+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
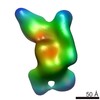
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20816 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of M-6-P/IGFII Receptor and IGFII complex | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information kringle domain binding / spongiotrophoblast cell proliferation / positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue growth / negative regulation of muscle cell differentiation / embryonic placenta morphogenesis / regulation of muscle cell differentiation / Signaling by Type 1 Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF1R) / IRS-related events triggered by IGF1R / kringle domain binding / spongiotrophoblast cell proliferation / positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue growth / negative regulation of muscle cell differentiation / embryonic placenta morphogenesis / regulation of muscle cell differentiation / Signaling by Type 1 Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF1R) / IRS-related events triggered by IGF1R /  insulin-like growth factor binding / insulin-like growth factor binding /  genomic imprinting ... genomic imprinting ... kringle domain binding / spongiotrophoblast cell proliferation / positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue growth / negative regulation of muscle cell differentiation / embryonic placenta morphogenesis / regulation of muscle cell differentiation / Signaling by Type 1 Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF1R) / IRS-related events triggered by IGF1R / kringle domain binding / spongiotrophoblast cell proliferation / positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue growth / negative regulation of muscle cell differentiation / embryonic placenta morphogenesis / regulation of muscle cell differentiation / Signaling by Type 1 Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF1R) / IRS-related events triggered by IGF1R /  insulin-like growth factor binding / insulin-like growth factor binding /  genomic imprinting / positive regulation of organ growth / exocrine pancreas development / positive regulation of multicellular organism growth / lysosomal transport / positive regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation / genomic imprinting / positive regulation of organ growth / exocrine pancreas development / positive regulation of multicellular organism growth / lysosomal transport / positive regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation /  transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activator activity / positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation / transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activator activity / positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation /  D-mannose binding / positive regulation of cell division / endocytic vesicle / embryonic placenta development / positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process / SHC-related events triggered by IGF1R / positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway / striated muscle cell differentiation / D-mannose binding / positive regulation of cell division / endocytic vesicle / embryonic placenta development / positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process / SHC-related events triggered by IGF1R / positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway / striated muscle cell differentiation /  insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division / insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway / platelet alpha granule lumen / insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division / insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway / platelet alpha granule lumen /  phosphoprotein binding / animal organ morphogenesis / phosphoprotein binding / animal organ morphogenesis /  growth factor activity / growth factor activity /  insulin receptor binding / insulin receptor binding /  trans-Golgi network / trans-Golgi network /  hormone activity / osteoblast differentiation / glucose metabolic process / Regulation of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) transport and uptake by Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) / positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / hormone activity / osteoblast differentiation / glucose metabolic process / Regulation of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) transport and uptake by Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) / positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation /  integrin binding / late endosome / Platelet degranulation / insulin receptor signaling pathway / integrin binding / late endosome / Platelet degranulation / insulin receptor signaling pathway /  signaling receptor activity / in utero embryonic development / positive regulation of MAPK cascade / signaling receptor activity / in utero embryonic development / positive regulation of MAPK cascade /  receptor ligand activity / positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / endosome membrane / receptor ligand activity / positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / endosome membrane /  Golgi membrane / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / Golgi membrane / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / regulation of DNA-templated transcription /  Golgi apparatus / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / Golgi apparatus / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II /  cell surface / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / cell surface / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II /  extracellular space / extracellular region / extracellular space / extracellular region /  plasma membrane plasma membraneSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Bos taurus (cattle) / Bos taurus (cattle) /   Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /   Bovine (cattle) Bovine (cattle) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 4.32 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 4.32 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang R / Qi X / Li X | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2020 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2020Title: Marked structural rearrangement of mannose 6-phosphate/IGF2 receptor at different pH environments. Authors: Rong Wang / Xiaofeng Qi / Philip Schmiege / Elias Coutavas / Xiaochun Li /  Abstract: Many cell surface receptors internalize their ligands and deliver them to endosomes, where the acidic pH causes the ligand to dissociate. The liberated receptor returns to the cell surface in a ...Many cell surface receptors internalize their ligands and deliver them to endosomes, where the acidic pH causes the ligand to dissociate. The liberated receptor returns to the cell surface in a process called receptor cycling. The structural basis for pH-dependent ligand dissociation is not well understood. In some receptors, the ligand binding domain is composed of multiple repeated sequences. The insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor (IGF2R) contains 15 β strand-rich repeat domains. The overall structure and the mechanism by which IGF2R binds IGF2 and releases it are unknown. We used cryo-EM to determine the structures of the IGF2R at pH 7.4 with IGF2 bound and at pH 4.5 in the ligand-dissociated state. The results reveal different arrangements of the receptor in different pH environments mediated by changes in the interactions between the repeated sequences. These results have implications for our understanding of ligand release from receptors in endocytic compartments. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20816.map.gz emd_20816.map.gz | 154.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20816-v30.xml emd-20816-v30.xml emd-20816.xml emd-20816.xml | 12.9 KB 12.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_20816.png emd_20816.png | 57.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20816 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20816 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20816 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20816 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6um2MC  6um1C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20816.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20816.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.86 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : IGFIIR and IGFII complex
| Entire | Name: IGFIIR and IGFII complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: IGFIIR and IGFII complex
| Supramolecule | Name: IGFIIR and IGFII complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: Cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor
| Supramolecule | Name: Cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Bos taurus (cattle) Bos taurus (cattle) |
-Supramolecule #3: Insulin-like growth factor II
| Supramolecule | Name: Insulin-like growth factor II / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli K-12 (bacteria) Escherichia coli K-12 (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: Cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor
| Macromolecule | Name: Cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Bovine (cattle) Bovine (cattle) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 274.830125 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MEAAAGRSSH LGPAPAGRPP RCPLLLQLQL LLLLLLLPPG WVPGAAGTQG AEFPELCSYT WEAVDTKNNM LYKINICGNM GVAQCGPSS AVCMHDLKTD SFHSVGDSLL KTASRSLLEF NTTVNCKQQN HKIQSSITFL CGKTLGTPEF VTATDCVHYF E WRTTAACK ...String: MEAAAGRSSH LGPAPAGRPP RCPLLLQLQL LLLLLLLPPG WVPGAAGTQG AEFPELCSYT WEAVDTKNNM LYKINICGNM GVAQCGPSS AVCMHDLKTD SFHSVGDSLL KTASRSLLEF NTTVNCKQQN HKIQSSITFL CGKTLGTPEF VTATDCVHYF E WRTTAACK KNIFKANKEV PCYAFDRELK KHDLNPLIKT SGAYLVDDSD PDTSLFINVC RDIEVLRASS PQVRVCPTGA AA CLVRGDR AFDVGRPQEG LKLVSNDRLV LSYVKEGAGQ PDFCDGHSPA VTITFVCPSE RREGTIPKLT AKSNCRFEIE WVT EYACHR DYLESRSCSL SSAQHDVAVD LQPLSRVEAS DSLFYTSEAD EYTYYLSICG GSQAPICNKK DAAVCQVKKA DSTQ VKVAG RPQNLTLRYS DGDLTLIYFG GEECSSGFQR MSVINFECNQ TAGNNGRGAP VFTGEVDCTY FFTWDTKYAC VHEKE ALLC GVSDGKQRFD LSALARHSEL EQNWEAVDGS QREAEKKHFF INICHRVLQT GQARGCPEDA AVCAVDKNGS KNLGRF ISS PTREKGNIQL SYSDGDECGG GQKIITNITL MCKPGDLESA PVLTTSRADG CFYEFEWRTA AACVLSRTEG DNCTVFD SQ AGFSFDLTPL TKKDAYKVET DKYEFHINVC GPVSVGACPP DSGACQVSRS DRKSWNLGRS NAKLSYYDGM IQLTYRDG T PYNNEKRTPR ATLITFLCDR DAGVGFPEYQ EEDNSTYNFR WYTSYACPEE PLECIVTDPV TLDQYDLSRL AKSEGGPGG NWYSLDNGGA RSTWRKYYIN VCRPLNPVPG CDRYASACQM KYQGEQGSYS ETVSISNLGV AKTGPMVEDS GSLLLEYVNG SACTTSDQR RTTYTTRIHL VCSTGSLYTH PIFSLNWECV VSFLWNTAAA CPIRITTDID QVCSIKDPNS GYVFDLNPLN N SRGYVVLG IGKTFLFNVC GDMPACGTLD GKPASGCEAE VQMDDMKTLK PGRLVGLEKS LQLSTEGFIT LNYTGLPSHP NG RADAFII RFVCNDDVYP GTPKFLHQDI DSSLGIRDTF FEFETALACV PSPVDCQVTD PAGNEYDLSG LSKARKPWTA VDT FDEGKK RTFYLSVCTP LPYIPGCHGT AVGCCLVTED SKLNLGVVQI SPQVGANGSL SLVYVNGDKC KNQRFSTRIN LECA HTTGS PTFQLQNDCE YVFLWRTVEA CPVVRAEGDY CEVRDPRHGN LYNLIPLGLN DTVVRAGEYT YYFRVCGELT SGVCP TSDK SKVISSCQEK RGPQGFQKVA GLFNQKLTYE NGVLKMNYTG GDTCHKVYQR STTIFFYCDR STQAPVFLQE TSDCSY LFE WRTQYACPPY DLTECSFKNE AGETYDLSSL SRYSDNWEAV TGTGSTEHYL INVCKSLSPQ AGSDPCPPEA AVCLLGG PK PVNLGRVRDS PQWSQGLTLL KYVDGDLCPD QIRKKSTTIR FTCSESHVNS RPMFISAVED CEYTFSWPTA AACAVKSN V HDDCQVTNPA TGHLFDLSSL SGRAGFTAAY SEKGLVYLSV CGDNENCANG VGACFGQTRI SVGKASKRLT YVDQVLQLV YEGGSPCPSK TGLSYKSVIS FVCRPEVGPT NRPMLISLDK RTCTLFFSWH TPLACEQTTE CSVRNGSSLI DLSPLIHRTG GYEAYDESE DDGSDTSPDF YINICQPLNP MHGLACPAGT AVCKVPVDGP PIDIGRVAGP PILNPIANEV YLNFESSTPC L ADRHFNYT SLITFHCKRG VSMGTPKLLR TSVCDFVFEW ETPLVCPDEV KTDGCSLTDE QLYYSFNLSS LSKSTFKVTR GP HTYSVGV CTAAAGLDEG GCKDGAVCLL SGSKGASFGR LASMKLDYRH QDEAVILSYA NGDTCPPETE DGEPCVFPFV FNG KSYEEC VVESRARLWC ATTANYDRDH EWGFCKHSTS HRTSVIIFKC DEDADVGRPQ VFSEVRGCEV TFEWKTKVVC PPKK MECKF VQKHRTYDLR LLSSLTGSWS FVHNGASYYI NLCQKIYKGP QDCSERASVC KKSTSGEVQV LGLVHTQKLD VVDDR VIVT YSKGHYCGDN KTASAVIELT CAKTVGRPSF TRFDVDSCTY HFSWDSRAAC AVKPQEVQMV NGTITNPANG RSFSLG DIY FKRFSASGDV RTNGDRYIYE IQLSSITGSS SPACSGASIC QRKANDQHFS RKVGTSNQTR YYVQDGDLDV VFTSSSK CG KDKTKSVSST IFFHCDPLVK DGIPEFSHET ADCQYLFSWH TSAVCPLGAG FDEEIAGDDA QEHKGLSERS QAVGAVLS L LLVALTACLL TLLLYKKERR EMVMSRLTNC CRRSANVSYK YSKVNKEEEA DENETEWLME EIQPPAPRPG KEGQENGHV AAKSVRAADT LSALHGDEQD SEDEVLTLPE VKVRPPGRAP GAEGGPPLRP LPRKAPPPLR ADDRVGLVRG EPARRGRPRA AATPISTFH DDSDEDLLHV |
-Macromolecule #2: Insulin-like growth factor II
| Macromolecule | Name: Insulin-like growth factor II / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 7.615667 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli K-12 (bacteria) Escherichia coli K-12 (bacteria) |
| Sequence | String: MAYRPSETLC GGELVDTLQF VCGDRGFYFS RPASRVSRRS RGIVEECCFR SCDLALLETY CATPAKSE |
-Macromolecule #3: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 7 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: DARK FIELD |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 100.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Initial angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
|---|---|
| Final angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.32 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 75821 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller