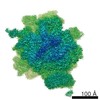 2646C 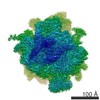 2649C  3j7oC  3j7pC  3j7rC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_2650.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 276 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_2650.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 276 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Final map for mammalian ribosome in complex with Sec61 in idle configuration with the large subunit masked along refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.34 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Supplemental map: 60S idle half1 unfil.map
| File | 60S_idle_half1_unfil.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Supplemental map: 60S idle half2 unfil.map
| File | 60S_idle_half2_unfil.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Mammalian ribosome in complex with Sec61 in a idle configuration ...
| Entire | Name: Mammalian ribosome in complex with Sec61 in a idle configuration with the large subunit (60S) masked during processing. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Mammalian ribosome in complex with Sec61 in a idle configuration ...
| Supramolecule | Name: Mammalian ribosome in complex with Sec61 in a idle configuration with the large subunit (60S) masked during processing. type: sample / ID: 1000 / Number unique components: 2 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #1: Mammalian ribosome
| Supramolecule | Name: Mammalian ribosome / type: complex / ID: 1 / Recombinant expression: No / Ribosome-details: ribosome-eukaryote: ALL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Sus scrofa domesticus (domestic pig) / synonym: Domestic Pig / Tissue: pancreas Sus scrofa domesticus (domestic pig) / synonym: Domestic Pig / Tissue: pancreas |
-Macromolecule #1: Sec61
| Macromolecule | Name: Sec61 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Recombinant expression: No |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Sus scrofa domesticus (domestic pig) / synonym: Domestic Pig Sus scrofa domesticus (domestic pig) / synonym: Domestic Pig |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Details: 50mM HEPES, 200mM K-acetate, 15mM Mg-acetate, 1mM DTT |
|---|---|
| Grid | Details: Quantifoil R2/2 400 mesh copper grids. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 120 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV Method: 3uL of sampled was incubated on the grid for 30 seconds before blotting for 9 second |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 0.003 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.001 µm / Nominal magnification: 47000 Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 0.003 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.001 µm / Nominal magnification: 47000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Date | Apr 7, 2014 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Number real images: 1900 / Average electron dose: 25 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Details: Each particle |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.4 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: Relion / Number images used: 80019 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller















 Z
Z Y
Y X
X

















