+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 1z8y | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
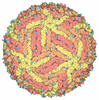
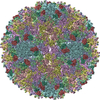
| Title | Mapping the E2 Glycoprotein of Alphaviruses | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  VIRUS / icosahedral enveloped virus / Icosahedral virus VIRUS / icosahedral enveloped virus / Icosahedral virus | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationicosahedral viral capsid, spike /  togavirin / T=4 icosahedral viral capsid / ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding / symbiont-mediated suppression of host toll-like receptor signaling pathway / clathrin-dependent endocytosis of virus by host cell / host cell cytoplasm / togavirin / T=4 icosahedral viral capsid / ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding / symbiont-mediated suppression of host toll-like receptor signaling pathway / clathrin-dependent endocytosis of virus by host cell / host cell cytoplasm /  membrane fusion / membrane => GO:0016020 / serine-type endopeptidase activity ...icosahedral viral capsid, spike / membrane fusion / membrane => GO:0016020 / serine-type endopeptidase activity ...icosahedral viral capsid, spike /  togavirin / T=4 icosahedral viral capsid / ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding / symbiont-mediated suppression of host toll-like receptor signaling pathway / clathrin-dependent endocytosis of virus by host cell / host cell cytoplasm / togavirin / T=4 icosahedral viral capsid / ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding / symbiont-mediated suppression of host toll-like receptor signaling pathway / clathrin-dependent endocytosis of virus by host cell / host cell cytoplasm /  membrane fusion / membrane => GO:0016020 / serine-type endopeptidase activity / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / membrane fusion / membrane => GO:0016020 / serine-type endopeptidase activity / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane /  viral envelope / host cell nucleus / structural molecule activity / virion attachment to host cell / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / viral envelope / host cell nucleus / structural molecule activity / virion attachment to host cell / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane /  proteolysis / proteolysis /  RNA binding / RNA binding /  membrane membraneSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Sindbis virus Sindbis virus | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 9 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 9 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Mukhopadhyay, S. / Zhang, W. / Gabler, S. / Chipman, P.R. / Strauss, E.G. / Strauss, J.H. / Baker, T.S. / Kuhn, R.J. / Rossmann, M.G. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Structure / Year: 2006 Journal: Structure / Year: 2006Title: Mapping the structure and function of the E1 and E2 glycoproteins in alphaviruses. Authors: Suchetana Mukhopadhyay / Wei Zhang / Stefan Gabler / Paul R Chipman / Ellen G Strauss / James H Strauss / Timothy S Baker / Richard J Kuhn / Michael G Rossmann /  Abstract: The 9 A resolution cryo-electron microscopy map of Sindbis virus presented here provides structural information on the polypeptide topology of the E2 protein, on the interactions between the E1 and ...The 9 A resolution cryo-electron microscopy map of Sindbis virus presented here provides structural information on the polypeptide topology of the E2 protein, on the interactions between the E1 and E2 glycoproteins in the formation of a heterodimer, on the difference in conformation of the two types of trimeric spikes, on the interaction between the transmembrane helices of the E1 and E2 proteins, and on the conformational changes that occur when fusing with a host cell. The positions of various markers on the E2 protein established the approximate topology of the E2 structure. The largest conformational differences between the icosahedral surface spikes at icosahedral 3-fold and quasi-3-fold positions are associated with the monomers closest to the 5-fold axes. The long E2 monomers, containing the cell receptor recognition motif at their extremities, are shown to rotate by about 180 degrees and to move away from the center of the spikes during fusion. | ||||||
| History |
| ||||||
| Remark 999 | SEQUENCE Author states that it appears even though the correct sequence utilizes a lysine, leucine ...SEQUENCE Author states that it appears even though the correct sequence utilizes a lysine, leucine was used in the model. |
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  1z8y.cif.gz 1z8y.cif.gz | 435 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb1z8y.ent.gz pdb1z8y.ent.gz | 369.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  1z8y.json.gz 1z8y.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z8/1z8y https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z8/1z8y ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z8/1z8y ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z8/1z8y | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 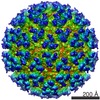 1121MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | x 60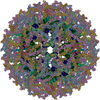
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 | x 5
|
| 4 | x 6
|
| 5 | 
|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: (Hermann–Mauguin notation : 532 / Schoenflies symbol : 532 / Schoenflies symbol : I (icosahedral : I (icosahedral )) )) |
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 31440.787 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Fragment: E1 ectodomain domains I+II, residues 1-290 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Sindbis virus / Genus: Alphavirus Sindbis virus / Genus: Alphavirus / Cell: Baby Hamster Kidney / Strain: TE12 / References: UniProt: P03316 / Cell: Baby Hamster Kidney / Strain: TE12 / References: UniProt: P03316#2: Protein | Mass: 9447.606 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Fragment: E1 ectodomain domain III, residues 295-383 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Sindbis virus / Genus: Alphavirus Sindbis virus / Genus: Alphavirus / Cell: Baby Hamster Kidney / Strain: TE12 / References: UniProt: P03316 / Cell: Baby Hamster Kidney / Strain: TE12 / References: UniProt: P03316#3: Protein/peptide | Mass: 3410.192 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Fragment: E1 transmembrane region, residues 409-439 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Sindbis virus / Genus: Alphavirus Sindbis virus / Genus: Alphavirus / Cell: Baby Hamster Kidney / Strain: TE12 / References: UniProt: P03316 / Cell: Baby Hamster Kidney / Strain: TE12 / References: UniProt: P03316#4: Protein/peptide | Mass: 3751.593 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Fragment: E2 transmembrane region, residues 363-398 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Sindbis virus / Genus: Alphavirus Sindbis virus / Genus: Alphavirus / Cell: Baby Hamster Kidney / Strain: TE12 / References: UniProt: P11259, UniProt: P03316*PLUS / Cell: Baby Hamster Kidney / Strain: TE12 / References: UniProt: P11259, UniProt: P03316*PLUS#5: Protein |  / coat protein C / coat protein CMass: 16545.631 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Fragment: Capsid protein, residues 114-264 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Sindbis virus / Genus: Alphavirus Sindbis virus / Genus: Alphavirus / Cell: Baby Hamster Kidney / Strain: TE12 / Cell: Baby Hamster Kidney / Strain: TE12References: UniProt: P03316,  Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Serine endopeptidases Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Serine endopeptidases |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Details of virus | Host category: EUKARYOTES / Type: VIRION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural host | Strain: Baby Hamster Kidney | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | Name: 50 mM Tris-Cl, 200 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM EDTA / pH: 7.4 / Details: 50 mM Tris-Cl, 200 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM EDTA | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: See Pletnev et al. (2001) Cell 105:127-136 for experimental details on sample preparation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: FEI/PHILIPS CM200FEG / Date: Jun 21, 2000 |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 38000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2580 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1100 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 38000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2580 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1100 nm / Cs : 2 mm : 2 mm |
| Specimen holder | Temperature: 93.15 K / Tilt angle max: 0 ° / Tilt angle min: 0 ° |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 18 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM Details: THE COORDINATES IN THIS ENTRY WERE GENERATED FROM ELECTRON MICROSCOPY DATA. |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Details: Fourier transform of each image was modified | ||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : I (icosahedral : I (icosahedral ) ) | ||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Method: cross-common lines / Resolution: 9 Å / Num. of particles: 7085 / Actual pixel size: 1.785 Å / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL / Details: REFINEMENT PROTOCOL--rigid body | ||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj