[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-2009: 3D reconstruction of an archaeal 70S ribosome in complex with aPe... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-2009 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
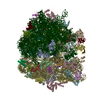
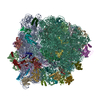
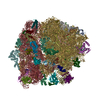
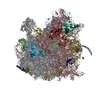
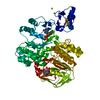
| Title | 3D reconstruction of an archaeal 70S ribosome in complex with aPelota and aABCE1 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | This is a 3D cryo-EM reconstruction of a Pyrococcus furiosus 70S ribosome in complex with aABCE1 and aPelota | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  translation / ribosome recycling / no-go mRNA decay translation / ribosome recycling / no-go mRNA decay | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRNA surveillance / nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, no-go decay / nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, non-stop decay / nonfunctional rRNA decay / ribosome disassembly /  ribonuclease P activity / tRNA 5'-leader removal / cytosolic ribosome / rRNA processing / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding ...RNA surveillance / nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, no-go decay / nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, non-stop decay / nonfunctional rRNA decay / ribosome disassembly / ribonuclease P activity / tRNA 5'-leader removal / cytosolic ribosome / rRNA processing / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding ...RNA surveillance / nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, no-go decay / nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, non-stop decay / nonfunctional rRNA decay / ribosome disassembly /  ribonuclease P activity / tRNA 5'-leader removal / cytosolic ribosome / rRNA processing / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / ribonuclease P activity / tRNA 5'-leader removal / cytosolic ribosome / rRNA processing / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding /  ribosome binding / large ribosomal subunit / ribosome binding / large ribosomal subunit /  ribosome biogenesis / ribosome biogenesis /  regulation of translation / small ribosomal subunit / regulation of translation / small ribosomal subunit /  5S rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / 5S rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit /  endonuclease activity / endonuclease activity /  tRNA binding / tRNA binding /  Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds /  rRNA binding / rRNA binding /  ribosome / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / structural constituent of ribosome /  ribonucleoprotein complex / ribonucleoprotein complex /  translation / translation /  RNA binding / zinc ion binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |    Pyrococcus furiosus (archaea) / Pyrococcus furiosus (archaea) /    Thermococcus kodakarensis (archaea) Thermococcus kodakarensis (archaea) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / cryo EM /  negative staining / Resolution: 6.6 Å negative staining / Resolution: 6.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Becker T / Franckenberg S / Wickles S / Shoemaker CJ / Anger AM / Armache J-P / Sieber H / Ungewickell C / Berninghausen O / Daberkow I ...Becker T / Franckenberg S / Wickles S / Shoemaker CJ / Anger AM / Armache J-P / Sieber H / Ungewickell C / Berninghausen O / Daberkow I / Karcher A / Thomm M / Hopfner K-P / Green R / Beckmann R | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2012 Journal: Nature / Year: 2012Title: Structural basis of highly conserved ribosome recycling in eukaryotes and archaea. Authors: Thomas Becker / Sibylle Franckenberg / Stephan Wickles / Christopher J Shoemaker / Andreas M Anger / Jean-Paul Armache / Heidemarie Sieber / Charlotte Ungewickell / Otto Berninghausen / Ingo ...Authors: Thomas Becker / Sibylle Franckenberg / Stephan Wickles / Christopher J Shoemaker / Andreas M Anger / Jean-Paul Armache / Heidemarie Sieber / Charlotte Ungewickell / Otto Berninghausen / Ingo Daberkow / Annette Karcher / Michael Thomm / Karl-Peter Hopfner / Rachel Green / Roland Beckmann /  Abstract: Ribosome-driven protein biosynthesis is comprised of four phases: initiation, elongation, termination and recycling. In bacteria, ribosome recycling requires ribosome recycling factor and elongation ...Ribosome-driven protein biosynthesis is comprised of four phases: initiation, elongation, termination and recycling. In bacteria, ribosome recycling requires ribosome recycling factor and elongation factor G, and several structures of bacterial recycling complexes have been determined. In the eukaryotic and archaeal kingdoms, however, recycling involves the ABC-type ATPase ABCE1 and little is known about its structural basis. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy reconstructions of eukaryotic and archaeal ribosome recycling complexes containing ABCE1 and the termination factor paralogue Pelota. These structures reveal the overall binding mode of ABCE1 to be similar to canonical translation factors. Moreover, the iron-sulphur cluster domain of ABCE1 interacts with and stabilizes Pelota in a conformation that reaches towards the peptidyl transferase centre, thus explaining how ABCE1 may stimulate peptide-release activity of canonical termination factors. Using the mechanochemical properties of ABCE1, a conserved mechanism in archaea and eukaryotes is suggested that couples translation termination to recycling, and eventually to re-initiation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_2009.map.gz emd_2009.map.gz | 23.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-2009-v30.xml emd-2009-v30.xml emd-2009.xml emd-2009.xml | 11.9 KB 11.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  EMBD_2009.gif EMBD_2009.gif | 551.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2009 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2009 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2009 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2009 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3j15MC  4v6uM  2008C  2010C  3j16C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_2009.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 185.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_2009.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 185.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | This is a 3D cryo-EM reconstruction of a Pyrococcus furiosus 70S ribosome in complex with aABCE1 and aPelota | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.2375 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Pyrococcus furiosus 70S ribosome in complex with aPelota and aABCE1
| Entire | Name: Pyrococcus furiosus 70S ribosome in complex with aPelota and aABCE1 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Pyrococcus furiosus 70S ribosome in complex with aPelota and aABCE1
| Supramolecule | Name: Pyrococcus furiosus 70S ribosome in complex with aPelota and aABCE1 type: sample / ID: 1000 Oligomeric state: One 70S ribosome binds one aPelota and one aABCE1 Number unique components: 3 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #1: Pyrococcus furiosus 70S ribosome
| Supramolecule | Name: Pyrococcus furiosus 70S ribosome / type: complex / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: Pyrococcus furiosus 70S ribosome / Recombinant expression: No / Ribosome-details: ribosome-prokaryote: ALL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:    Pyrococcus furiosus (archaea) Pyrococcus furiosus (archaea) |
-Macromolecule #1: aABCE1
| Macromolecule | Name: aABCE1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: ABCE1 / Oligomeric state: Monomer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:    Pyrococcus furiosus (archaea) Pyrococcus furiosus (archaea) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
-Macromolecule #2: aPelota
| Macromolecule | Name: aPelota / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Name.synonym: Pelota / Oligomeric state: Monomer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:    Thermococcus kodakarensis (archaea) Thermococcus kodakarensis (archaea) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Recombinant plasmid: pET28 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Recombinant plasmid: pET28 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  negative staining, negative staining,  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8.2 Details: 56 mM Tris pH 8.2, 250 mM KOAc, 80 mM NH4OAc, 50 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 2 mM ADPNP |
|---|---|
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Details: cryo-EM |
| Grid | Details: Quantifoil grids (3/3) with 2 nm carbon on top |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Instrument: OTHER / Details: Vitrification instrument: Vitrobot Method: Blot for 10 seconds before plunging, use 2 layer of filter paper |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.6 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 75000 Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.6 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 75000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: autoloader / Specimen holder model: OTHER |
| Details | Final magnification of the object on the CCD image is 148721 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: TVIPS TEMCAM-F416 (4k x 4k) / Digitization - Sampling interval: 15.6 µm / Number real images: 10000 / Average electron dose: 25 e/Å2 / Bits/pixel: 16 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Details: Wiener Filter |
|---|---|
| Final angle assignment | Details: SPIDER |
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 6.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: SPIDER Details: sorting for ribosome conformation and ligand presence was performed Number images used: 51000 |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - Chain ID: A |
|---|---|
| Software | Name: MDFF |
| Details | PDBEntryID_givenInChain. Protocol: rigid body followed by molecular dynamics flexible fitting. rigid body fitting of individual domains followed by molecular dynamics flexible fitting |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
| Output model |  PDB-3j15:  PDB-4v6u: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller