[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
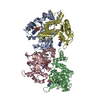
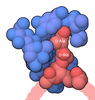
Yorodumi- EMDB-24617: Cryo-EM structure of murine Dispatched in complex with Sonic hedgehog -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-24617 | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of murine Dispatched in complex with Sonic hedgehog | ||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | DISP1-A:ShhN complex - auto-sharpened map from cryoSPARC nonuniform refinement (paper version), units of standard deviation above mean density. | ||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RND transporter /  Hedgehog binding / Sterol sensing domain / Hedgehog binding / Sterol sensing domain /  sodium binding / sodium binding /  MEMBRANE PROTEIN MEMBRANE PROTEIN | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationforebrain regionalization /  cell proliferation in external granule layer / zona limitans intrathalamica formation / positive regulation of neurotrophin production / positive regulation of photoreceptor cell differentiation / fungiform papilla development / Release of Hh-Np from the secreting cell / digestive tract mesoderm development / epithelial-mesenchymal signaling involved in prostate gland development / fungiform papilla morphogenesis ...forebrain regionalization / cell proliferation in external granule layer / zona limitans intrathalamica formation / positive regulation of neurotrophin production / positive regulation of photoreceptor cell differentiation / fungiform papilla development / Release of Hh-Np from the secreting cell / digestive tract mesoderm development / epithelial-mesenchymal signaling involved in prostate gland development / fungiform papilla morphogenesis ...forebrain regionalization /  cell proliferation in external granule layer / zona limitans intrathalamica formation / positive regulation of neurotrophin production / positive regulation of photoreceptor cell differentiation / fungiform papilla development / Release of Hh-Np from the secreting cell / digestive tract mesoderm development / epithelial-mesenchymal signaling involved in prostate gland development / fungiform papilla morphogenesis / ventral spinal cord interneuron specification / tongue morphogenesis / respiratory tube development / Ligand-receptor interactions / patched ligand maturation / Activation of SMO / mesenchymal-epithelial cell signaling involved in prostate gland development / positive regulation of oligodendrocyte progenitor proliferation / trachea development / positive regulation of skeletal muscle cell proliferation / anatomical structure formation involved in morphogenesis / right lung development / left lung development / primary prostatic bud elongation / regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in prostate gland development / mesenchymal smoothened signaling pathway involved in prostate gland development / positive regulation of sclerotome development / tracheoesophageal septum formation / negative regulation of ureter smooth muscle cell differentiation / positive regulation of ureter smooth muscle cell differentiation / negative regulation of kidney smooth muscle cell differentiation / positive regulation of kidney smooth muscle cell differentiation / cell proliferation in external granule layer / zona limitans intrathalamica formation / positive regulation of neurotrophin production / positive regulation of photoreceptor cell differentiation / fungiform papilla development / Release of Hh-Np from the secreting cell / digestive tract mesoderm development / epithelial-mesenchymal signaling involved in prostate gland development / fungiform papilla morphogenesis / ventral spinal cord interneuron specification / tongue morphogenesis / respiratory tube development / Ligand-receptor interactions / patched ligand maturation / Activation of SMO / mesenchymal-epithelial cell signaling involved in prostate gland development / positive regulation of oligodendrocyte progenitor proliferation / trachea development / positive regulation of skeletal muscle cell proliferation / anatomical structure formation involved in morphogenesis / right lung development / left lung development / primary prostatic bud elongation / regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in prostate gland development / mesenchymal smoothened signaling pathway involved in prostate gland development / positive regulation of sclerotome development / tracheoesophageal septum formation / negative regulation of ureter smooth muscle cell differentiation / positive regulation of ureter smooth muscle cell differentiation / negative regulation of kidney smooth muscle cell differentiation / positive regulation of kidney smooth muscle cell differentiation /  regulation of odontogenesis / positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in ureter development / polarity specification of anterior/posterior axis / trunk neural crest cell migration / hindgut morphogenesis / striated muscle tissue development / negative regulation of alpha-beta T cell differentiation / regulation of glial cell proliferation / regulation of prostatic bud formation / metanephric mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in metanephros development / positive regulation of penile erection / neural tube formation / formation of anatomical boundary / lung epithelium development / positive regulation of striated muscle cell differentiation / myotube differentiation / trachea morphogenesis / regulation of epithelial cell proliferation involved in prostate gland development / cholesterol-protein transferase activity / bud outgrowth involved in lung branching / diaphragm development / telencephalon regionalization / epithelial-mesenchymal cell signaling / regulation of odontogenesis / positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in ureter development / polarity specification of anterior/posterior axis / trunk neural crest cell migration / hindgut morphogenesis / striated muscle tissue development / negative regulation of alpha-beta T cell differentiation / regulation of glial cell proliferation / regulation of prostatic bud formation / metanephric mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in metanephros development / positive regulation of penile erection / neural tube formation / formation of anatomical boundary / lung epithelium development / positive regulation of striated muscle cell differentiation / myotube differentiation / trachea morphogenesis / regulation of epithelial cell proliferation involved in prostate gland development / cholesterol-protein transferase activity / bud outgrowth involved in lung branching / diaphragm development / telencephalon regionalization / epithelial-mesenchymal cell signaling /  laminin-1 binding / vasculogenesis involved in coronary vascular morphogenesis / Hedgehog ligand biogenesis / salivary gland cavitation / negative regulation of cholesterol efflux / determination of left/right asymmetry in lateral mesoderm / spinal cord dorsal/ventral patterning / negative regulation of mesenchymal cell apoptotic process / positive regulation of cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation / laminin-1 binding / vasculogenesis involved in coronary vascular morphogenesis / Hedgehog ligand biogenesis / salivary gland cavitation / negative regulation of cholesterol efflux / determination of left/right asymmetry in lateral mesoderm / spinal cord dorsal/ventral patterning / negative regulation of mesenchymal cell apoptotic process / positive regulation of cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation /  cell development / negative regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus / spinal cord motor neuron differentiation / positive regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus / cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation / intermediate filament organization / mesenchymal cell apoptotic process / embryonic skeletal system development / male genitalia morphogenesis / limb bud formation / lung lobe morphogenesis / prostate gland development / skeletal muscle fiber differentiation / establishment of epithelial cell polarity / fungiform papilla formation / cell development / negative regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus / spinal cord motor neuron differentiation / positive regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus / cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation / intermediate filament organization / mesenchymal cell apoptotic process / embryonic skeletal system development / male genitalia morphogenesis / limb bud formation / lung lobe morphogenesis / prostate gland development / skeletal muscle fiber differentiation / establishment of epithelial cell polarity / fungiform papilla formation /  patched binding / thalamus development / embryonic digestive tract morphogenesis / embryonic foregut morphogenesis / somite development / epithelial cell proliferation involved in salivary gland morphogenesis / hindbrain development / positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue development / animal organ formation / ectoderm development / neuron fate commitment / stem cell development / branching involved in prostate gland morphogenesis / dorsal/ventral neural tube patterning / negative regulation of dopaminergic neuron differentiation / mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in lung development / negative thymic T cell selection / skeletal muscle cell proliferation / positive regulation of immature T cell proliferation in thymus / lymphoid progenitor cell differentiation / mesenchymal cell proliferation patched binding / thalamus development / embryonic digestive tract morphogenesis / embryonic foregut morphogenesis / somite development / epithelial cell proliferation involved in salivary gland morphogenesis / hindbrain development / positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue development / animal organ formation / ectoderm development / neuron fate commitment / stem cell development / branching involved in prostate gland morphogenesis / dorsal/ventral neural tube patterning / negative regulation of dopaminergic neuron differentiation / mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in lung development / negative thymic T cell selection / skeletal muscle cell proliferation / positive regulation of immature T cell proliferation in thymus / lymphoid progenitor cell differentiation / mesenchymal cell proliferationSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Mus musculus (house mouse) Mus musculus (house mouse) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.7 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.7 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Asarnow D / Wang Q | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 5 items United States, 5 items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: Dispatched uses Na flux to power release of lipid-modified Hedgehog. Authors: Qianqian Wang / Daniel E Asarnow / Ke Ding / Randall K Mann / Jason Hatakeyama / Yunxiao Zhang / Yong Ma / Yifan Cheng / Philip A Beachy /   Abstract: The Dispatched protein, which is related to the NPC1 and PTCH1 cholesterol transporters and to H-driven transporters of the RND family, enables tissue-patterning activity of the lipid-modified ...The Dispatched protein, which is related to the NPC1 and PTCH1 cholesterol transporters and to H-driven transporters of the RND family, enables tissue-patterning activity of the lipid-modified Hedgehog protein by releasing it from tightly -localized sites of embryonic expression. Here we determine a cryo-electron microscopy structure of the mouse protein Dispatched homologue 1 (DISP1), revealing three Na ions coordinated within a channel that traverses its transmembrane domain. We find that the rate of Hedgehog export is dependent on the Na gradient across the plasma membrane. The transmembrane channel and Na binding are disrupted in DISP1-NNN, a variant with asparagine substitutions for three intramembrane aspartate residues that each coordinate and neutralize the charge of one of the three Na ions. DISP1-NNN and variants that disrupt single Na sites retain binding to, but are impaired in export of the lipid-modified Hedgehog protein to the SCUBE2 acceptor. Interaction of the amino-terminal signalling domain of the Sonic hedgehog protein (ShhN) with DISP1 occurs via an extensive buried surface area and contacts with an extended furin-cleaved DISP1 arm. Variability analysis reveals that ShhN binding is restricted to one extreme of a continuous series of DISP1 conformations. The bound and unbound DISP1 conformations display distinct Na-site occupancies, which suggests a mechanism by which transmembrane Na flux may power extraction of the lipid-linked Hedgehog signal from the membrane. Na-coordinating residues in DISP1 are conserved in PTCH1 and other metazoan RND family members, suggesting that Na flux powers their conformationally driven activities. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_24617.map.gz emd_24617.map.gz | 82.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-24617-v30.xml emd-24617-v30.xml emd-24617.xml emd-24617.xml | 30.8 KB 30.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_24617.png emd_24617.png | 129.6 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_24617_msk_1.map emd_24617_msk_1.map emd_24617_msk_2.map emd_24617_msk_2.map | 91.1 MB 91.1 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-24617.cif.gz emd-24617.cif.gz | 8.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_24617_additional_1.map.gz emd_24617_additional_1.map.gz emd_24617_additional_2.map.gz emd_24617_additional_2.map.gz emd_24617_half_map_1.map.gz emd_24617_half_map_1.map.gz emd_24617_half_map_2.map.gz emd_24617_half_map_2.map.gz | 44.8 MB 85.9 MB 84.5 MB 84.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24617 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24617 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24617 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24617 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7rpkMC  7rphC  7rpiC  7rpjC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_24617.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 91.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_24617.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 91.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | DISP1-A:ShhN complex - auto-sharpened map from cryoSPARC nonuniform refinement (paper version), units of standard deviation above mean density. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.835 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_24617_msk_1.map emd_24617_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Mask #2
| File |  emd_24617_msk_2.map emd_24617_msk_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: DISP1-A:ShhN complex - raw map from cryoSPARC nonuniform...
| File | emd_24617_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | DISP1-A:ShhN complex - raw map from cryoSPARC nonuniform refinement (paper version). | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: DISP1-A:ShhN complex - auto-sharpened map from cryoSPARC nonuniform...
| File | emd_24617_additional_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | DISP1-A:ShhN complex - auto-sharpened map from cryoSPARC nonuniform refinement (paper version). | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: DISP1-A:ShhN complex - half map 1 from cryoSPARC...
| File | emd_24617_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | DISP1-A:ShhN complex - half map 1 from cryoSPARC nonuniform refinement (paper version). | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: DISP1-A:ShhN complex - half map 2 from cryoSPARC...
| File | emd_24617_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | DISP1-A:ShhN complex - half map 2 from cryoSPARC nonuniform refinement (paper version). | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Dispatched protein complexed with Sonic hedgehog 26-189
+Supramolecule #1: Dispatched protein complexed with Sonic hedgehog 26-189
+Macromolecule #1: Protein dispatched homolog 1
+Macromolecule #2: Sonic hedgehog protein
+Macromolecule #3: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE
+Macromolecule #4: Lauryl Maltose Neopentyl Glycol
+Macromolecule #5: SODIUM ION
+Macromolecule #6: (2S)-3-{[(S)-(2-aminoethoxy)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]oxy}-2-(hexanoylo...
+Macromolecule #7: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
+Macromolecule #8: CALCIUM ION
+Macromolecule #9: ZINC ION
+Macromolecule #10: SULFATE ION
+Macromolecule #11: water
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.56 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 281 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV Details: Wait time 20 seconds, blot time 4 seconds, blotting force 0. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Calibrated magnification: 59880 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 |
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Details | Automated data collection in SerialEM using 3x3 image shift pattern (one shot per hole), using beam tilt compensation. |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 1687 / Average electron dose: 66.7 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Particle selection | Number selected: 1406648 |
|---|---|
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER / Details: Ab initio reconstruction from cryoSPARC |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: RANDOM ASSIGNMENT / Software - Name: cryoSPARC |
| Final 3D classification | Number classes: 4 / Software - Name: cryoSPARC |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: cryoSPARC |
| Final reconstruction | Number classes used: 1 / Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: cryoSPARC / Number images used: 204786 |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Overall B value: 69.9 |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-7rpk: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



















 Z
Z Y
Y X
X